List of ethnic groups of Africa

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP 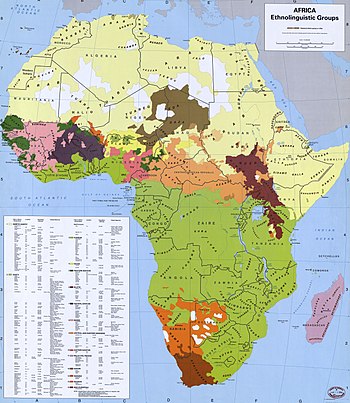
1996 map of the major ethnolinguistic groups of Africa, by the Library of Congress Geography and Map Division (substantially based on G.P. Murdock, Africa, its peoples and their cultural history, 1959). Colour-coded are 15 major ethnolinguistic super-groups, as follows:
Afroasiatic
Hamitic (Berber, Cushitic) + Semitic (Ethiopian, Arabic)
Hausa (Chadic)
Niger–Congo
Bantu
"Guinean" (Volta-Niger, Kwa, Kru)
"Western Bantoid" (Atlantic)
"Central Bantoid" (Gur, Senufo)
"Eastern Bantoid" (Southern Bantoid)
Mande
Nilo-Saharan (unity debated)
Nilotic
Central Sudanic, Eastern Sudanic (besides Nilotic)
Kanuri
Songhai
other
Khoi-San (unity doubtful; Khoikhoi, San, Sandawe + Hadza)
Malayo-Polynesian (Malagasy)
Indo-European (Afrikaaner)
The ethnic groups of Africa number in the thousands, with each population generally having its own language (or dialect of a language) and culture. The ethnolinguistic groups include various Afroasiatic, Khoisan, Niger-Congo and Nilo-Saharan populations.
The official population count of the various ethnic groups in Africa is highly uncertain, both due to limited infrastructure to perform censuses and due to the rapid population growth. There have also been accusations of deliberate misreporting in order to give selected ethnicities numerical superiority (as in the case of Nigeria's Hausa, Fulani, Yoruba and Igbo people).[1][2][3]
A 2009 genetic clustering study, which genotyped 1327 polymorphic markers in various African populations, identified six ancestral clusters. The clustering corresponded closely with ethnicity, culture and language.[4] A 2018 whole genome sequencing study of the world's populations observed similar clusters among the populations in Africa. At K=9, distinct ancestral components defined the Afrosiatic-speaking populations inhabiting North Africa and Northeast Africa; the Nilo-Saharan-speaking populations in Northeast Africa and East Africa; the Ari populations in Northeast Africa; the Niger-Congo-speaking populations in West-Central Africa, West Africa, East Africa and Southern Africa; the Pygmy populations in Central Africa; and the Khoisan populations in Southern Africa.[5]
Contents
1 Lists
1.1 By linguistic phylum
1.2 Major ethnic groups
1.3 Ethnic groups by region
1.3.1 Central Africa
1.3.2 Horn of Africa
1.3.3 North Africa
1.3.4 Southeast Africa
1.3.5 Southern Africa
1.3.6 West Africa
2 See also
3 References
Lists
By linguistic phylum
It has been suggested that this section be split out into another article titled List of Bantu peoples. (Discuss) (May 2018) |
As a first overview, the following table lists major groups by ethno-linguistic affiliation, with rough population estimates (as of 1016) :[citation needed]
| Phylum | Region | Major groups | Pop. (millions) (2016)[citation needed] | Number of groups |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afro-Asiatic | North Africa, Horn of Africa, Sahel | Amhara, Hausa, Oromo, Somali, Tachelhit Berber | 100 | 200-300[6] |
| Niger-Congo | West Africa, Central Africa, Southern Africa, East Africa | Bambara, Fula, Igbo, Mooré, Swahili, Yoruba, Zulu | 100 | 1650[6] |
| Nilo-Saharan | Nile Valley, Sahel, East Africa | Dinka, Kanuri, Luo, Maasai, Nuer | 60 | 80[6] |
| Khoisan | Southern Africa, Tanzania | Nama, San, Sandawe, Kung ǃXóõ | 1 | 40-70[6] |
| Austronesian | Madagascar | Malagasy | 20 | 1[7] |
| Indo-European | Central Africa, East Africa, North Africa, Southern Africa, West Africa | Afrikaners, British, French | 6 | 3[8] |
| Total | Africa | 1.2 billion (UN 2016) | c. 2,000[9] |
Major ethnic groups
The following is a table of major ethnic groups (10 million people or more):
| Major ethnic groups | Region | Countries | Language family | Pop. (millions) (year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akan | West Africa | Ghana, Ivory Coast | Niger–Congo, Kwa | 20[year needed] |
| Abyssinians | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia, Eritrea | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | |
| Amhara | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | 22 (2007) |
| Bantu | Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa | most of Equatorial Africa | Niger-Congo, Bantu | [10] |
| Berbers | Maghreb, Nile Valley | Morocco, Tunisia, Algeria, Mauritania, Libya, Egypt, Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso | Afro-Asiatic, Berber | |
| Chewa | Central Africa | Malawi, Zambia | Niger–Congo, Bantu | 12 (2007) |
Egyptians[11] | North Africa | Egypt, Sudan | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic & Coptic | 93 (2017) |
| Fulani | West Africa | Mauritania, Gambia. Guinea-Bissau, Guinea, Nigeria, Cameroon, Senegal, Mali, Burkina Faso, Benin, Niger, Chad, Sudan, CAR, Ghana, Togo, Sierra Leone | Niger–Congo, Senegambian | 20[year needed] |
| Hausa | West Africa | Nigeria, Niger, Benin, Ghana, Cameroon, Chad, Sudan | Afro-Asiatic, Chadic | 43[year needed] |
| Hutu | Central Africa | Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo | Niger–Congo, Bantu | 15[year needed] |
| Igbo | West Africa | Nigeria | Niger–Congo, Volta–Niger | 34 (2017) |
| Kanuri | Central Africa | Nigeria,[12]Niger,[13]Chad[14] and Cameroon[15] | Nilo-Saharan, Saharan | 10 |
| Khoisan | Southern Africa | South Africa, Namibia | Khoisan | |
| Kongo | Central Africa | Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, Republic of the Congo | Niger–Congo, Bantu | 10[year needed] |
| Luba | Central Africa | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Niger–Congo, Bantu | 15[year needed] |
Maghrebis (Arab-Berber) | North Africa | Maghreb (Mauritania, Morocco, Western Sahara), Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | 100[year needed] |
| Mongo | Central Africa | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Niger–Congo, Bantu | 15[year needed] |
| Nilotes | Nile Valley, East Africa, Central Africa | South Sudan, Sudan, Chad, Central African Republic, Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Ethiopia | Nilo-Saharan, Nilotic | 22 (2007) |
| North African Arabs | North Africa, Sahel | Morocco, Tunisia, Algeria, Mauritania, Libya, Egypt, Chad, Sudan, Mali, Niger, Nigeria | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | [16] |
| Nubians | Nile Valley | Sudan, Egypt | Nilo-Saharan, Eastern Sudanic | |
| Oromo | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | 35 (2016) |
| Shona | East Africa | Zimbabwe and Mozambique | Niger–Congo, Bantoid | 15 (2000) |
| Somali | Horn of Africa | Somalia, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | 20 (2009) |
| Wolof | West Africa | Senegal, Gambia, Mauritania | Niger-Congo, Atlantic | |
| Yoruba | West Africa | Nigeria, Benin, Togo, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Sierra Leone | Niger–Congo, Volta–Niger | 40[year needed] |
| Zulu | Southern Africa | South Africa | Niger–Congo, Bantu | 12 (2016) |
Ethnic groups by region
This article contains embedded lists that may be poorly defined, unverified or indiscriminate. (May 2018) |
Central Africa
| Name | Family | Language | Region | Country | Population (million)[year needed] | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aka | Nilo-Saharan, Pygmy | Aka | Central/Northern | Western Central African Republic, Northwest Congo | The Aka are one of three groups of pygmies, collectively called BaMbuti, of the Ituri Rainforest. | |
| Baka | Pygmy | Baka | Central/Northern | Western Equatoria in South Sudan | 0.25 | There is also another ethnic group called Baka living across West Africa. |
| Banda | Niger-Congo, Ubangian | Banda language | Chad Basin | Central African Republic[17] | 1.5 | |
| Chewa | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Chichewa | Central/Southern | Botswana, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | 9 | |
| Chokwe | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Chokwe | Central | Angola, Congo (Kinshasa), Zambia | 1.1 | |
| Efé | Nilo-Saharan, Pygmy | Efe | Central/Northern | Ituri Rainforest of Congo | The Efe are one of three groups of pygmies, collectively called BaMbuti, of the Ituri Rainforest. | |
| Gbaya | Niger-Congo, Ubangian | Gbaya language | Chad Basin | Central African Republic[17] | 1.5 | |
| Kongo | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Kongo | Central | Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, Republic of the Congo | 10 | |
| Kanuri | Nilo-Saharan, Western Saharan | Kanuri | Chad Basin | Nigeria,[12] Niger,[13] Cameroon,[15] Chad[14] | 10 | |
| Lingala | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Lingala | Central | Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Angola, Central African Republic | ||
| Luba | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Luba-Kasai, Luba-Katanga | Central | Democratic Republic of the Congo | 13 | |
| Kotoko | Afro-Asiatic, Chadic | Lagwan | Chad Basin | Cameroon, Chad | < 1 | |
| Mbunda | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Mbúùnda, Chimbúùnda, Mpuono | Central | Angola, Zambia | 0.5 | |
| Mbundu | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Kimbundu | Central | Angola | 2.4 | |
| Moghamo | Niger-Congo, Southern Bantoid | Moghamo | Central/West | Cameroon | 0.018 | |
| Mongo | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Mongo | Central | Democratic Republic of the Congo | 12 | |
| Ngamambo | Niger-Congo, Southern Bantoid | Ngamambo | Central/West | Cameroon | 0.011 | |
| Ovimbundu | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Umbundu | Central | Angola | 4.6 | |
| Sara | Nilo-Saharan, Central Sudanic | Sara | Chad Basin | Chad,[14] Cameroon,[18] Central African Republic[19] | 3.5 | |
| Sua | Nilo-Saharan, Pygmy | Sua | Central/Northern | Ituri Rainforest of Congo | The Sua are one of three groups of pygmies, collectively called BaMbuti, of the Ituri Rainforest. | |
| Zande | Niger–Congo, Ubangian | Zande | Chad Basin | South Sudan,[20] Central African Republic[17] | 1-4 | |
| Zaghawa | Nilo-Saharan, Eastern Saharan | Zaghawa | Chad Basin | Chad, Sudan | < 1 |
Horn of Africa
| Name | Family | Language | Region | Country | Population (million) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afar | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | Afar | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia, Djibouti, Eritrea | 2.5 | |
| Agaw | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | Agaw | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia, Eritrea | 1 | |
| Amhara | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Amharic | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia | 24 | |
| Beja | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | Beja | Horn of Africa | Sudan, Eritrea | 2 | |
| Bilen | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | Bilen | Horn of Africa | Eritrea | 0.2 | |
| Gurage | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Gurage | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia | 1.9 | |
| Oromo | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | Oromo | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia, Sudan, Kenya | 40 | |
| Rashaida | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Arabic | Horn of Africa | Eritrea, Sudan | 0.2 | |
| Saho | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | Saho | Horn of Africa | Eritrea, Ethiopia | 0.2 | |
| Sidama | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | Sidama | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia | 3 | |
| Somali | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | Somali | Horn of Africa | Somalia, Ethiopia, Djibouti and Kenya | 21 | |
| Tigrayan | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Tigrinya | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia, Eritrea | 9.3 | |
| Tigre | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Tigre | Horn of Africa | Eritrea, Sudan | 1.5 | |
| Tigrinya | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Tigrinya | Horn of Africa | Eritrea | 3.4 | |
| Welayta | Afro-Asiatic, Omotic | Wolaytta | Horn of Africa | Ethiopia | 2 |
North Africa
| Name | Family | Language | Region | Country | Population (million) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baggara | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Sudanese Arabic | Chad Basin | Sudan, Chad | 6 | |
| Berbers | Afro-Asiatic, Berber | Berber | Maghreb | Morocco, Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Tunisia, Egypt | 27 | Berber speakers |
| Copts | Afro-Asiatic, Egyptian | Coptic | Nile Valley | Egypt, Sudan | 10 | |
| Egyptians | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Egyptian Arabic | Nile Valley | Egypt | 85 | excl. Copts |
Fur[21] | Nilo-Saharan, Eastern Sudanic | Fur | Nile Valley | Sudan | 1.0 | |
| Haratin | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Hassaniya Arabic | Maghreb | Mauritania, Morocco | 2 | |
| Maghrebis | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Maghrebi Arabic | Maghreb | Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya | 72 | Arabic speakers only |
| Moors | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Hassaniya Arabic | Maghreb | Mauritania, Morocco | 2 | |
| Nubians | Nilo-Saharan, Eastern Sudanic | Nobiin | Nile Valley | Sudan, Egypt | 1.0[21] | |
| Sudanese Arabs | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | Sudanese Arabic | Nile Valley | Sudan | 28 | |
| Toubou | Nilo-Saharan | Tebu | Tibesti | Libya, Chad, Niger, Sudan | 0.35 | |
| Tuareg | Afro-Asiatic, Berber | Tuareg | Maghreb/Sahara | Algeria, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia, Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso | 1.2 | |
| Zaghawa | Nilo-Saharan, Eastern Saharan | Zaghawa | Chad Basin | Chad, Sudan | 0.2 |
Southeast Africa
| Name | Family | Language | Region | Country | Population (million) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alur | Nilo-Saharan, Nilotic, Luo | Alur | East/Central | Uganda, Democratic Republic of the Congo | ||
| Anuak | Nilo-Saharan, Nilotic, Luo | Anuak | Southeast/Horn | South Sudan, Ethiopia | ||
| Acholi | Nilo-Saharan, Nilotic, Luo | Acholi | East | Uganda, South Sudan | ||
| Banyoro | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Nyoro (Runyakitara) | East | Uganda | 1.4 | |
| Basoga | Niger-Congo, Bantu | Soga | East | Uganda | 2.9 | |
| Chagga | Niger-Congo, Bantu | Bantu | Kilimanjaro | Tanzania | 8 | |
| Dinka | Nilo-Saharan, Eastern Sudanic | Dinka | Nile Valley | South Sudan[20] | 5 | |
| Ganda | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Ganda | East | Uganda | 5.5 | |
| Langi | Nilo-Saharan, Nilotic, Luo | Lango | East | Uganda | 2.2 | |
| Hutu | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Rwanda-Rundi | East, Central | Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda | 16 | |
| Kamba | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Kamba | East | Kenya | ||
| Kalenjin | Nilo-Saharan, Nilotic, Highland | Kalenjin | East | Kenya, Uganda | 3 | |
| Kikuyu | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Gikuyu | East | Kenya | 5.3 | |
| Kwama | Nilo-Saharan | Kwama | East/Horn | South Sudan, Ethiopia | ||
| Lugbara people | Nilo-Saharan, Central Sudanic | Lugbara | East | Uganda, Democratic Republic of the Congo | 11 | |
| Luo | Nilo-Saharan, Luo, River-Lake | Luo | East | Kenya, Uganda | ||
| Luhya | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Luhya | East | Kenya, Uganda | 5.4 | |
| Maasai | Nilo-Saharan, Nilotic, Plains | Maasai | East | Kenya, Tanzania | 0.9 | |
| Makonde | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Makonde | Southeast | Tanzania, Mozambique | 1.3 | |
| Ameru | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Meru | East | Kenya | ||
| Nuer | Nilo-Saharan, Eastern Sudanic | Nuer | Nile Valley | South Sudan[20] | 3 | |
| Samburu | Nilo-Saharan, Nilotic, Plains | Samburu | East | Kenya | 0.1 | |
| Shilluk | Nilo-Saharan, Eastern Sudanic, Nilotic, Luo | Shilluk | Nile Valley | South Sudan[20] | 1.5 | |
| Swahili | Niger-Congo, Bantu | Swahili | East | Tanzania, Kenya, Mozambique | 0.1 | |
| Tutsi | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Rwanda-Rundi | East, Central | Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda | 3 | |
| Twa | Pygmy | Rundi, Kiga | East, Central | Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda, Democratic Republic of the Congo | 0.8 |
Southern Africa
| Name | Family | Language | Region | Country | Population (million) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afrikaner | Indo-European | Afrikaans | South | South Africa, Namibia | 3.5 | |
| Bemba | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Bemba | South | Zambia | 5.0 | |
| Cape Coloured | Indo-European | Afrikaans | South | South Africa | 4.7 | |
| Herero | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Herero | South | Namibia, Botswana, Angola | 0.2 | |
| Himba | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Otjihimbo (Herero dialect) | South | Namibia | 0.05 | |
| Goffal | Indo-European | Zimbabwean English | South | Zimbabwe | 0.03 | |
| Kalanga | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Shona | South | Zimbabwe, Botswana | 0.1 | |
| Khoikhoi | Khoisan | Khoekhoegowab | South | - | ||
| Lemba | Niger-Congo, Bantu | Venda | South | Zimbabwe, South Africa, Malawi, Mozambique | 0.05 | |
| Makua | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Makua | South/East | Mozambique, Tanzania | 1.1 | |
| Nambya | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Shona | South | Zimbabwe | 0.1 | |
| North Ndebele | Niger-Congo, Bantu, Nguni | Sindebele | South | Zimbabwe | 1.5 | |
Ovambo (Ambo, Owambo) | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Ovambo | South | Namibia | 0.9 | |
| San | Khoisan | Khoisan | South | South Africa, Zimbabwe, Lesotho, Mozambique, Swaziland, Botswana, Namibia, Angola | 0.09 | |
| South Ndebele | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Southern Ndebele | South | South Africa | 0.7 | |
| Shona | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Shona | South | Mozambique, Zimbabwe | 10.6 | |
| Sotho | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Sotho | South | Lesotho, South Africa, Zimbabwe (Gwanda District) | 5.3 | |
| Swazi | Niger-Congo, Bantu, Nguni | Swazi | South | Swaziland, South Africa, Mozambique | 3.5 | |
| Tonga | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Shona | South | Zimbabwe, Zambia | 2 | |
| Tsonga | Niger-Congo, Bantu, Nguni | Tsonga | South | Swaziland, South Africa, Mozambique, Zimbabwe (Chiredzi and Mwenezi Districts) | 5.5 | |
| Tswana | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Tswana | South | Botswana, South Africa, Zimbabwe | 6 | |
| Venda | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Venda | South | South Africa, Zimbabwe | 1 | |
| Xhosa | Niger-Congo, Bantu, Nguni | Xhosa | South | South Africa | 7.9 | |
| Yeyi | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Shiyeyi | South | Namibia, Botswana, Angola | 0.3 | |
| Zulu | Niger-Congo, Bantu, Nguni | Zulu | South | South Africa | 12 | |
| Kwangali | Niger–Congo, Bantu Angola Central Africa | Rukwangali | South | Namibia, Botswana, Angola | 0.7 |
West Africa
| Name | Family | Language | Region | Country | Population (million) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adele | Niger–Congo, Gbe | Adele | West | Ghanaian-Togo Borderlands | .05[22] | |
| Akan | Niger–Congo, Kwa | Akan | West | South Ghana, Ivory Coast | 20 | An ethnic group of related sub-groups. The largest subgroups are the Ashanti and the Fante |
| Aku | (Creole) | Aku | West | Gambia | 0.01 | |
| Baka | Niger Congo, Ubangian | Baka | West/Central | Southeastern Cameroon, Northern Congo, Northern Gabon | 0.3-0.4 | The Baka are also known as Bebayaka, Bebayaga, or Bibaya, or (along with the other Mbenga peoples) the derogatory Babinga. |
| Bambara | Niger–Congo, Mande | Bambara | West | Mali | 3 | |
| Basaa | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Basaa | West | Cameroon | 0.2 | |
| Bassa | Niger–Congo, Kru | Bassa | West | Liberia | 0.3 | |
| Beti-Pahuin | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Ewondo, Fang, Bulu | West | Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, São Tomé and Príncipe | 3.3 | group of 20 sub-ethnicities |
| Biafada | Niger–Congo | Biafada | West | Senegal, Gambia, Guinea-Bissau | 0.04 | |
| Mole-Dagbani | Niger–Congo, Gur | Dagbani | West | Ghana, Burkina Faso | 8.6 | Dagomba, Mamprusi, Nanumba, Mossi, Gurma |
| Dendi | Niger–Congo | Dendi | West | Benin | 0.1 | |
Edo (also called Bini, or Benin) | Niger–Congo, Volta-Niger | Edo | West | Nigeria | 1.6 | |
| Efik | Niger–Congo, Cross River | Ibibio-Efik | West | Nigeria, Cameroon | 0.9 | |
| Eket | Niger–Congo, Cross River | Eket (Ibibio dialect) | West | Nigeria, Cameroon | 0.3 | |
| Esan | Niger–Congo, Volta-Niger | Esan | West | Nigeria | 0.5 | |
| Ewe | Niger–Congo, Gbe | Ewe | West | Togo, Benin, Nigeria, Volta Region (British Togoland), Togoland | 6.0 | |
| Fon | Niger–Congo | Fon | West | Benin, Nigeria | 3.5 | |
| Fulɓe | Niger–Congo, Senegambian | Pular/Fulfulde | West | Guinea, Nigeria, Cameroon, Mali, Burkina Faso, Benin, Niger, Sierra Leone, Gambia, Guinea Bissau, Chad, Togo, Ivory Coast | 20 | |
| Ga | Niger–Congo, Kwa | Ga, Ga-Adangme | West | Togo, Greater Accra | 2 | |
| Gwari, Nupe | Niger-Congo, Volta-Niger | West | Nigeria | 1 | ||
| Hausa | Afro-Asiatic, Chadic | Hausa | West/Northern | Nigeria, Niger, Ghana, Benin, Chad, Cameroon, Sudan | 37 | |
Igbo (Ibo) | Niger–Congo, Volta–Niger | Igbo | West | Nigeria, Equatorial Guinea | 34[23] | Includes various subgroups. |
| Ijaw | Niger–Congo, Ijoid | Ijaw | West | Nigeria | 14[12] | Sub-groups include Andoni, Ibani, Kalabari, Nembe, Ogbia and Okrika. |
| Jola | Niger–Congo, Senegambian | Jola, Kriol | West | Senegal, The Gambia, Guinea-Bissau | 0.5 | |
| Kanuri | Nilo-Saharan, Western Saharan | Kanuri | Chad Basin | Nigeria,[12] Niger,[13] Cameroon,[15] Chad[14] | 10 | |
| Mandinka | Niger–Congo, Mande | Mandingo | West/Central | The Gambia, Guinea, Mali, Sierra Leone, Ivory Coast, Senegal, Burkina Faso, Liberia, Guinea Bissau, Ghana, Benin, Niger, Nigeria, Mauritania, Chad | 13 | |
| Mande South | Niger–Congo, Mande | Dan, Mano and Kpelle | West | Guinea, Ivory Coast, Liberia, | 3.5 | |
| Marka | Niger–Congo, Mande | Marka | West/Northern | Mali | 0.4 | |
| Mende | Niger–Congo, Mande | Mende | West | Sierra Leone | 2 | |
| Papel | Niger–Congo | Papel | West | Senegal, Gambia, Guinea-Bissau | 0.1 | |
| Serer | Niger–Congo, Senegambian | Serer, Cangin | West | Found mostly in Senegal and The Gambia. Small number in Mauritania. Also found in the West. | 1.9[24][25] | The Serer people include: Serer-Sine, Serer-Safene, Serer-Ndut, Serer-Palor, Serer-Niominka, Serer-Laalaa, Serer-Noon. Apart from the Serer-Sine, they speak Cangin languages rather than Serer. |
Songhai[13] | Nilo-Saharan | Songhai | West | Mali | 5 | |
| Tiv | Niger–Congo, Bantu | Tiv | West | Nigeria, Cameroon | 2 | |
| Urhobo | Niger–Congo, Volta–Niger | Urhobo, Isoko, Uvwie, Erhowa, Okpe | West | Nigeria | 2 | |
| Wolof | Niger–Congo, Atlantic | Wolof | West | Senegal, Gambia, Mauritania | 4 | |
| Yoruba, Itsekiri | Niger–Congo, Volta–Niger | Yoruba | West | Nigeria, Benin, Togo, Ghana, Ivory Coast[26]Sierra Leone[27] | 45 | |
Zarma[13][28] | Nilo-Saharan | Zarma | West | Niger | 5 |
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ethnic groups in Africa. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Maps of ethnic groups in Africa. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Africans. |
- African diaspora
- Bantu peoples
- Native Africans
- Brown (racial classification)
- Capoid
- Caucasoid
- Demographics of Africa
- Demographics of the Arab League
- Indigenous peoples of Africa
- Languages of Africa
- Negroid
- Recent African origin of modern humans
- Native Europeans
References
^ Onuah, Felix (29 December 2006). "Nigeria gives census result, avoids risky details". Reuters. Retrieved 2008-11-23.
^ Lewis, Peter (2007). Growing Apart: Oil, Politics, and Economic Change in Indonesia and Nigeria. University of Michigan Press. p. 132. ISBN 0-472-06980-2. Retrieved 2008-11-23.
^ Suberu, Rotimi T. (2001). Federalism and Ethnic Conflict in Nigeria. US Institute of Peace Press. p. 154. ISBN 1-929223-28-5. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
^ Tishkoff, SA; et al. (2009). "The Genetic Structure and History of Africans and African Americans" (PDF). Science. 324 (5930): 1037–39. Bibcode:2009Sci...324.1035T. doi:10.1126/science.1172257. PMC 2947357 . PMID 19407144.
. PMID 19407144. We incorporated geographic data into a Bayesian clustering analysis, assuming no admixture (TESS software) (25) and distinguished six clusters within continental Africa (Fig. 5A). The most geographically widespread cluster (orange) extends from far Western Africa (the Mandinka) through central Africa to the Bantu speakers of South Africa (the Venda and Xhosa) and corresponds to the distribution of the Niger-Kordofanian language family, possibly reflecting the spread of Bantu-speaking populations from near the Nigerian/Cameroon highlands across eastern and southern Africa within the past 5000 to 3000 years (26,27). Another inferred cluster includes the Pygmy and SAK populations (green), with a noncontiguous geographic distribution in central and southeastern Africa, consistent with the STRUCTURE (Fig. 3) and phylogenetic analyses (Fig. 1). Another geographically contiguous cluster extends across northern Africa (blue) into Mali (the Dogon), Ethiopia, and northern Kenya. With the exception of the Dogon, these populations speak an Afroasiatic language. Chadic-speaking and Nilo-Saharan–speaking populations from Nigeria, Cameroon, and central Chad, as well as several Nilo-Saharan–speaking populations from southern Sudan, constitute another cluster (red). Nilo-Saharan and Cushitic speakers from the Sudan, Kenya, and Tanzania, as well as some of the Bantu speakers from Kenya, Tanzania, and Rwanda (Hutu/Tutsi), constitute another cluster (purple), reflecting linguistic evidence for gene flow among these populations over the past ~5000 years (28,29). Finally, the Hadza are the sole constituents of a sixth cluster (yellow), consistent with their distinctive genetic structure identified by PCA and STRUCTURE.
^ Schlebusch, Carina M.; Jakobsson, Mattias (2018). "Tales of Human Migration, Admixture, and Selection in Africa". Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics. 0: 10.9–10.10; Figure 3.3 Population structure analysis and inferred ancestry components for selected choices of assumed number of ancestries. Retrieved 28 May 2018.
^ abcd Childs, G. Tucker (2003). An Introduction to African Languages. John Benjamins Publishing. p. 23. ISBN 9027295883. Retrieved 31 May 2018. : c. 1,650 Niger-Congo, c. 200-300 Afro-Asiatic, 80 Nilo-Saharan, 40-70 Khoisan.
^ Childs, G. Tucker (2003). An Introduction to African Languages. John Benjamins Publishing. p. x. ISBN 9027295883. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
^ Childs, G. Tucker (2003). An Introduction to African Languages. John Benjamins Publishing. pp. x, 206, 211. ISBN 9027295883. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
^ The total number of languages natively spoken in Africa is variously estimated (depending on the delineation of language vs. dialect) at between 1,250 and 2,100.
Heine, Bernd; Heine, Bernd, eds. (2000). African Languages: an Introduction. Cambridge University Press.
Some counts estimate "over 3,000", e.g. Epstein, Edmund L.; Kole, Robert, eds. (1998). The Language of African Literature. Africa World Press. p. ix. ISBN 0-86543-534-0. Retrieved 2011-06-23.over 3,000 indigenous languages by some counts, and many creoles, pidgins, and lingua francas.
. Niger-Congo alone accounts for the majority of languages (and the majority of population), estimated at 1,560 languages by SIL Ethnologue) ("Ethnologue report for Nigeria". Ethnologue Languages of the World. )
^ Bantu peoples: 350M population, 450-650 groups: "Guthrie (1967-71) names some 440 Bantu 'varieties', Grimes (2000) has 501 (minus a few 'extinct' or 'almost extinct', Bastin et al. (1999) have 542, Maho (this volume) has some 660, and Mann et al. (1987) have c. 680." Derek Nurse, 2006, "Bantu Languages", in the Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics, p. 2.
Ethnologue report for Southern Bantoid lists a total of 535 languages. The count includes 13 Mbam languages which are not always included under "Narrow Bantu".
^ including Copts in Egypt and Sudan (c. 15 million) and tribes such as the two largest in North Sinai, the al-Tarabin tribe and the al-Sawarka tribe. Sakr, Taha (16 May 2017). "North Sinai's second largest tribe al-Sawarka declares war against Sinai Province". Egypt Independent.
^ abcd "The World Factbook: Nigeria". World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
^ abcde "The World Factbook: Niger". World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
^ abcd "The World Factbook: Chad". World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 2013-04-24. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
^ abc Peter Austin, One Thousand Languages (2008), p. 75, https://books.google.com/books?isbn=0520255607:"Kanuri is a major Saharan language spoken in the Lake Chad Basin in the Borno area of northeastern Nigeria, as well as in Niger, Cameroon, and Chad (where the variety is known as Kanembul[)]."
^ "Ethnicity" of Arabic-speaking groups either "Arab" or "Berber-Arab", or by nationality,
with "Arabs" having numerous subgroups, usually named clans or tribes (Libyans, Algerians, Tunisians, Moroccans, Badawi, Juba, Nubi, Egyptians, Sudanese, Shuwa/Baggara, Chadians), see dialects of Arabic
^ abc "The World Factbook: Central African Republic". World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
^ Stefan Goodwin, Africas Legacies Of Urbanization (2006),p. 191, https://books.google.com/books?isbn=0739133489:"...and further west the even more numerous Sara [western Central African Republic, southern Chad, and northern Cameroon."
^ Peoples of Africa: Burkina Faso-Comoros - Volume 2 (2001), p. 86, https://books.google.com/books?isbn=076147160X:"The Central African Republic is a land of many different peoples... The Sara (SAHR) live in the grain-growing lands of the north as well as across the border in Chad."
^ abcd "The World Factbook: South Sudan". World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
^ ab "The World Factbook: Sudan". World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2013-12-31.
^ "People Cluster: Guinean". joshuaproject.net. The Joshua Project. 2018. Retrieved 23 January 2018.
^ Nigeria at CIA World Factbook: "Igbo 18%" out of a population of 177 million (2014 estimate)
^ Agence Nationale de la Statistique et de la Démographie. In Senegal alone, estimated figure for 2007 is 1,840,712.1
^ Gambia keep poor records of its ethnic minorities. Estimated Gambian figure is 31,900 (2006) Ethnologue.com
^ Joshua Project. "Yoruba". United States Center for World Mission. Retrieved March 3, 2014.
^ National African Language Resource Center. "Yoruba" (pdf). Indiana University. Retrieved March 3, 2014.
^ "The World Factbook: Sudan". World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2013-12-31.