War flag

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP 
A knight (Jan I van Brabant) flying a heraldic flag in battle, in addition to the heraldic device displayed on his shield (Codex Manesse, ca. 1304)
A war flag, also known as a military flag, battle flag, or standard,[1] is a variant of a national flag for use by a country's military forces when on land. The nautical equivalent is a naval ensign. Under the strictest sense of the term, few countries today currently have proper war flags, most preferring to use instead their state flag or standard national flag for this purpose.
Contents
1 History
2 Current war flags
2.1 Used by armed forces only
2.2 Army (land) use only
2.3 War flags that are also naval ensigns
2.4 Other war flags
3 Former war flags
4 See also
5 References
6 Further reading
7 External links
History
.mw-parser-output .templatequoteoverflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequoteciteline-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0
Sound trumpets! Let our bloody colours wave! And either victory, or else a grave.
— Edward, Prince of Wales, in Henry VI, Part 3, Act II, Scene II
Field signs were used in early warfare at least since the Bronze Age.
The word standard itself is from an Old Frankish term for a field sign (not necessarily a flag).

Babur and his Mughal Army saluting the Nine Standards of Timur.
The use of flags as field signs apparently emerges in Asia, during the Iron Age, possibly in either China or India.[2] in Achaemenid Persia, each army division had its own standard, and "all officers had banners over their tents".[3] Early field signs that include, but are not limited to a flag, are also called vexilloid or "flag-like", for example the Roman Eagle standard or the dragon standard of the Sarmatians. The Roman Vexillum itself is also "flag-like" in the sense that it was suspended from a horizontal crossbar as opposed to a simple flagpole.
Use of simple flags as military ensigns becomes common during the medieval period, developing in parallel with heraldry as a complement to the heraldic device shown on shields. The maritime flag also develops in the medieval period. The medieval Japanese Sashimono carried by foot-soldiers are a parallel development.
Some medieval free cities or communes did not have coats of arms, and used war flags that were not derived from a coat of arms. Thus, the city of Lucerne used a blue-white flag as a field sign from the mid 13th century, without deriving it from a heraldic shield design.
Current war flags
Used by armed forces only

War flag of Bolivia

War flag of Brunei

Canadian Armed Forces ensign

War flag of the People's Liberation Army (China)

Georgia

Flag of the Japan Self-Defense Forces and the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force

Flag of the Armed Forces of Moldova
Officially not the war flag of Moldova

Myanmar

War flag of Portugal

Banner of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation
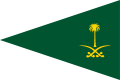
War flag of the Royal Staff of Saudi Arabian Armed Forces

Flag of the Armed Forces of Serbia

Sri Lanka

Flag of the Armed Forces of Ukraine
Army (land) use only

Bulgaria

War flag of the Chinese army

War flag of the Republic of China armed forces

Georgia

War flag of Hungary

India

Army ensign of Malaysia

Myanmar

Pakistan Army

Polish Land Forces

Russian Ground Forces

Saudi Arabian Army

South Korean army

Royal Thai Army

Flag of Turkish Land Forces Command

Ukrainian army flag

British Army non-ceremonial flag

Flag of Vietnam People's Army

Army flag of the United States of America

War ensign of Finland

War ensign of Peru

Flag of Saudi Arabian naval bases

Ensign of the Singaporean navy

War ensign of Sweden

The Ukrainian Navy's ensign
Other war flags
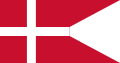
State, war flag, and state ensign of Denmark

State, war flag, and state ensign of Germany
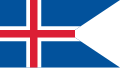
State and state/naval ensign of Iceland

State/war flag and state/naval ensign of Norway

Flag of the Philippines at war

War flag (regimental color) of the Hellenic Army

The Ukrainian Air Force's flag

State, war flag, state, and naval ensign of Venezuela
Former war flags

Battle flag of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army

The original Eureka Flag specimen, rebel warflag at the 1854 Battle of Eureka Stockade.

Battle flag of the Confederate States (1861–65)

Cross of Burgundy Flag, Spain (1506–1843)

War flag of the Japanese imperial army

War flag of the People's Republic of Congo (1970–91)

The "Gadsden flag", used by some Continental forces during the American Revolutionary War (1775–83)

Battle flag of the United Irishmen, used at the 1798 Rebellion Battle of Arklow

War flag of East Germany (1960–90)

(currently banned in some European Union countries due to usage by neo-fascist groups)
Reichskriegsflagge, the war flag for the German Wehrmacht and official flag of the Kriegsmarine

State and war flag of the Kingdom of Greece (1863–1924 and 1935–70)

War flag of the Italian Social Republic (1943–45)

War flag of Prussia (1816)

War flag of the German Empire (1903–19)

War flag of the Roman Republic of 1849

South Vietnam

Flag of the Red Army (Unofficial)

Naval ensign of the Soviet Union

Royal Siamese Army (1892–1936)

Royal Siamese Army in Haw wars (1885–1890)

United States Cavalry guidon.

The United States of America's naval jack (1912–59)

War flag of the Royal Italian Army

War ensign of the Slovak Republic (puppet state of Nazi Germany 1939–45)

War flag of the Independent State of Croatia (puppet state of Nazi Germany 1941–45)

War flag of the Royal Hungarian Army (1939–45)
See also
- Colours, standards and guidons
References
^ "standard". Oxford English Dictionary (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. September 2005..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
^ flag. (2008). Encyclopædia Britannica. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica.
^ E. Pottier, Douris, London, 1909, p. 105 fig. 20, Plate XXV.b
Further reading
- Wise, Terence (1978) Military flags of the world, in color. New York: Arco Publishing. 184p.
ISBN 0668044721. War flags of 1618–1900.
External links
FIAV Flag Information Symbols at Flags of the World








































































