United States Department of Education

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
 Seal of the U.S. Department of Education | |
 Flag of the U.S. Department of Education | |
 Lyndon Baines Johnson Building, Department Headquarters | |
| Department overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | October 17, 1979 (1979-10-17) |
| Preceding agencies |
|
| Jurisdiction | Federal government of the United States |
| Headquarters | Lyndon Baines Johnson Building 400 Maryland Avenue Southwest, Washington, D.C., U.S. Coordinates: 38°53′11.5″N 77°1′7.9″W / 38.886528°N 77.018861°W / 38.886528; -77.018861 |
| Employees | 3912 (2018)[1] |
| Annual budget | $68 billion (2016)[2] |
| Department executives |
|
| Key document |
|
| Website | www.ed.gov |
The United States Department of Education (ED or DoED), also referred to as the ED for (the) Education Department, is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government. It began operating on May 4, 1980, having been created after the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare was split into the Department of Education and the Department of Health and Human Services by the Department of Education Organization Act, which President Jimmy Carter signed into law on October 17, 1979.[3][4]
The Department of Education is administered by the United States Secretary of Education. It has under 4,000 employees (2018)[1] and an annual budget of $68 billion (2016).[2] The 2019 Budget also supports $129.8 billion in new postsecondary grants, loans, and work-study assistance to help an estimated 11.5 million students and their families pay for college.[5] Its official abbreviation is "ED" ("DOE" refers to the United States Department of Energy) and is also often abbreviated informally as "DoEd".
Contents
1 Functions
2 Budget
3 History
3.1 Establishment
3.2 Early history
3.3 Later history
4 Organization
5 See also
5.1 Related legislation
6 References
7 Further reading
8 External links
Functions
The primary functions of the Department of Education are to "establish policy for, administer and coordinate most federal assistance to education, collect data on US schools, and to enforce federal educational laws regarding privacy and civil rights."[6] The Department of Education does not establish schools or colleges.[7]
Unlike the systems of most other countries, education in the United States is highly decentralized, and the federal government and Department of Education are not heavily involved in determining curricula or educational standards (with the exception of the No Child Left Behind Act). This has been left to state and local school districts. The quality of educational institutions and their degrees is maintained through an informal private process known as accreditation, over which the Department of Education has no direct public jurisdictional control.
The Department of Education is a member of the United States Interagency Council on Homelessness,[8] and works with federal partners to ensure proper education for homeless and runaway youth in the United States.
Opposition to the Department of Education mainly stems from conservatives, who see the department as an undermining of states rights, and libertarians who believe it results in a state-imposed leveling towards the bottom and low value for taxpayers' money.[9]
Budget
The U.S. Department of Education oversees the nation's education system. The Department sets uniform rules and standards which are applied nationwide. “Since the Department of Education (Education) began operations in fiscal year 1980, its mission has included promoting student achievement and ensuring equal access to educational opportunity. To do so, Education partners with state and local governments, which provide most of the resources to school districts for K-12 programs".[10]
Civil Rights and Equal Opportunity is one of the most forefront issues that is discussed about within the U.S. Department of Education’s four walls. The goal of this agency is to make sure that every student in primary and secondary education has the tools that they need to succeed. Not all of their ideas always work out in the best favor of the students. Throughout recent history, the educational system has not always been focused on furthering the development of all students (in regards to race and gender). However, coming out of the 20th century this ideal has been turned around and many new legislations have been put in place to break down these invisible walls that were surrounding the people who were affected by this hindrance. “The U.S., like other countries in the 21st century, is increasingly operating in an interconnected world. New structures require that teachers and our next generations of students prepare and expand ideas about their responsibilities as citizens".
For 2006, the ED discretionary budget was $56 billion and the mandatory budget contained $23 billion.[12] In 2009 it received additional ARRA funding of $102 billion.[13] As of 2011, the discretionary budget is $70 billion.[12]
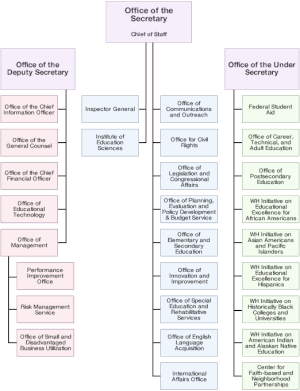
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Program | |
|---|---|
Secretary of Education | Office of Communications and Outreach |
| Office of the General Counsel | |
| Office of Inspector General | |
| Office of Legislation and Congressional Affairs | |
Office for Civil Rights | |
Office of Educational Technology | |
Institute of Education Sciences *National Center for Education Statistics **National Assessment of Educational Progress **Education Resources Information Center | |
Office of Innovation and Improvement | |
| Office of the Chief Financial Officer | |
| Office of Management | |
| Office of the Chief Information Officer | |
| Office of Planning, Evaluation and Policy Development *Budget Service | |
| Risk Management Service | |
Deputy Secretary of Education | Office of Elementary and Secondary Education *Education Facilities Clearinghouse *Office of Migrant Education *Office of Safe and Healthy Students *Student Achievement and School Accountability Programs *White House Initiative on Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders *White House Initiative on Educational Excellence for Hispanics *White House Initiative on American Indian and Alaska Native Education *White House Initiative on Educational Excellence for African Americans |
| Office of English Language Acquisition | |
Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services *National Institute on Disability and Rehabilitation Research *Office of Special Education Programs *Rehabilitation Services Administration | |
Office of Innovation and Improvement | |
Under Secretary of Education | Office of Postsecondary Education |
Office of Career, Technical, and Adult Education | |
Office of Federal Student Aid | |
| President's Advisory Board on Tribal Colleges and Universities | |
| President's Advisory Board on Historically Black Colleges and Universities | |
| Associated federal organizations | Advisory Councils and Committees |
| National Assessment Governing Board (NAGB)[1] | |
| National Advisory Council on Indian Education | |
| Federal Interagency Committee on Education | |
| Advisory Commission on Accessible Instructional Materials in Postsecondary Education for Students with Disabilities | |
| National Board for Education Sciences | |
| National Board of the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education | |
| Federally aided organizations | Gallaudet University |
Howard University | |
National Technical Institute for the Deaf | |
See also
- Council for Higher Education Accreditation
- Educational attainment in the United States
- Free Application for Federal Student Aid
- FICE code
- Federal Student Aid
- National Diffusion Network
- School Improvement Grant
- Title 34 of the Code of Federal Regulations
Related legislation
- 1965: Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA)
- 1965: Higher Education Act of 1965 (HEA) (Pub. L. No. 89-329)
- 1974: Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
- 1974: Equal Educational Opportunities Act of 1974 (EEOA)
- 1975: Education for All Handicapped Children Act (EHA) (Pub. L. No. 94-142)
- 1978: Protection of Pupil Rights Amendment
- 1980: Department of Education Organization Act (Pub. L. No. 96-88)
- 1984: Equal Access Act
- 1990: The Jeanne Clery Disclosure of Campus Security Policy and Campus Crime Statistics Act (Clery Act)
- 1994: Improving America's Schools Act of 1994
- 2001: No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB)
- 2004: Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
- 2005: Higher Education Reconciliation Act of 2005 (HERA) (Pub. L. No. 109-171)
- 2006: Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Improvement Act
- 2007: America COMPETES Act
- 2008: Higher Education Opportunity Act (HEOA) (Pub. L. No. 110-315)
- 2009: Race to the Top
- 2009: Student Aid and Fiscal Responsibility Act
- 2010: Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010
- 2015: Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)
References
^ ab Stratford, Michael (January 22, 2018). "Education Department goes into shutdown mode". Politico. Retrieved January 25, 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ ab "Overview and Mission Statement - U.S. Department of Education". www2.ed.gov.
^ Pub.L. 96–88, S. 210, 93 Stat. 668, enacted October 17, 1979
^ "Department of Education Organization Act, 1979". wordpress.com. 15 April 2011.
^ U.S. Secretary of Education (14 February 2018). "ED FY2019 Budget" (PDF). ed.gov.
^ What We Do. ED.gov. Retrieved on 2013-07-17.
^ "An Overview of the U.S. Department of Education, p. 2". United States Department of Education. Retrieved August 25, 2012.
^ "Department of Education | Member Agency | United States Interagency Council on Homelessness (USICH)". Usich.gov. Retrieved 2012-08-25.
^ "Laissez-faire-learning". 2012-06-25. Retrieved 2012-06-28.
^ Hubbard, Janie; Swain, Holly Hilboldt (July 2017). "Using the U.S. Civil Rights Movement to explore social justice education with K-6 pre-service teachers". The Journal of Social Studies Research. 41 (3): 217–233. doi:10.1016/j.jssr.2016.09.002. ISSN 0885-985X.
^ "ED History" (PDF). U.S. Department of Education. 2015-09-25. Retrieved 2017-02-28.
^ ab "Overview". U.S. Department of Education Budget Office. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-03-27.
^ "Wayback Machine" (PDF). archive.org. 13 January 2017.
^ "Act to Establish a Federal Department of Education, 1867". wordpress.com. 19 February 2011.
^ Chap. CLVIII. 14 Stat. 434 from "A Century of Lawmaking for a New Nation: U. S. Congressional Documents and Debates, 1774–1875". Library of Congress, Law Library of Congress. Retrieved April 25, 2012.
^ abcd "Department of Education Outlined". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette, via Google News. Associated Press. February 9, 1979.
^ "House Narrowly Passes Department of Education Bill". Spokane, Washington: The Spokesman-Review, via Google News. The New York Times. July 12, 1979.
^ Hechinger, Fred M (September 3, 1979). "Federal Education Branch Is Foundering, Leaderless". Lexington, North Carolina: The Dispatch, via Google News. New York Times News Service.
^ "Education Department Created". The Palm Beach Post, via Google News. United Press International. October 18, 1979.
^ Educational Horizons: "The Educational Legacy of Ronald Reagan", Summer 2004 v. 82 n. 4 p. 256
^ "Online Backgrounders: The Department of Education". PBS. Fall 1996. Retrieved 2005-07-26.
^ abcde Veronique de Rugy and Marie Gryphon (2004-02-11). "Elimination Lost: What happened to abolishing the Department of Education?". Cato Institute. Retrieved February 15, 2017.This article originally appeared in National Review Online on February 11, 2004.
^ "Education". 2007. Retrieved 2007-09-14.
^ Stossel, John (2007-12-10). "Ron Paul Unplugged". ABC News. Retrieved 2008-01-30.
^ "Paige Fields Team to Leave No Child Behind". United States Department of Education. April 11, 2002. Archived from the original on September 24, 2003.
^ Young, Michelle D.; Winn, Kathleen M.; Reedy, Marcy A. (2017-10-13). "The Every Student Succeeds Act: Strengthening the Focus on Educational Leadership". Educational Administration Quarterly. 53 (5): 705–726. doi:10.1177/0013161x17735871. ISSN 0013-161X.
^ "President Bush Signs H.R. 584, Designates U.S. Department of Education as the Lyndon Baines Johnson Federal Building". Georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov. 2007-03-23. Retrieved 2012-08-25.
^ "Rep. Massie Introduces Bill to Abolish Federal Department of Education". house.gov. 7 February 2017.
Further reading
- Radin, Beryl A., and Willis D. Hawley (1988). Politics of Federal Reorganization: Creating the U.S. Department of Education,
ISBN 978-0080339771 - Heffernan, Robert V. (2001). Cabinetmakers: Story of the Three-Year Battle to Establish the U.S. Department of Education,
ISBN 978-0595158706
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to United States Department of Education. |
Official website
Department of Education in the Federal Register
ERIC Digests – Informational digests on educational topics produced by the U.S. Department of Education before 1983.
Works by United States Department of Education at Project Gutenberg
Works by or about United States Department of Education at Internet Archive- United States Government Manual, Department of Education