Rib cage

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
| Rib cage | |
|---|---|
 The human rib cage. (Source: Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body, 20th ed. 1918.) | |
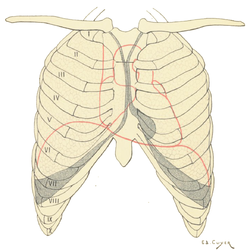 Projection on the rib cage of the heart, lungs and diaphragm. The shaded areas indicate the extent of the pleural cavities not filled by the lungs. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cavea thoracis |
| MeSH | D000070602 |
| TA | A02.3.04.001 |
| FMA | 7480 |
Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
The rib cage is the arrangement of ribs attached to the vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, that encloses and protects the heart and lungs. In humans, the rib cage, also known as the thoracic cage, is a bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the human skeleton. A typical human rib cage consists of 24 ribs in 12 pairs, the sternum and xiphoid process, the costal cartilages, and the 12 thoracic vertebrae.
Together with the skin and associated fascia and muscles, the rib cage makes up the thoracic wall and provides attachments for the muscles of the neck, thorax, upper abdomen, and back.
The rib cage has a major function in the respiratory system.
Contents
1 Structure
1.1 Attachment
1.2 Parts of rib
1.3 Bones
1.3.1 Ribs and vertebrae
1.3.2 Sternum
1.4 Development
1.5 Variation
2 Function
3 Clinical significance
4 Society and culture
5 History
6 Other animals
7 Additional images
8 See also
9 Notes
10 References
11 External links
Structure

Ribs are described based on their location and connection with the sternum. All ribs are attached behind to the thoracic vertebrae and are numbered accordingly one to twelve. Ribs that articulate directly with the sternum are called true ribs, whereas those that connect indirectly via cartilage are termed false ribs. Floating ribs (eleven and twelve) are not attached to the sternum at all.
Attachment

true / fixed ribs
false ribs
false and floating ribs
The terms true ribs and false ribs describe rib pairs that are directly or indirectly attached to the sternum. The first seven rib pairs known as the fixed or vertebrosternal ribs are the true ribs (Latin: costae verae) as they connect directly to the sternum; the next five pairs (eighth to twelfth) are the false ribs (Latin: costae spuriae), or vertebrochondral ribs as they connect indirectly to the sternum via the costal cartilages of the ribs above them.[1][2] Their elasticity allows rib cage movement for respiratory activity.
The phrase floating rib (Latin: costae fluctuantes) refers to the two lowermost, the eleventh and twelfth rib pairs; so-called because they are attached only to the vertebrae–and not to the sternum or cartilage of the sternum. These ribs are relatively small and delicate, and include a cartilaginous tip.[3]
The spaces between the ribs are known as intercostal spaces; they contain the intercostal muscles, and neurovascular bundles containing the nerves, arteries, and veins.[4]
Parts of rib

The parts of the rib.
Each rib consists of a head, neck, and a shaft. All ribs are attached posteriorly to the thoracic vertebrae. They are numbered to match the vertebra they attach to – one to twelve, from top (T1) to bottom. The head of the rib is the end part closest to the vertebrae with which it articulates. It is marked by a kidney-shaped articular surface which is divided by a horizontal crest into two articulating regions. The upper region articulates with the inferior costal facet on the vertebra above, and the larger region articulates with the superior costal facet on the vertebra with the same number. The transverse process of a thoracic vertebra also articulates at the transverse costal facet with the tubercle of the rib of the same number. The crest gives attachment to the intra-articular ligament.[5]
The neck of the rib is the flattened part that extends laterally from the head. The neck is about 3 cm long. Its anterior surface is flat and smooth, whilst its posterior is perforated by numerous foramina and its surface rough, to give attachment to the ligament of the neck. Its upper border presents a rough crest (crista colli costae) for the attachment of the anterior costotransverse ligament; its lower border is rounded.
On the posterior surface at the neck, is an eminence—the tubercle that consists of an articular and a non-articular portion. The articular portion is the lower and more medial of the two and presents a small, oval surface for articulation with the transverse costal facet on the end of the transverse process of the lower of the two vertebrae to which the head is connected. The non-articular portion is a rough elevation and affords attachment to the ligament of the tubercle. The tubercle is much more prominent in the upper ribs than in the lower ribs.
The angle of a rib (costal angle) may both refer to the bending part of it, and a prominent line in this area, a little in front of the tubercle. This line is directed downward and laterally; this gives attachment to a tendon of the iliocostalis muscle. At this point, the rib is bent in two directions, and at the same time twisted on its long axis.
The distance between the angle and the tubercle is progressively greater from the second to the tenth ribs. The area between the angle and the tubercle is rounded, rough, and irregular, and serves for the attachment of the longissimus dorsi muscle.
Bones
Ribs and vertebrae
The first rib (the topmost one) is the most curved and usually the shortest of all the ribs; it is broad and flat, its surfaces looking upward and downward, and its borders inward and outward.
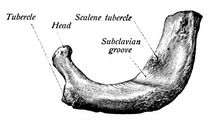
First rib seen from above.

Costal groove position on a central rib.
The head is small and rounded, and possesses only a single articular facet, for articulation with the body of the first thoracic vertebra. The neck is narrow and rounded. The tubercle, thick and prominent, is placed on the outer border. It bears a small facet for articulation with the transverse costal facet on the transverse process of T1. There is no angle, but at the tubercle, the rib is slightly bent, with the convexity upward, so that the head of the bone is directed downward. The upper surface of the body is marked by two shallow grooves, separated from each other by a slight ridge prolonged internally into a tubercle, the scalene tubercle, for the attachment of the anterior scalene; the anterior groove transmits the subclavian vein, the posterior the subclavian artery and the lowest trunk of the brachial plexus. Behind the posterior groove is a rough area for the attachment of the medial scalene. The under surface is smooth and without a costal groove. The outer border is convex, thick, and rounded, and at its posterior part gives attachment to the first digitation of the serratus anterior. The inner border is concave, thin, and sharp, and marked about its center by the scalene tubercle. The anterior extremity is larger and thicker than that of any of the other ribs.
The second rib is the second uppermost rib in humans or second most frontal in animals that walk on four limbs. In humans, the second rib is defined as a true rib since it connects with the sternum through the intervention of the costal cartilage anteriorly (at the front). Posteriorly, the second rib is connected with the vertebral column by the second thoracic vertebra. The second rib is much longer than the first rib, but has a very similar curvature. The non-articular portion of the tubercle is occasionally only feebly marked. The angle is slight and situated close to the tubercle. The body is not twisted so that both ends touch any plane surface upon which it may be laid; but there is a bend, with its convexity upward, similar to, though smaller than that found in the first rib. The body is not flattened horizontally like that of the first rib. Its external surface is convex, and looks upward and a little outward; near the middle of it is a rough eminence for the origin of the lower part of the first and the whole of the second digitation of the serratus anterior; behind and above this is attached the posterior scalene. The internal surface, smooth, and concave, is directed downward and a little inward: on its posterior part there is a short costal groove between the ridge of the internal surface of the rib and the inferior border. It protects the intercostal space containing the intercostal veins, intercostal arteries, and intercostal nerves.[6][4]
The ninth rib has a frontal part at the same level as the first lumbar vertebra. This level is called the transpyloric plane, since the pylorus is also at this level.[7]
The tenth rib attaches directly to the body of vertebra T10 instead of between vertebrae like the second through ninth ribs. Due to this direct attachment, vertebra T10 has a complete costal facet on its body.[3]

The four floating ribs indicated
The eleventh and twelfth ribs, the floating ribs, have a single articular facet on the head, which is of rather large size. They have no necks or tubercles, and are pointed at their anterior ends. The eleventh has a slight angle and a shallow costal groove, whereas the twelfth does not. The twelfth rib is much shorter than the eleventh rib, and its head is inclined slightly downward.[citation needed]
Sternum
The sternum is a long, flat bone that forms the front of the rib cage. The cartilages of the top seven ribs (the true ribs) join with the sternum at the sternocostal joints. The costal cartilage of the second rib articulates with the sternum at the sternal angle making it easy to locate.[8]
The transversus thoracis muscle is innervated by one of the intercostal nerves and superiorly attaches at the posterior surface of the lower sternum. Its inferior attachment is the internal surface of costal cartilages two through six and works to depress the ribs.[9]
Development
Expansion of the rib cage in males is caused by the effects of testosterone during puberty.[10] Thus, males generally have broad shoulders and expanded chests, allowing them to inhale more air to supply their muscles with oxygen.

A C7 rib on the right
Variation
Variations in the number of ribs occur. About 1 in 200-500 people have an additional cervical rib, and there is a female predominance.[11] Intrathoracic supernumerary ribs are extremely rare.[12] The rib remnant of the 7th cervical vertebra on one or both sides is occasionally replaced by a free extra rib called a cervical rib, which can mechanically interfere with the nerves (brachial plexus) going to the arm.
In several ethnic groups, most significantly the Japanese, the tenth rib is sometimes a floating rib, as it lacks a cartilaginous connection to the seventh rib.[3]
Function

The effect of the contraction of the accessory muscles of inhalation, pulling the front of the rib cage upwards, a movement known as the 'pump handle movement'. This increases the antero-posterior diameter of the thorax, contributing to the expansion in the volume of the chest. A similar effect, known as the 'bucket handle movement' causes the transverse diameter of the chest to increase, because not only do the ribs slant downwards from the back to the front, but, in the case of the lower ribs, also from the midline downwards to the sides of the chest.
The human rib cage is a component of the human respiratory system. It encloses the thoracic cavity, which contains the lungs. An inhalation is accomplished when the muscular diaphragm, at the floor of the thoracic cavity, contracts and flattens, while the contraction of intercostal muscles lift the rib cage up and out.
Expansion of the thoracic cavity is driven in three planes; the vertical, the anteroposterior and the transverse. The vertical plane is extended by the help of the diaphragm contracting and the abdominal muscles relaxing to accommodate the downward pressure that is supplied to the abdominal viscera by the diaphragm contracting. A greater extension can be achieved by the diaphragm itself moving down, rather than simply the domes flattening. The second plane is the anteroposterior and this is expanded by a movement known as the 'pump handle.' The downward sloping nature of the upper ribs are as such because they enable this to occur. When the external intercostal muscles contract and lift the ribs, the upper ribs are able also to push the sternum up and out. This movement increases the anteroposterior diameter of the thoracic cavity, and hence aids breathing further. The third, transverse, plane is primarily expanded by the lower ribs (some say it is the 7th to 10th ribs in particular), with the diaphragm's central tendon acting as a fixed point. When the diaphragm contracts, the ribs are able to evert and produce what is known as the bucket handle movement, facilitated by gliding at the costovertebral joints. In this way, the transverse diameter is expanded and the lungs can fill.
The circumference of the normal adult human rib cage expands by 3 to 5 cm during inhalation.[13]
Clinical significance
Rib fractures are the most common injury to the rib cage. These most frequently affect the middle ribs. When several adjacent ribs incur two or more fractures each, this can result in a flail chest which is a life-threatening condition.
A dislocated rib can be painful and can be caused simply by coughing, or for example by trauma or lifting heavy weights.[14]
One or more costal cartilages can become inflamed – a condition known as costochondritis; the resulting pain is similar to that of a heart attack.
Abnormalities of the rib cage include pectus excavatum ("sunken chest") and pectus carinatum ("pigeon chest"). A bifid rib is a bifurcated rib, split towards the sternal end, and usually just affecting one of the ribs of a pair. It is a congenital defect affecting about 1.2% of the population. It is often without symptoms though respiratory difficulties and other problems can arise.
Rib removal is the surgical removal of one or more ribs for therapeutic or cosmetic reasons. Rib resection is the removal of part of a rib.
Society and culture
Their position can be permanently altered by a form of body modification called tightlacing, which uses a corset to compress and move the ribs.
The ribs, particularly their sternal ends, are used as a way of estimating age in forensic pathology, due to their progressive ossification.[15]
History
The number of ribs as 24 (12 pairs) was noted by the Flemish anatomist Vesalius in his key work of anatomy De humani corporis fabrica in 1543, setting off a wave of controversy, as it was traditionally assumed from the Biblical story of Adam and Eve that men's ribs would number one fewer than women's.[16]
Other animals

Tyrannosaurus rib cage, University of California Museum of Paleontology
In herpetology, costal grooves refer to lateral indents along the integument of salamanders. The grooves run between the axilla to the groin. Each groove overlies the myotomal septa to mark the position of the internal rib.[17][18]
Birds and reptiles have bony uncinate processes on their ribs that project caudally from the vertical section of each rib.[19] These serve to attach sacral muscles and also aid in allowing greater inspiration. Crocodiles have cartilaginous uncinate processes.
Additional images
Anterior surface of sternum and costal cartilages.

X-ray image of a human chest, with ribs labelled.

3D model of rib cage
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rib cage. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Human_anatomy, ribs. |
- Articulation of head of rib
- Terms for anatomical location
- Terms for bones
Notes
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
^ "The Thoracic Cage · Anatomy and Physiology". Retrieved 10 March 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Hyman, Libbie Henrietta (1992). Hyman's Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy. University of Chicago Press. p. 230. ISBN 9780226870137. Retrieved 10 March 2018.
^ abc Saladin, Kenneth (2010). Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. USA: The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. p. 485. ISBN 978-0-07-352569-3.
^ ab Smith, Sarah. "Intercostal spaces | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". radiopaedia.org.
^ http://www.teachmeanatomy.com/osteology-of-the-thorax/[permanent dead link]
^ Moore, Dalley & Agur. 2009. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6th Edition. 90 Pp. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins,
ISBN 0-7817-7525-6,
ISBN 978-0-7817-7525-0
^ Bålens ytanatomi (surface anatomy). Godfried Roomans, Mats Hjortberg and Anca Dragomir. Institution for Anatomy, Uppsala. 2008.
^ Agur, Anne M.R.; Dalley, Arthur F. II (2009). Grant's Atlas of Anatomy, Twelfth Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-7817-7055-2.
^ Agur, Anne M.R.; Dalley, Arthur F. II (2009). Grant's Atlas of Anatomy, Twelfth Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-7817-7055-2.
^ Testosterone causes expansion of rib cage during puberty as one of secondary sex characteristics."Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-09-11. Retrieved 2013-12-31.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ Kurihara Y; Yakushiji YK; Matsumoto J; Ishikawa T; Hirata K (Jan–Feb 1999). "The Ribs: Anatomic and Radiologic Considerations" (PDF). RadioGraphics. Radiological Society of North America. 19 (1): 105–119. doi:10.1148/radiographics.19.1.g99ja02105. ISSN 1527-1323. PMID 9925395. Retrieved August 13, 2009.
^ Kamano H; Ishihama T; Ishihama H; Kubota Y; Tanaka T; Satoh K (June 1, 2006). "Bifid intrathoracic rib: a case report and classification of intrathoracic ribs" (PDF). Internal Medicine. The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine. 45 (9): 627–630. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.45.1502. PMID 16755094. Retrieved August 13, 2009.
[permanent dead link]
^ Respiratory system examination Archived 2012-03-23 at the Wayback Machine citing: Health & Physical Assessment, Mosby-Year Book, inc. School of Nursing, Peking University, 2003
^ "Anatomy of the Human ribs - Dislocated Rib". Dislocated Rib. 2 February 2016. Archived from the original on 12 August 2016.
^ Franklin, D (Jan 2010). "Forensic age estimation in human skeletal remains: current concepts and future directions". Legal medicine (Tokyo, Japan). 12 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.legalmed.2009.09.001. PMID 19853490.
^ "Chapter 19 On the Bones of the Thorax". Archived from the original on 2007-07-06. Retrieved 2007-08-23.
^ Duellman, W.E., Trueb, L. (1986). Biology of Amphibians. 670 Pp. McGraw - Hill Book Company, New York, New York,
ISBN 0-8018-4780-X, 9780801847806
^ J. W. Petranka. 1998. Salamanders of the United States and Canada. 587 Pp. Smithsonian Institution Press,
ISBN 1-56098-828-2,
ISBN 978-1-56098-828-1
^ Kardong, Kenneth V. (1995). Vertebrates: comparative anatomy, function, evolution. McGraw-Hill. pp. 55, 57. ISBN 0-697-21991-7.
References
Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 4th ed. Keith L. Moore and Robert F. Dalley. pp. 62–64
Principles of Anatomy Physiology, Tortora GJ and Derrickson B. 11th ED. John Wiley and Sons, 2006.
ISBN 0-471-68934-3
De Humani Corporis Fabrica: online English translation of Vesalius' books on human anatomy.
External links
- Diagram at mhhe.com




