Western New Guinea

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP Coordinates: 4°00′S 136°00′E / 4.000°S 136.000°E / -4.000; 136.000
| Western New Guinea (Papua) | |
Irian Barat Irian Jaya West Papua | |
| Region | |
| Country | |
|---|---|
| Autonomous Region | Papua, West Papua |
| Cities | Jayapura, Manokwari, Sorong, Wamena, Timika, Merauke |
| Highest point | Puncak Jaya |
| - location | Sudirman Range |
| - elevation | 4,884 m (16,024 ft) |
| - coordinates | 4°5′S 137°11′E / 4.083°S 137.183°E / -4.083; 137.183 |
| Area | 420,540 km2 (162,371 sq mi) |
| Population | 4,363,869 (2014) |
| Density | 10/km2 (26/sq mi) |
| Timezone | Indonesia Eastern Time (UTC+9) |
ISO 3166-2 | ID-IJ |
| License plate | DS/PA PB |
 | |
Western New Guinea, also known as Papua (formerly Irian Jaya) and West Papua,[1] is the part of the island of New Guinea (also known as Papua) incorporated into Indonesia in 1962. Lying to the west of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, it is the only Indonesian territory to be situated in Oceania. The territory also includes nearby islands, including the Schouten and Raja Ampat archipelagoes. Most of the territory is in the Southern Hemisphere, with a few small northwestern islands such as Sajang Island in the Northern Hemisphere. The region is predominantly covered with ancient rainforest where numerous traditional tribes live such as the Dani of the Baliem Valley, although a large proportion of the population live in or near coastal areas, now a majority of which consists of recent transmigrants from Java and other provinces of Indonesia.[2]
The largest city in the region is Jayapura. The official and most commonly spoken language is Indonesian[citation needed]. Estimates of the number of tribal languages in the region range from 200 to over 700, with the most widely spoken including Dani, Yali, Ekari and Biak. The predominant religion is Christianity (often combined with traditional beliefs) followed by Islam. The main industries include agriculture, fishing, oil production, and mining.
The territory has been administered by Indonesia since May 1963 and officially included into its territory after a vote (dubbed the "Act of Free Choice") supervised by the Indonesian military junta in 1969, marred by political threats against native Papuans.[3][1] The indigenous Melanesian population at the end of 1961 estimated at 718,055[4] has been estimated to have grown by year 2005 to 1,559,000[5] representing a growth rate of 1.6% per year the Asiatic population at the end of 1961 estimated at 16,581[4] has been estimated to have grown by year 2005 to 1,088,000[5] representing a growth rate of 10% per year. Transmigration from the Indonesian islands of Sumatera, Java, Bali and Sulawesi is the main cause of the inflation of the Asiatic population.[2] Meanwhile, the population growth of the Melanesian population has been slowed by over half a century of what has been described as genocidal policies from the Indonesian state apparatus.[2][6]
Human habitation is estimated to have begun between 42,000 and 48,000 years ago.[7] The Netherlands claimed the region and commenced missionary work in the nineteenth century. The region was annexed by Indonesia in the 1960s,[1] and has faced a separatist movement since then, resulting in continued repression and in the deaths of 100,000 up to 500,000 indigenous West Papuans.[6][8]
Following the 1998 commencement of reforms across Indonesia, Papua and other Indonesian provinces received greater regional autonomy. In 2001, "Special Autonomy" status was granted to Papua province, although to date, implementation has been partial and often criticized.[9] The region was administered as a single province until 2003, when it was split into the provinces of Papua and West Papua.
Access to Western New Guinea by foreign journalists, non-governmental organizations, and academic researchers is under close control by the Indonesian administration, which often rejects visa applications. As formerly in East Timor, Indonesia's former colonial territory, the Indonesian administration takes great effort at filtering the information that gets out of Western New Guinea.[10]
Contents
1 Name
2 Geography
3 Ecology
3.1 Flora and fauna on the Bird's Head Peninsula
4 Demographics
4.1 Haplogroups
4.2 Extinction
5 Culture
6 History
6.1 European conquest
6.2 Netherlands New Guinea
6.3 Incorporation into Indonesia
7 Administration
8 See also
9 References
10 External links
Name
Speakers align themselves with a political orientation when choosing a name for the western half of the island of New Guinea.[11] "West Papua", which is not the official Indonesian name for the western half of the island, is the name preferred by ethnic Papuans.[12][1][13] The region has had the official names of Netherlands New Guinea (1895–1962), West New Guinea (1962–63), West Irian (or Irian Barat) (1963–73), Irian Jaya (1973–2001), and Papua (2002–2003). When the region was administratively one in Indonesia, Indonesian officials criticised activists' use of the term "West Papua", because they thought that the term implied that the province was not a part of Indonesia. Indonesian president Abdurrahman Wahid considered his short-lived use of the name "Papua" in 2002 as a concession to the West Papuans.[14] Since 2003, western New Guinea has had two provinces: the province of Irian Jaya Barat on the west, renamed West Papua in 2007, and the province of Papua on the east. Since 2014, the official name of the political group that represents the Melanesian population of western New Guinea in the Melanesian Spearhead Group is the United Liberation Movement for West Papua (ULMWP).
In brief, Indonesian officials and administrators refer to the newly created province when they say "West Papua"; while most of the Melanesian population, independence activists, and non-governmental organizations mean the whole of western New Guinea.[1][10][15][16]
Geography
The region is 1,200 kilometres (750 miles) from east to west and 736 kilometres (457 miles) from north to south. It has an area of 420,540 square kilometres (162,371 square miles), which equates to approximately 22% of Indonesia's land area. The border with Papua New Guinea mostly follows the 141st meridian east, with one section defined by the Fly River.[17]
The island of New Guinea was once part of the Australian landmass and lie on the Sahul. The collision between the Indo-Australian Plate and Pacific plate resulting in the Maoke Mountains run through the centre of the region and are 600 km (373 mi) long and 100 km (62 mi) across.[citation needed] The range includes about ten peaks over 4,000 metres (13,000 feet),[18] including Puncak Jaya (4,884 m or 16,024 ft), Puncak Mandala (4,760 m or 15,620 ft) and Puncak Trikora (4,750 m or 15,580 ft).[19] The range ensures a steady supply of rain from the tropical atmosphere. The tree line is around 4,000 m (13,100 ft)[citation needed] and the tallest peaks feature small glaciers and are snowbound year-round. Both north and west of the central ranges the land remains mountainous – mostly 1,000 to 2,000 metres (3,300 to 6,600 feet) high with a warm humid climate year-round. The highland areas feature alpine grasslands, jagged bare peaks, montane forests, rainforests, fast flowing rivers, and gorges. Swamps and low-lying alluvial plains of fertile soil dominate the southeastern section around the town of Merauke. Swamps also extend 300 kilometres (190 miles) around the Asmat region.
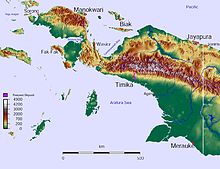
The rugged and hilly topography of Western New Guinea.
The province has 40 major rivers, 12 lakes, and 40 islands.[citation needed] The Mamberamo river is the province's largest and runs through the north of the province. The result is a large area of lakes and rivers known as the Lakes Plains region. The southern lowlands, habitats of which included mangrove, tidal and freshwater swamp forest and lowland rainforest, are home to populations of fishermen and gatherers such as the Asmat people. The Baliem Valley, home of the Dani people, is a tableland 1,600 m (5,250 ft) above sea level in the midst of the central mountain range.[citation needed]
The dry season across the region is generally between May and October; although drier in these months, rain persists throughout the year.[citation needed] Strong winds and rain are experienced along the north coast in November through to March. However, the south coast experiences an increase in wind and rain between April and October, which is the dry season in the Merauke area, the only part of Western New Guinea to experience distinct seasons.[citation needed] Coastal areas are generally hot and humid, whereas the highland areas tend to be cooler.[citation needed]
Ecology
Lying in the Asia-Australian transition zone near Wallacea, the region's flora and fauna include Asiatic, Australian, and endemic species.[citation needed] The region is 75% forest and it has a high degree of biodiversity. The island has an estimated 16,000 species of plant, 124 genera of which are endemic.[citation needed] The mountainous areas and the north are covered with dense rainforest. Highland vegetation also includes alpine grasslands, heath, pine forests, bush and scrub. The vegetation of the south coast includes mangroves and sago palms, and in the drier southeastern section, eucalypts, paperbarks, and acacias.
Marsupial species dominate the region; there are an estimated 70 marsupial species (including possums, wallabies, tree-kangaroos, cuscus), and 180 other mammal species (including the endangered long-beaked echidna).[citation needed] The region is the only part of Indonesia to have kangaroos, marsupial mice, bandicoots, and ring-tailed possums. The approximately 700 bird species include cassowaries (along the southern coastal areas), bowerbirds, kingfishers, crowned pigeons, parrots, and cockatoos). Approximately 450 of these species are endemic.[citation needed]Birds of paradise can be found in Kepala Burung and Yapen.[citation needed] The region is also home to around 800 species of spiders, 200 frogs, 30,000 beetles, 70 bat species, one of the world's longest lizards (Papuan monitor) and some of the world's largest butterflies.[citation needed] The waterways and wetlands of Papua are habitat for salt and freshwater crocodiles, tree monitors, flying foxes, ospreys, and other animals; while the equatorial glacier fields remain largely unexplored.[citation needed]
In February 2005, a team of scientists exploring the Foja Mountains discovered numerous new species of birds, butterflies, amphibians, and plants, including a species of rhododendron which may have the largest bloom of the genus.[20]
Environmental issues include deforestation, the spread of the introduced crab-eating macaque which now threatens the existence of native species, and discarded copper and gold tailings from the Grasberg mine.[21]
Flora and fauna on the Bird's Head Peninsula

The king bird-of-paradise is one of over 300 bird species on the peninsula.
The Bird's Head Peninsula, also known as the Doberai Peninsula, is covered by the Vogelkop Montane Rain Forests Ecoregion. It includes more than 22,000 km2 of montane forests at elevations of 1,000 metres (3,300 feet) and higher.[citation needed][22] Over 50% of these forests are located within protected areas. There are over 300 bird species on the peninsula, of which at least 20 are unique to the ecoregion, and some live only in very restricted areas. These include the grey-banded munia, Vogelkop bowerbird, and the king bird-of-paradise.[23]
Road construction, illegal logging, commercial agricultural expansion and ranching potentially threaten the integrity of the ecoregion.[23] The south-eastern coast of the Bird's Head Peninsula forms part of the Teluk Cenderawasih National Park.[24]
Demographics
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1971 | 923,440 | — |
| 1980 | 1,173,875 | +27.1% |
| 1990 | 1,648,708 | +40.5% |
| 1995 | 1,942,627 | +17.8% |
| 2000 | 2,220,934 | +14.3% |
| 2010 | 3,593,803 | +61.8% |
The population of the region was estimated to be 3,593,803 in 2010.[25] The interior is predominantly populated by ethnic Papuans and coastal towns are inhabited by descendants of intermarriages between Papuans, Melanesians and Austronesians, including the Indonesian ethnic groups. Migrants from the rest of Indonesia also tend to inhabit the coastal regions. The two largest cities in the territory are Manokwari in the northeast of the Bird's Head Peninsula and Jayapura in the northeast. Both cities have a population of approximately 200,000.[citation needed]

The language families in Ross' conception of Trans-New Guinea
The region is home to around 312 different tribes, including some uncontacted peoples.[26] The Dani, from the Baliem Valley, are one of the most populous tribes of the region. The Manikom and Hatam inhabit the Anggi Lakes area, and the Kanum and Marind are from near Merauke. The semi-nomadic Asmat inhabit the mangrove and tidal river areas near Agats and are renowned for their woodcarving. Other tribes include the Amungme, Bauzi, Biak (Byak), Korowai, Lani, Mee, Mek, Sawi, and Yali. Estimates of the number of distinct languages spoken in the region range from 200 to 700. A number of these languages are permanently disappearing.[citation needed]
As in Papua New Guinea and some surrounding east Indonesian provinces, a large majority of the population is Christian. In the 2000 census 54% identified themselves as Protestant, 24% as Catholic, 21% as Muslim, and less than 1% as either Hindu or Buddhist.[citation needed] There is also substantial practice of animism among the major religions, but this is not recorded by the census.[citation needed]
Haplogroups
There are 6 main Y-chromosome haplogroups in Western New Guinea; Y-chromosome haplogroup M is the most common, with Y-chromosome haplogroup O2a as a small minority in second place and Y-chromosome haplogroup S back in third position across the mountain highlands; while D, C2 and C4 are of negligible numbers.
Haplogroup M is the most frequently occurring Y-chromosome haplogroup in Western New Guinea.[27]- In a 2005 study of Papua New Guinea's ASPM gene variants, Mekel-Bobrov et al. found that the Papuan people have among the highest rate of the newly evolved ASPM haplogroup D, at 59.4% occurrence of the approximately 6,000-year-old allele.[28]
Haplogroup O2a (M95) is typical of Austroasiatic peoples, Tai–Kadai peoples, Malays, Indonesians, and Malagasy, with a moderate distribution throughout South, Southeast, East, and Central Asia.
Haplogroup S occurs in eastern Indonesia (10–20%) and Island Melanesia (~10%), but reaches greatest frequency in the highlands of Papua New Guinea (52%).[29]
Extinction
In 2012, the Tampoto tribe in Skow Mabo village, Jayapura, was on the brink of extinction, with only a single person (a man in his twenties) still living; the Dasem tribe in Waena area, Jayapura, also is near extinction, with only one family consisting of several people still alive. A decade ago, the Sebo tribe in the Kayu Pulau region, Jayapura Bay, died out. Hundreds of Papuan tribes have their own individual languages; they are unable to compete in the acculturation process with other groups, and some tribes have resisted acculturation.
Culture
Western New Guineans have significant cultural affinities with the inhabitants of Papua New Guinea.[citation needed] As in Papua New Guinea the peoples of the highlands have traditions and languages distinct from the peoples of the coast, though Papuan scholars and activists have recently detailed cultural links between coast and highlands as evidenced by close similarity of family names. In some parts of the highlands, the koteka (penis gourd) is worn by males in ceremonies. The use of the koteka as everyday dress by Dani males in Western New Guinea is still common.
History
Papuan habitation of the region is estimated to have begun between 42,000 and 48,000 years ago.[7] Research indicates that the highlands were an early and independent center of agriculture, and show that agriculture developed gradually over several thousands of years and that banana has been cultivated in this region since at least 7,000 years ago.[30]
Austronesian peoples migrating through Maritime Southeast Asia settled in the area at least 3,000 years ago, and populated especially in Cenderawasih Bay. Diverse cultures and languages have developed in situ; there are over 300 languages and two hundred additional dialects in the region (See Papuan languages, Austronesian languages, Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian languages).
The 14th century Majapahit poem Nagarakretagama mentioned Wwanin or Onin as a recognized territory in the east, today identified as Onin peninsula in Fakfak Regency, western part of larger Bomberai Peninsula, south of Bird's Head region of Western New Guinea.[31] Wanin or Onin was probably the oldest name in recorded history to refer to the western part of the New Guinea island.[32]
European conquest
In 1526–27, the Portuguese explorer Jorge de Menezes accidentally came upon the principal island in the Biak archipelago and is credited with naming it Papua, from a Malay word pepuah, for the frizzled quality of Melanesian hair.[33] Heading east, he eventually reported the northern coast of the Bird's Head Peninsula and the Waigeo Island, and named the region Ilhas dos Papuas (Islands of Papuans).[34]
In 1545 the Spaniard Yñigo Ortiz de Retez sailed along the north coast as far as the Mamberamo River near which he landed, naming the island Nueva Guinea. In 1606 Spanish navigator Luís Vaz de Torres[35] sailed along the southwestern part of the island in present-day Papua, and also claimed the territory for the King of Spain.
Near the end of the sixteenth century, Sultanate of Ternate under Sultan Baabullah (1570–1583), had influence over parts of Papua.[36]
Netherlands New Guinea

Fort Du Bus in 1828
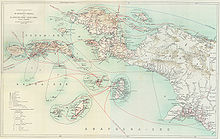
Dutch expeditions in Netherlands New Guinea 1907–1915.
In 1660, the Dutch recognised the Sultan of Tidore's sovereignty over New Guinea. New Guinea thus became notionally Dutch as the Dutch held power over Tidore. In 1793, Britain established a settlement near Manokwari. However, it failed. By 1824 Britain and the Netherlands agreed that the western half of the island would become part of the Dutch East Indies. In 1828 the Dutch established a settlement in Lobo (near Kaimana) which also failed. Great Britain and Germany had recognised the Dutch claims on western New Guinea in treaties of 1885 and 1895. Dutch activity in the region remained minimal in the first half of the twentieth century. Dutch, US, and Japanese mining companies explored the area's rich oil reserves in the 1930s. In 1942, the northern coast of West New Guinea and the nearby islands were occupied by Japan.[37] In 1944, Allied forces gained control of the region through four-phase campaign from neighbouring Papua New Guinea. The United States constructed a headquarters for MacArthur at Hollandia (Jayapura) intended as a staging point for operations taking of the Philippines. Papuan men and resources were used to support the Allied war effort in the Pacific. After the war's end the Dutch regained possession of the region.
Since the early twentieth century, Indonesian nationalists had sought an independent Indonesia based on all Dutch colonial possessions in the Indies, including western New Guinea. In December 1949, the Netherlands recognised Indonesian sovereignty over the Dutch East Indies with the exception of Dutch New Guinea, the issue of which was to be discussed within a year. The Dutch successfully argued that Western New Guinea is geographically very different to Indonesia and the people also very ethnically different. In an attempt to prevent Indonesia taking control of the region and to prepare the region for independence, the Dutch significantly raised development spending off its low base,[38] began investing in Papuan education, and encouraged Papuan nationalism. A small western elite developed with a growing political awareness attuned to the idea of independence, with close links to neighbouring eastern New Guinea which was administered by Australia.[39] A national parliament was elected in 1961 and the Morning Star flag raised on 1 December, with independence planned in exactly 9 years time.
Incorporation into Indonesia

The Sukarno-era "West Irian Liberation Statue" in Jakarta.
Sukarno made the takeover of Western New Guinea a focus of his continuing struggle against Dutch imperialism and part of a broader Third World conflict with the West.[40] Although Indonesian seaborne and paratroop incursions into the territory met with little success,[41] the Dutch knew that a military campaign to retain the region would require protracted jungle warfare, and, unwilling to see a repeat of their futile efforts in the armed struggle for Indonesian independence in the 1940s, agreed to American mediation. US President Kennedy wrote to the then Dutch Prime Minister Jan de Quay, encouraging the Netherlands to relinquish control of Western New Guinea to Indonesia and warning of Indonesia's potential alliance with communist powers if Sukarno was not appeased.[42] The negotiations resulted in the UN-ratified New York Agreement of September 1962,[43] which transferred administration to a United Nations Temporary Executive Authority (UNTEA) and proposed that the administration could be assumed by Indonesia until such time as a plebiscite could be organized to allow Papuans to determine whether they wanted independence or union with Indonesia.
Under the terms of the New York Agreement, all Western New Guinean men and women were to be given an independence referendum, one person-one vote; this was to be called the "Act of Free Choice". However, when the act was due to take place under the new dictator Suharto, the Indonesian government claimed that Western New Guineans were too "primitive" to cope with democracy and instead used a musyawarah (a traditional Indonesian consensus of elders) to decide the region's status. The 1,026 elders were hand-picked by the Indonesian government and many were coerced into voting for union with Indonesia. Soon after, the region became the 26th province of Indonesia.[44] The 1969 Act of Free Choice is considered contentious, with even United Nations observers recognizing the elders were placed under duress and forced to vote yes.[45]
The "Act of free choice" has often been criticized as the "Act of no choice", and many independence activists continuously protest for a fresh referendum for every single Western New Guinean. After the fall of Suharto in 1998, celebrity Archbishop Desmond Tutu and some American and European parliamentarians requested United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan to review the United Nations' role in the vote and the validity of the Act of Free Choice.[46] There have been calls for the United Nations to conduct its own referendum, with as broad an electorate as critics say the New York Agreement obliged but the Act of Free Choice did not fulfill. Those calling for a vote also point to the 30-year license which Indonesia sold to the Freeport-McMoRan company for Papuan mining rights in 1967, and to the Indonesian military's response to the East Timor referendum as support to discredit the 1969 Act of Free Choice.[citation needed] The Indonesian Government position is that the United Nations' noting of the results validates the conduct and results.
A new referendum is supported by many international organisations including the Free West Papua Campaign, which works with Western New Guineans to provide all West Papuans with self-determination and full independence from Indonesian rule.[47]
The Federal Republic of West Papua, formed on 19 October 2011 at the Third West Papuan People's Congress, has declared the New York Agreement and The Act of Free Choice null and invalid, and seeks recognition by the United Nations as an independent nation according to international and customary law.[citation needed]
The Free Papua Movement (OPM) has engaged in a pro-independence conflict with the Indonesian military since the 1960s. This has been in response to the initial take over of the region and multiple killings and other human rights violations by Indonesian troops, causing many West Papuans and international organisations to describe the situation in West Papua as genocide.[48]Rebellions occurred in remote mountainous areas in 1969, 1977, and the mid-1980s, occasionally spilling over into Papua New Guinea. In the Post-Suharto era, the national government began a process of decentralisation of the provinces, including, in December 2001, "Special Autonomy" status for Papua province and a reinvestment into the region of 80% of the taxation receipts generated by the region. In 2003, the province of "West Papua" was created in the Bird's Head Peninsula and surrounding islands to its west.
In 2011, Indonesia submitted an application for membership to the Melanesian Spearhead Group (MSG) for the two Papua provinces and was granted observer status.[49] The West Papua National Council for Liberation independence movement made an unsuccessful application for membership to the MSG in 2013 after which the United Liberation Movement for West Papua (ULMWP) was established in December 2014 to unite the three main political independence movements under a single umbrella organisation. In June 2015, the ULMWP was granted MSG observer status as representative of West Papuans outside the country while Indonesia was upgraded to associate member.[50][51]
In 2016, at the 71st Session of the UN General Assembly, leaders of several Pacific Islands countries called for UN action on alleged human rights abuses committed on Papua's indigenous Melanesians with some leaders calling for self-determination.[52][53] Indonesia accused the countries of interfering with Indonesia's national sovereignty.[53] In 2017, at the 72nd Session, the leaders called for an investigation into killings and various alleged human rights abuses by Indonesian security forces and appealed to world leaders to support a referendum on independence from Indonesia.[54]
Administration

Papua province
West Papua province
The Western New Guinea region is currently administered as two Indonesian provinces:
- The province of Papua contains 28 regencies (kabupaten) and one city (kota) at the 2010 Census, which were subdivided into 385 districts (kecamatan), and thence into "villages" (kelurahan and desa). The 28 existing regencies are: Asmat; Biak-Numfor; Boven Digoel; Central Mamberamo; Deiyai; Dogiyai; Intan Jaya; Jayapura; Jayawijaya; Keerom; Lanny Jaya; Mamberamo Raya; Mappi; Merauke; Mimika; Nabire; Nduga; Paniai; Pegunungan Bintang; Puncak; Puncak Jaya; Sarmi; Supiori; Tolikara; Waropen; Yahukimo; Yalimo; and Yapen Islands. The city of Jayapura, which also has the status equivalent to a regency, is the largest city in the Western New Guinea region.
- The province of West Papua contains twelve regencies (kabupaten) and one city (kota) at the 2010 Census, which were subdivided into 154 districts (kecamatan). The existing regencies in West Papua are: Arfak Mountains; Fakfak; Kaimana; Manokwari; Maybrat; Raja Ampat; Sorong; South Manokwari; South Sorong; Tambrauw; Teluk Bintuni; and Teluk Wondama. The city of Sorong, which also has the status equivalent to a regency, is the largest city in the West Papua province, but the current capital city is Manokwari.
- Reports suggest that the formation of three new provinces has recently been approved by Indonesia's House of Representatives: South Papua, Central Papua and Southwest Papua.[55] 25 new regencies and 3 new municipalities are also to be created.
From Papua province, the 17 new regencies to be created are those of Gili Menawa, Moyo, Balin Senter, Bogogha, Puncak Trikora, Muara Digul, Admi Korbay, Katengban, Okika, Northwest Yapen, East Yapen, Numfor Island, Yalimek, Mambera Hulu, Southwest Yahukimo, East Yahukimo and Gondumisisare, while the 2 new municipalities are Merauke City and Baliem Valley.
In West Papua, the 8 new regencies to be created are those of Malamoy, Maibratsau, North Raja Ampat, South Raja Ampat, Raja Maskona, Okas, West Manokwari and Imeo, while the new municipality is Manokwari City.
See also
- List of rivers of Western Papua
- Manseren Manggoendi
References
- Specific
^ abcde Saltford, J. (2003). The United Nations and the Indonesian takeover of West Papua, 1962-1969: The anatomy of betrayal, 1st edn. Routledge, London.
^ abc Elmslie, Jim (2017), "The great divide: West Papuan demographics revisited; Settlers dominate coastal regions but the Highlands still overwhelmingly Papuan", Asia-Pacific Journal, 15 (2): 1–12
^ United Nations Archives and Records Section, Summary of AG-059 United Nations Temporary Executive Authority in West Irian (UNTEA) (1962–1963). "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 26 May 2017.
^ ab Appendix 4, REPORT ON NETHERLANDS NEW GUINEA FOR THE YEAR 1961, Presented to the Secretary General of the United Nations pursuant to Article 73(e) of the Charter
^ ab Demographic transition in West Papua and claims of genocide
"Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 December 2016. Retrieved 6 November 2016.
^ ab Elmslie, Jim and Webb-Gannon, Camellia (2013), "A slow-motion genocide: Indonesian rule in West Papua", Griffith Journal of Law and Human Dignity, 1 (2): 142–165 CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ ab Gillespie, Richard (2002). "Dating the First Australians" (PDF). Radiocarbon. 44 (2): 455–72. Retrieved 24 May 2010. Archived 19 August 2014
^ Robinson, Jennifer. "The UN's chequered record in West Papua". www.aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 17 October 2017. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
^ U.S. Dept. of Defence; International Crisis Group; and International Crisis Group Archived 8 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine.. Archived 19 August 2014.
^ ab Budiardjo, Carmel and Liong, Liem Soei (1988). West Papua: The obliteration of a people, 3rd edn. Tapol. CS1 maint: Uses authors parameter (link)
^ Leith, Denise (2003). The Politics of Power: Freeport in Suharto's Indonesia. University of Hawaii Press. p. xxv.
^ "Cursed by plenty: Paying a covert visit to Papua's fighters in the forest". The Economist. 8 July 2010. Archived from the original on 9 November 2010. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
^ Cribb, R.B.; Kahin, Audrey (2004). Historical Dictionary of Indonesia. Scarecrow Press. p. 313.
^ Rees, Stuart (2003). Passion for Peace: Exercising Power Creatively. UNSW Press. p. 150.
^ Ver Berkmoes, Ryan (2010). Indonesia. Lonely Planet. p. 775.
^ Doherty, Ben; Lamb, Kate (2017), "Banned West Papua independence petition handed to UN", The Guardian "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 23 October 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
^ Frank Jacobs (13 March 2012). "Who Bit My Border?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 17 March 2012.
^ (Whitten (1992), p. 182
^ List at GunungBagging.com Archived 31 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 26 January 2012.
^ Robin McDowell: 'Lost world' yields exotic new species Archived 28 March 2006 at the Wayback Machine. – The Vancouver Sun – 8 February 2006
^ "Grasberg - IntelligenceMine". Archived from the original on 20 June 2014. Retrieved 15 July 2017.
^ Flip van Helden: A bird's eye view of the Bird's Head Peninsula, in Irian Jaya Studies Programme for Interdisciplinary Research (IIAS) Newsletter nr.37, June 2005 Archived 11 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine., retrieved 11 May 2010
^ ab WWF: Bird wonders of New Guinea's western-most province Archived 16 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine., retrieved 11 May 2010
^ Ministry of Forestry: Teluk Cenderawasih NP Archived 29 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine., retrieved 11 May 2010
^ "Hasil Final Jumlah Penduduk Indonesia 2010". Indonesiadata.co.id. 9 June 2011. Archived from the original on 27 December 2012. Retrieved 7 November 2012.
^ International, Survival. "Papuan Tribes". www.survival-international.org. Archived from the original on 29 July 2009. Retrieved 15 July 2017.
^ Kayser M, Brauer S, Weiss G, Schiefenho¨vel W, Underhill P, Shen P, Oefner P, Tommaseo-Ponzetta M, Stoneking (2003) Reduced Y-Chromosome, but Not Mitochondrial DNA, Diversity in Human Populations from West New Guinea Am J Hum Genet 72:281–302
^ "Ongoing Adaptive Evolution of ASPM, a Brain Size Determinant in Homo sapiens" Archived 24 June 2008 at the Wayback Machine., Science, 9 September 2005: Vol. 309. no. 5741, pp. 1720–1722.
^ Murray P. Cox and Marta Mirazón Lahr, "Y-Chromosome Diversity Is Inversely Associated With Language Affiliation in Paired Austronesian- and Papuan-Speaking Communities from Solomon Islands," American Journal of Human Biology 18:35–50 (2006)
^ T. P. Denham et al 2003, Origins of Agriculture at Kuk Swamp in the Highlands of New Guinea. Archived 5 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Science 11 July 2003: Vol. 301 no. 5630 pp. 189–193 doi:10.1126/science.1085255
^ "Onin Peninsula". Geographic Names. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
^ Martin Slama and Jenny Munro, ed. (2015). From 'Stone Age' to 'Real Time' Exploring Papuan Temporalities, Mobilities, and Religiosities. Canberra: Australian National University Press. p. 110. ISBN 9781925022438. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
^ The World Almanac and Book of Facts 1985
^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 7 January 2016. J.H.F. SOLLEWUN GELPKE, On the Origin of the Name Papua
^ Translation of Torres's report to the king in Collingridge, G. (1895) Discovery of Australia pp. 229–237. Golden Press Edition, 1983, Gradesville, NSW. ISBN 0-85558-956-6
^ Witton, Patrick (2003). Indonesia (7th edition). Melbourne: Lonely Planet. p. 821. ISBN 1-74059-154-2.
^ Klemen, L. "The Fall of Dutch New Guinea, April 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942. Archived from the original on 23 February 2012.
^ McDonald (1980), p. 65
^ McDonald (1980), p. 64.
^ Vickers (2005), p. 139
^ McDonald, Hamish (28 January 2008). "No End to Ambition". Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on 3 November 2012.
^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
^ McDonald, Hamish (1980). Suharto's Indonesia. Blackburn, Victoria: Fontana Books. p. 36. ISBN 0-00-635721-0.
^ Friend (2003), p. 72 (expand reference)
^ Singh, Bilveer Papua: Geopolitics and the Quest for Nationhood, Transaction Publishing, 2008 p. 86
^ "Indonesia's 1969 Takeover of West Papua". nsarchive.gwu.edu. Archived from the original on 19 July 2017. Retrieved 15 July 2017.
^ "Campaign for a free and independent West Papua". Free West Papua Campaign. Archived from the original on 9 January 2016.
^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 April 2015. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
^ Sally Andrews (3 April 2015). "West Papua: Melanesian Spearhead Group has a tough decision to make". Lowly Interpreter. Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 3 October 2017.
^ Armbruster, Stefan (26 June 2015). "Melanesia takes lead on future West Papuan peace". SBS News. Archived from the original on 2 October 2017. Retrieved 2 October 2017.
^ Fox, Liam (25 June 2015). "Indonesia admitted to Melanesian Spearhead Group, West Papuan group given observer status". ABC News Pacific Beat. Archived from the original on 14 January 2017. Retrieved 2 October 2017.
^ "Pacific leaders raise West Papua at the UN". Radio New Zealand. 26 September 2016. Archived from the original on 5 October 2017. Retrieved 4 October 2017.
^ ab "Indonesia accuses Pacific nations of 'misusing' the United Nations assembly after Papua criticisms". ABC News Pacific Beat. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 26 September 2016. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 4 October 2017.
^ "Fiery debate over West Papua at UN General Assembly". Radio New Zealand. 27 September 2017. Archived from the original on 1 October 2017. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
^ "New Provinces Receive the Nod - Jakarta Globe". thejakartaglobe.com. 26 October 2013. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- Bibliography
Monbiot, George. 1989, 2003. Poisoned Arrows: An investigative journey through the forbidden lands of West Papua. London: Michael Joseph, Green Books. ISBN 1903998271- Leith, Denise. 2002. The Politics of Power: Freeport in Suharto's Indonesia. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 0-8248-2566-7
- Conboy, Ken. 2003. Kopassus. Equinox Publishing, Jakarta Indonesia. ISBN 979-95898-8-6
- Penders, C.L.M., The West New Guinea débâcle. Dutch decolonisation and Indonesia 1945–1962, Leiden 2002, KITLV
- "Arrow Against the Wind." Narrative of documentary on people of Asmat and Dani, their culture, and their relationship with the nature http://www.dgmoen.net/video_trans/004.html
Throwim Way Leg by Tim Flannery- Neles Tebay : West Papua. The struggle for peace with justice. Catholic Institute for International Relations: London 2005, ISBN 1 85287 316 7.
- Marshall, A.J. and B. Beehler (eds.), "The Ecology of Papua". 2007. Parts 1 & 2 as Vol. 6 in "The Ecology of Indonesia" series. Singapore: Periplus Press.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Papua. |
- Free West Papua Campaign