Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
 Charlotte Amalie, St. Thomas | |
 St. Thomas | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Caribbean Sea |
| Coordinates | 18°20′N 64°55′W / 18.333°N 64.917°W / 18.333; -64.917Coordinates: 18°20′N 64°55′W / 18.333°N 64.917°W / 18.333; -64.917 |
| Archipelago | Virgin Islands, Leeward Islands |
| Area | 32 sq mi (83 km2) |
| Highest elevation | 1,555 ft (474 m) |
| Highest point | Crown Mountain[1] |
| Administration | |
United States | |
| Insular area | Virgin Islands |
| Largest settlement | Charlotte Amalie (pop. 18,481) |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym | Saint Thomian |
| Population | 51,634 (2010) |
| Pop. density | 638.17 /km2 (1,652.85 /sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Afro-Caribbean, Hispanic, Caucasian |
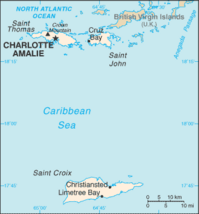
Map of U.S. Virgin Islands
Saint Thomas (Danish: Sankt Thomas) is one of the Virgin Islands in the Caribbean Sea and, together with Saint John, Water Island and Saint Croix, a former Danish colony, form a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincorporated territory of the United States. Located on the island is the territorial capital and port of Charlotte Amalie. As of the 2010 census, the population of Saint Thomas was 51,634[2] about 48.5% of the US Virgin Islands total. The district has a land area of 32 square miles (83 km2).[3]
Contents
1 History
1.1 Pre-colonial history
1.2 Danish and German colonial period
1.3 Freedom of the press
1.4 United States acquisition
2 Geography
2.1 Climate
3 Demographics
4 Transportation
5 Education
6 Notable people
7 Points of interest
8 Gallery
9 References
10 External links
History
Pre-colonial history
The island was originally settled around 1500 BC by the Ciboney people. They were later replaced by the Arawaks and then the Caribs. Christopher Columbus sighted the island in 1493 on his second voyage to the New World.
Danish and German colonial period
The Dutch West India Company established a post on Saint Thomas in 1657. The first congregation was the St. Thomas Reformed Church, which was established in 1660 and was associated with the Dutch Reformed Church.
Denmark-Norway's first attempt to settle the island in 1665 failed. However, the Danes did resettle St. Thomas in 1671, under the sponsorship of the Glueckstadt Co., later the Danish West India Company. The first slave ships arrived in 1673, and St. Thomas became a slave market. The island became a Danish crown colony in 1754, and was granted free port status in 1764.[4]
The land was divided into plantations and sugarcane production became the primary economic activity. As a result, the economies of Saint Thomas and the neighboring islands of Saint John and Saint Croix became highly dependent on slave labor and the slave trade. In 1685, the Brandenburgisch-Africanische Compagnie took control of the slave trade on Saint Thomas, and for some time the largest slave auctions in the world were held there.
Danish West Indies, Saint Thomas, 1 dollar (1889)
Saint Thomas's fine natural harbor became known as "Taphus" for the drinking establishments located nearby. ("Tap Hus" translates as "rum shop" or "tap house" referring to the drinking establishments.[5]) In 1691, the primary settlement there was renamed Charlotte Amalie in honor of the wife of Denmark's King Christian V. It was later declared a free port by Frederick V. In December 1732, the first two of many Moravian Brethren missionaries came from Herrnhut Saxony in present-day Germany to minister to them. Distrusted at first by the white masters, they lived among the slaves and soon won their confidence.[6]
From 1796 a small Jewish community developed in Charlotte Amalie. It established a historic synagogue, Beracha Veshalom Vegmiluth Hasidim, the oldest synagogue in continuous use anywhere in the United States or its external territories.[7]
The first British invasion and occupation of the island occurred in 1801. The islands were returned to Denmark in 1802, under the terms of the Treaty of Amiens. Fire destroyed hundreds of homes in Charlotte Amalie in 1804.
The second British occupation of the island occurred from 1807-1815, after the Invasion of the Danish West Indies (1807), during which they built Fort Cowell on Hassel Island.[4]
While the sugar trade had brought prosperity to the island's free citizens, by the early 19th century Saint Thomas was in decline. The continued export of sugar was threatened by hurricanes, drought, and American competition. Following the Danish Revolution of 1848, slavery was abolished and the resulting rise in labor costs further weakened the position of Saint Thomas's sugar producers.
Given its harbors and fortifications, Saint Thomas still retained a strategic importance, and thus, in the 1860s, during the American Civil War and its aftermath, the United States government considered buying the island and its neighbors from Denmark for $7.5 million. However, the proponents of the purchase failed to gain legislative support for the bid.
Freedom of the press
As the islands were poorly managed by the Danes[citation needed], a local islander, David Hamilton Jackson, was instrumental in persuading the Danish to allow the US to purchase the islands of Saint Thomas, Saint John, and Saint Croix. In 1915, he traveled to Denmark and convinced the King of Denmark to allow freedom of the press in the islands.[8] He began the first newspaper in the islands, known as The Herald. After this, he organized labor unions among the islanders for better working conditions. The islands now have an annual celebration in November to honor the legacy of David Hamilton Jackson.[9]
United States acquisition
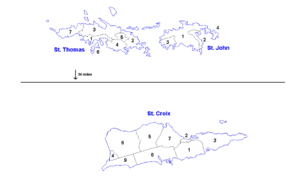
Districts and subdistricts of the US Virgin Islands
In 1917, Saint Thomas was purchased (along with Saint John and Saint Croix) by the United States for $25 million in gold ($489 million today),[10] as part of a defensive strategy to maintain control over the Caribbean and the Panama Canal during the First World War. The transfer occurred on March 31, 1917, behind Fort Christian before the barracks that now house the Legislature of the U.S Virgin Islands. The baccalaureate service for the transfer was held at the St. Thomas Reformed Church as it was identified as the American church in the Danish West Indies.
The United States granted citizenship to the residents in 1927. The U.S. Department of the Interior took over administrative duties in 1931. American forces were based on the island during the Second World War. In 1954, passage of the U.S. Virgin Islands Organic Act officially granted territorial status to the three islands, and allowed for the formation of a local senate with politics dominated by the American Republican and Democratic parties. Full home rule was achieved in 1970.
The post-war era also saw the rise of tourism on the island. With relatively cheap air travel and the American embargo on Cuba, the numbers of visitors greatly increased. Despite natural disasters such as Hurricane Hugo (1989) and Hurricanes Luis and Marilyn (1995), the island's infrastructure continues to improve as the flow of visitors continues. Hotels have been built from the West End to the East End.
Geography
The island has a number of natural bays and harbors including Magens Bay, Great Bay, Jersey Bay, Long Bay, Fortuna Bay, and Hendrik Bay. Passenger ships dock and anchor in Long Bay, near Charlotte Amalie. Ships dock at Havensight Pier.
Climate
| Climate data for Saint Thomas, United States Virgin Islands | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 93 (34) | 93 (34) | 94 (34) | 96 (36) | 97 (36) | 99 (37) | 98 (37) | 99 (37) | 98 (37) | 97 (36) | 95 (35) | 92 (33) | 99 (37) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 85.1 (29.5) | 85.1 (29.5) | 85.7 (29.8) | 86.7 (30.4) | 87.6 (30.9) | 89.1 (31.7) | 89.9 (32.2) | 90.2 (32.3) | 90.0 (32.2) | 88.7 (31.5) | 87.1 (30.6) | 85.6 (29.8) | 87.6 (30.9) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 72.4 (22.4) | 72.3 (22.4) | 72.9 (22.7) | 74.1 (23.4) | 76.2 (24.6) | 77.7 (25.4) | 78.0 (25.6) | 78.1 (25.6) | 78.0 (25.6) | 76.9 (24.9) | 75.2 (24.0) | 73.7 (23.2) | 75.5 (24.2) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 63 (17) | 62 (17) | 56 (13) | 58 (14) | 66 (19) | 67 (19) | 57 (14) | 59 (15) | 64 (18) | 66 (19) | 52 (11) | 62 (17) | 52 (11) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.16 (55) | 1.47 (37) | 1.05 (27) | 2.62 (67) | 3.05 (77) | 2.62 (67) | 2.82 (72) | 3.51 (89) | 4.82 (122) | 5.94 (151) | 6.00 (152) | 2.88 (73) | 38.95 (989) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 14.3 | 11.8 | 8.1 | 10.7 | 11.9 | 11.1 | 14.8 | 14.2 | 14.6 | 17.7 | 17.8 | 16.7 | 163.6 |
| Source #1: NOAA (normals 1981−2010)[11] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Weather Channel [12] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Saint Thomas is divided into the following subdistricts (with population as per the 2010 U.S. Census):
Charlotte Amalie (pop. 18,481) Charlotte Amalie town (pop. 10,354)
East End (pop. 8,403)
Northside (pop. 10,049)
Southside (pop. 5,411)
Tutu (pop. 6,867)
Water Island (pop. 182)
West End (pop. 2,241)
Transportation

Cab at Red Hook
The island is serviced by the Cyril E. King International Airport.
Passenger and limited car-ferry services to neighboring islands such as Water Island, Saint John, Saint Croix, and the British Virgin Islands run regularly out of the Red Hook Terminal, Charlotte Amalie, and Crown Bay Marina.
The United States Virgin Islands is the only place under United States jurisdiction where the rule of the road is to drive on the left. This was inherited from what was the then-current Danish practice at the time of the American acquisition in 1917. However, because Saint Thomas is a U.S. territory, most cars are imported from the mainland United States and therefore the steering column is located on the left side of the vehicle.
The island has many regular taxis from compact size to large vans, as well as open-air, covered trucks called "safaris" with bench seats. The latter usually operate only between high-traffic points, e.g., cruise-ship terminals at Havensight and Crown Bay and downtown Charlotte Amalie.
Education
St. Thomas-St. John School District operates public schools on Saint Thomas.
Private schools:
- Antilles School (www.antilles.vi)
- Virgin Islands Montessori School & International Academy
- Calvary Christian Academy
Parochial schools:
- All Saints Cathedral School
- Saints Peter & Paul Catholic School
- Weslyan Academy Bible School
Colleges and universities:
- University of the Virgin Islands
Notable people
Mike Bassett- Appeared on the HBO alcohol documentary 'Risky Drinking.'
Alton Augustus Adams − first African-American band master for the United States Navy
Jabari Blash - Major League Baseball player, outfielder for the San Diego Padres
Edward Wilmot Blyden − ambassador, an Igbo in Diaspora, is credited in some history books as having laid the foundation of West African nationalism and Pan-Africanism
Callix Crabbe − Major League Baseball player
Midre Cummings − Major League Baseball player
Vanessa Daou − singer-songwriter, dancer, writer, poet
Charles Joseph Sainte-Claire Deville − a French geologist
Henri Étienne Sainte-Claire Deville − a French chemist
Gabriel Milan - Governor from 7 May 1684 to 27 February 1686
Jeffrey Epstein − American financier
Jeff Faulkner − National Football League player
Kelsey Grammer − actor, director, and producer born in Saint Thomas
Emile Griffith − former boxer who won world championships in both the Welterweight and Middleweight divisions.
Elrod Hendricks − Major League Baseball player
Abdul Hodge − National Football League player
Daryl Homer, Olympic fencer
Roy Innis − civil rights leader
Julian Jackson − boxer born in Saint Thomas
Hannah Jeter - Sports Illustrated Swimsuit cover model and wife of Derek Jeter of the New York Yankees
J. Raymond Jones − political activist
Christine Jowers − choreographer, producer, and dance critic
Al McBean − Major League Baseball player
Ralph Moses Paiewonsky − governor
Calvin Pickering − Major League Baseball player
Camille Pissarro − a key member of the French Impressionist group of painters
Rashawn Ross − trumpeter who tours with Dave Matthews Band
Roy Lester Schneider − governor and physician
Karrine Steffans − former hip-hop music video performer and actress and the author of Confessions of A Video Vixen.
Morris Simmonds − German physician, pathologist, described a syndrome of pituitary failure with emaciation (Simmonds syndrome)
Edward Teach, pirate and privateer; may have been given a letter of marque from St. Thomas after being pardoned for pirating
Terence Todman − ambassador
Jean Toussaint - jazz tenor and soprano saxophonist
Peter von Scholten − governor general
Denmark Vesey − leader of planned slave uprising in Charleston, South Carolina
Tiphanie Yanique – award-winning writer
David Levy Yulee − an American politician and the first member of the United States Senate to have been, at one time, a practicing Jew.
Points of interest
- Blackbeard's Castle
- Buck Island National Wildlife Refuge
- Cathedral Church of All Saints
- Fort Christian
- Magens Bay Arboretum
- Magens Bay
- Red Hook
- Saints Peter and Paul Cathedral
- St. Thomas Synagogue
- Coral World Ocean Park
Gallery
Blackbeard's Castle in Charlotte Amalie.

Magens Bay as seen from Drake's Seat, St. Thomas, USVI.

View From Bluebeard's Castle, St Thomas US Virgin Islands

Magens Bay
References
^ "Where is the U.S. Virgin Islands: Geography". vinow.com. Retrieved April 8, 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Kossler, Bill (August 24, 2011). "USVI Population Down Since 2000". stthomassource.com. V.I. Source Publications. Retrieved January 11, 2017.
^ This is the figure given on page 1 of the United States Geological Survey's Open-File Report 72-201. It is also the figure given in the article at the on-line edition of the Encyclopedia Britannica. The Virgin Islands (United States) page at the United Nations Environmental Programme's Island Directory gives a substantially lower figure, reporting the area as 69.7 square kilometers, equivalent to 26.9 square miles. And although the U.S. Census Bureau does not report the areas of geographic entities, it does report their population densities (equal to the total population divided by the area). In the 2010 census, the population was reported as 51,634 (Table P1, "Total Population") and the population density was reported as 1,649.1 per square mile (Table P40, "Population Density"). Together, these figures imply an area of 31.3 square miles.
^ ab U.S. Virgin Islands: a guide to national parklands in the United States Virgin Islands. Washington, D.C.: Division of Publications, National Park Service, U.S. Dept. of the Interior. pp. 24–25, 37–39. ISBN 0912627689.
^ "Charlotte Amalie St. Thomas U.S. Virgin Islands". guidetocaribbeanvacations.com.
^ Hamilton, J. Taylor and Hamilton, Kenneth G., History of the Moravian Church, Bethlehem, PA, 1969.
^ Arts & Culture US Virgin Island Tourism
^ "David Hamilton Jackson - Famous Virgin Islander". here.vi.
^ Liberty Day festivities to include parade, re-enactment about D. Hamilton Jackson, The Virgin Islands Daily News.
^ "United States Virgin Islands Department of Tourism site". Visitusvi.com. Retrieved December 17, 2011.
^
"NOWData - NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved January 19, 2013.
^ "Average Conditions Saint Thomas, VI". weather.com. Retrieved May 16, 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Saint Thomas, United States Virgin Islands. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Saint Thomas. |
- Official sites
United States Virgin Islands – Official Website for the United States Virgin Islands Department of Tourism- Districts of the United States Virgin Islands, United States Census Bureau
- Map
St. Thomas USVI Google Map – Satellite Map of St. Thomas, USVI




