United Progressive Alliance

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP United Progressive Alliance | |
|---|---|
| Abbreviation | UPA |
| Chairperson | Sonia Gandhi[1] |
| Lok Sabha leader | Mallikarjun Kharge |
| Rajya Sabha leader | Ghulam Nabi Azad |
| Former Prime Minister(s) | Manmohan Singh (2004-2014) |
| Founder | Indian National Congress |
| Founded | 2004 |
| Political position | Centre-left |
No. of members | 14 Parties |
| Seats in Lok Sabha | 66 / 545 |
| Seats in Rajya Sabha | 66 / 245 Present Members 240 |
| Number of states and union territories in government | 4 / 36 |
| |
The United Progressive Alliance (UPA) is a coalition of centre-left political parties in India formed after the 2004 general election.[3] The largest member party of the UPA is the Indian National Congress, whose Former National President Sonia Gandhi is chairperson of the UPA. It formed a government with support from some other left-aligned parties in 2004.
Contents
1 History
2 Current membership
3 UPA presence in various states
3.1 List of current INC and UPA governments
4 Congress Strength in State Legislative Assemblies
5 Past members
6 Initial support
6.1 Withdrawals
6.1.1 Telangana Rashtra Samithi
6.1.2 Marumalarchi Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
6.1.3 Bahujan Samaj Party
6.1.4 Left Front
6.1.5 Jammu and Kashmir Peoples Democratic Party
6.1.6 Pattali Makkal Katchi
6.1.7 All India Majlis-e-Ittehadul Muslimeen
6.1.8 Trinamool Congress
6.1.9 Jharkhand Vikas Morcha
6.1.10 Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
7 Past general election alliances of Congress (before 2004)
8 Controversies
9 See also
10 References
11 External links
History
The UPA was formed soon after the 2004 general elections when it had become clear that no party had won an absolute majority. The hitherto ruling Bharatiya Janata Party-led National Democratic Alliance (NDA) had won 181 seats[4] in the 543-member 14th Lok Sabha, as opposed the UPA's tally of 218 seats.
The Left Front with 59 MPs (excluding the speaker of the Lok Sabha), the Samajwadi Party with 39 MPs and the Bahujan Samaj Party with 19 MPs were other significant blocks that opted to support UPA at various phases of its rule.[5][6] The UPA did not enjoy a simple majority on its own in the parliament, rather it has relied on the external support to ensure that it enjoys the confidence of the Indian parliament similar to the formula adopted by the previous minority governments of the United Front, the NDA, the Congress government of P. V. Narasimha Rao, and earlier governments of V. P. Singh and Chandra Shekhar.
An informal alliance had existed prior to the elections as several of the current constituent parties had developed seat-sharing agreements in many states. However, it was only after the election that the results of negotiations between parties were announced. The UPA government's policies were initially guided by a common minimum programme that the alliance hammered out with fruitful consultations with Jyoti Basu and Harkishan Singh Surjeet of the 59-member Left Front.[7] Hence, government policies were generally perceived as centre-left, reflecting the centrist policies of the INC.
During the tenure of Jharkhand Chief Minister Madhu Koda, the constituents of the UPA were, by mutual consent, supporting his government.[8]
On 22 July 2008, the UPA narrowly survived a vote of confidence in the parliament brought on by the Left Front withdrawing their support in protest at the India–United States Civil Nuclear Agreement.[9] The Congress party and its leaders along with then SP leader Amar Singh were accused for cash for vote scam (see: Cash-for-votes scandal) in which they were accused for buying votes in Lok Sabha to save the government.[10][11][12] In the Indian General Election in 2009, the UPA won 262 seats, of which the INC accounted for 206.
Current membership
| No | Party | Current No. of MPs in Lok Sabha (As of 30 June 2018) | Current No. of MPs in Rajya Sabha (As of 30 June 2018) | Base State | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Indian National Congress | 48 | 50 | National Party | [13] |
| 2 | Nationalist Congress Party | 7 | 4 | National Party | [14][15] |
| 3 | Rashtriya Janata Dal | 3 | 5 | Bihar | [16] |
| 4 | Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam | 0 | 4 | Tamil Nadu | |
| 5 | Indian Union Muslim League | 2 | 1 | Kerala | |
| 6 | Jharkhand Mukti Morcha | 2 | 0 | Jharkhand | [17] |
| 7 | Janata Dal (Secular) | 1 | 1 | Karnataka | |
| 8 | Kerala Congress (M) | 1 | 1 | Kerala | |
| 9 | Rashtriya Lok Dal | 1 | 0 | Uttar Pradesh | [18] |
| 10 | Revolutionary Socialist Party | 1 | 0 | Kerala | |
| 11 | Communist Marxist Party (John) | 0 | 0 | Kerala | |
| 12 | Kerala Congress (Jacob) | 0 | 0 | Kerala | |
| 13 | Peace Party of India | 0 | 0 | Uttar Pradesh | |
| 14 | Mahan Dal | 0 | 0 | Uttar Pradesh | |
| - | Total | 66 | 66 | India |
UPA presence in various states
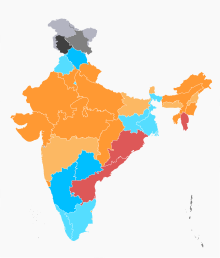
Current ruling parties in India
President's rule
BJP
Coalition with BJP
INC
Coalition with INC
Other parties (AITC, BJD, TRS, TDP, AIADMK, CPI(M), AAP)
As of June 2018, UPA is in power in 3 states and in 1 union territory - Karnataka, Mizoram, Punjab and Puducherry respectively. Previously, UPA governed states are Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, West Bengal, Jammu and Kashmir and Maharashtra.
List of current INC and UPA governments
| State/UT | Chief Minister | Party/alliance partner | CM since | Seats in Assembly | Last election |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Karnataka | H. D. Kumaraswamy (JD(S)) | INC (79), JD(S) (36), BSP (1), KPJP (1), Independent (1) | 23 May 2018 | 118/224 | 12 May 2018 |
Mizoram | Lal Thanhawla (INC) | INC (34) | 11 December 2008 | 34/40 | 25 November 2013 |
Puducherry | V. Narayanasamy (INC) | INC (15), DMK (2) | 6 June 2016 | 17/30 | 16 May 2016 |
Punjab | Amarinder Singh (INC) | INC (78) | 16 March 2017 | 78/117 | 4 February 2017 |
Congress Strength in State Legislative Assemblies
| No | State/UT | Seats in Assembly | Seats- Congress | Seats- UPA Partners | Government | Ref(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | 175 | 0 | NA | TDP | [19] |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | 60 | 3 | NA | BJP | [20] |
| 3 | Assam | 126 | 25 | NA | BJP | [21] |
| 4 | Bihar | 243 | 27 | RJD (81) | NDA | [22] |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | 90 | 39 | NA | BJP | [23] |
| 6 | Goa | 40 | 16 | NCP (1) | BJP | [24] |
| 7 | Gujarat | 182 | 78 | BTP (2), IND (1) | BJP | [25] |
| 8 | Haryana | 90 | 17 | NA | BJP | [26] |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | 68 | 21 | NA | BJP | [27] |
| 10 | Jammu and Kashmir | 87 | 12 | NA | President's rule | [28] |
| 11 | Jharkhand | 81 | 07 | NA | BJP | [29] |
| 12 | Karnataka | 224 | 79 | JD(S) (36), BSP (1), KPJP (1), Independent (1) | UPA | [30] |
| 13 | Kerala | 140 | 22 | IUML (18), KC(M) (6), KC(J) (1) | LDF | [31] |
| 14 | Madhya Pradesh | 230 | 58 | NA | BJP | [32] |
| 15 | Maharashtra | 288 | 42 | Nationalist Congress Party (41) | BJP | [33] |
| 16 | Manipur | 60 | 19 | NA | BJP | [34] |
| 17 | Meghalaya | 60 | 21 | NA | NDA | [35] |
| 18 | Mizoram | 40 | 34 | NA | Congress | [36] |
| 19 | Nagaland | 60 | 0 | NA | NDA | [37] |
| 20 | Odisha | 147 | 16 | NA | BJD | [38] |
| 21 | Punjab | 117 | 78 | NA | Congress | [39] |
| 22 | Rajasthan | 200 | 25 | NA | BJP | [40] |
| 23 | Sikkim | 32 | 0 | NA | NDA | [41] |
| 24 | Tamil Nadu | 234 | 8 | DMK (89), IUML (1), IND (1) | AIADMK | [42] |
| 25 | Telangana | 119 | 13 | NA | TRS | [43] |
| 26 | Tripura | 60 | 0 | NA | BJP | [44] |
| 27 | Uttar Pradesh | 403 | 07 | Samajwadi Party (47) | BJP | [45] |
| 28 | Uttarakhand | 70 | 11 | NA | BJP | [46] |
| 29 | West Bengal | 294 | 42 | CPI(M) (26), CPI (1) | AITC | [47] |
| 30 | Delhi | 70 | 0 | NA | AAP | [48] |
| 31 | Puducherry | 30 | 15 | DMK (2) | Congress | [49] |
Total | 4120 | 734 | 312 | UPA States - 04 |
Past members
| No | Party | Base State | Withdrawal Date | Reason for Withdrawal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Telangana Rashtra Samithi | Telangana | 2006 | Differences over proposed statehood for Telangana[50] |
| 2 | Marumalarchi Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam | Tamil Nadu | 2007 | Allied with All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam led Front[51] |
| 3 | Bahujan Samaj Party | National Party | 2008 | Congress opposed the UP government where the BSP was the ruling party |
| 4 | Communist Party of India (Marxist) | National Party | 2008 | Due to Indo-US nuclear deal.[52] |
| 5 | Communist Party of India | National Party | 2008 | Due to Indo-US nuclear deal[52] |
| 6 | Jammu and Kashmir Peoples Democratic Party | Jammu and Kashmir | 2009 | Congress decided to support National Conference Government in Jammu and Kashmir[53] |
| 7 | Pattali Makkal Katchi | Tamil Nadu | 2009 | PMK declared that it would join the AIADMK led front |
| 8 | All India Majlis-e-Ittehadul Muslimeen | Telangana | 2012 | Accused Congress led State Government of Communalism[54][55] |
| 9 | All India Trinamool Congress | West Bengal | 2012 | TMC's demands on rollbacks and reforms not met, including the governments decision to allow FDI in retail[56][57] |
| 10 | Jharkhand Vikas Morcha (Prajatantrik) | Jharkhand | 2012 | Opposition to the governments decision to allow FDI in retail |
| 13 | Socialist Janata (Democratic) | Kerala | 2014 | It merged with Janata Dal (United) on 29 December 2014.[58][59] |
Initial support
Initially, UPA was given external support from the Left Front which totalled 59 MPs. Similar external support was also promised by several smaller parties that were not a member of any coalition, including the Samajwadi Party with 39 MPs, the All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam party with 4 MPs, the Janata Dal (Secular) with 3 MPs, and Bahujan Samaj Party with 19 MPs, who promised to support the government if it faced a vote of confidence. Nevertheless, these parties were not a part of the government. The UPA thus had at least 335 MPs out of 543 supporting it at the time of its formation.
The Left parties, despite ideological differences with the Congress, supported the UPA to ensure a secular government.[60]
Withdrawals
Telangana Rashtra Samithi
The Telangana Rashtra Samithi (TRS) was the first party to quit the alliance, first when its ministers quit the Andhra Pradesh government, and finally when an official withdrawal was done at the national level by its president K. Chandrashekar Rao, who resigned his Lok Sabha seat.[61]
Marumalarchi Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
Marumalarchi Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (MDMK), began its drift when it tied up with the UPA's rival All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (AIADMK) during the Tamil Nadu elections, and on 16 March 2007 officially withdrew support from the government.[51]
Bahujan Samaj Party
On 21 June 2008, the Bahujan Samaj Party, or the BSP, with 18 seats, announced withdrawal of its support after the Congress starting opposing the UP government where the BSP was the ruling party. Their leader Mayawati said that she wouldn't enter an electoral alliance with either the Congress or the BJP. She also accused both parties of misusing the Central Bureau of Investigation or the CBI and attempting to implicate her in the Taj Corridor Case. She also accused Congress of making false promises to help the people of Bundelkhand and Poorvanchal regions as they were suffering from drought.
Left Front
On 8 July 2008, Prakash Karat, the general secretary of the Communist Party of India (Marxist) (CPI (M)), announced that the Left Front would be withdrawing support over the decision by the government to go ahead with the Indo-US nuclear deal, a Section 123 Agreement with the United States.[52]
Jammu and Kashmir Peoples Democratic Party
On 4 January 2009, Mehbooba Mufti, president of the Jammu and Kashmir Peoples Democratic Party announced the withdrawal of the PDP from the UPA given that the Congress had decided to support the Omar Abdullah-led National Conference Government in Jammu & Kashmir after the 2008 state elections.[62]
Pattali Makkal Katchi
On 26 March 2009, PMK declared that it would join the AIADMK led front and withdrew from the UPA and the party president declared that two union ministers of his party will resign shortly.
All India Majlis-e-Ittehadul Muslimeen
On 12 November 2012, Barrister Asaduddin Owaisi, leader of the AIMIM announced the decision of the party's executive and declared that his party would now go after the state government for its "communal" and "anti-people" policies. Addressing a news conference, Owaisi said his party was compelled to take the decision due to "the communal behaviour of Kiran Kumar Reddy's government in Andhra Pradesh". Giving a detailed account of communal riots in the state and Hyderabad since 2010, he alleged that the Congress government not only turned a blind eye to MIM's demands to withdraw cases against innocent Muslims and take action against the guilty but pandered to the Sangh Parivar. The MIM's decision came after the government allegedly allowed construction of a canopy over a temple abutting the historic Charminar in alleged violation of court orders to maintain status quo. Owaisi criticised the chief minister for ignoring the high court order to maintain status quo.[54][55]
Trinamool Congress
On 18 September 2012, TMC Chief, Mamata Banerjee, announced her decision to withdraw support to the UPA after the TMC's demands of rollback of reforms including FDI in retail, increase in the price of diesel and limiting the number of subsidised cooking gas cylinders for households, were not met.[56][57]
Jharkhand Vikas Morcha
On 1 October 2012 the Jharkhand Vikas Morcha, led by Babulal Marandi, withdrew the support of its two MPs to the UPA government. The JVM was part of the UPA. Though this did not impact the stability of the government, the JVM's withdrawal of support came two weeks after a major UPA ally, the Trinamool Congress, pulled out of the alliance.
The reason for JVM's withdrawal was the same as the Trinamool's; against the decision to implement 51% FDI in Retail Businesses and the Hike in Diesel Prices.[citation needed]
Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
On 17 October 2012 14 DMK MPs, including central ministers T.R. Baalu and A. Raja were forced to hand in their post-dated resignation letters to the head of the party, due to Spectrum corruption Scandal. The party leader M. K. Karunanithi's daughter Kanimozhi was involved in the 2G case with then Information Technology minister Andimuthu Raja and caused billions of rupees of loss to Government of India.[citation needed] During the investigation, they found a huge sum of money has been exchanged to DMK party leader Karunanithi's wives' TV channel.[citation needed]
In 2016, The DMK rejoins alliance with Congress.[63]
Past general election alliances of Congress (before 2004)
| Election Year | Prime Minister Candidate | Parties |
|---|---|---|
1977 | Indira Gandhi | Indian National Congress (Indira) Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam |
1980 | Indira Gandhi | Indian National Congress (Indira) Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam |
1984 | Rajiv Gandhi | Indian National Congress |
1989 | None | None |
1991 | P. V. Narasimha Rao | INC |
1998 | None | Indian National Congress Kerala Congress (Mani) |
1999 | None | Indian National Congress (Indira) Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam |
Controversies
During the discussion for the vote of confidence,[which?][when?] BJP MPs produced cash in the parliament, as viewed on Lok Sabha TV, alleging a bribe by the Samajwadi Party to vote for the government. The BJP claimed to have documentary evidence in a "cash for vote" scam and submitted a report before the parliamentary committee probing the matter.[citation needed] The BJP also wrote a 17-page letter to the Parliamentary committee headed by Congress member V Kishore Chandradeo in this regard. Arun Jaitley said Samajwadi MP Reoti Raman Singh had offered his party's MPs the cash on the night of 21 July.[citation needed] He also alleged that SP leader Amar Singh was behind the entire episode. Jaitley said: "The investigating agencies did not do their job. So we inquired into the matter and gathered documentary evidence in the case." He alleged the 'cash for vote' scam reflected the subversion of the Indian Parliament, as well as a section of the media.[64]
The winter session of parliament in October 2008 came under intense criticism from the Left parties and the BJP to demand a full-fledged winter session instead of what was seen as the UPA to having "scuttled the voice of Parliament" by bringing down the sittings to a record low of 30 days in the year. The tensions between the UPA and the opposition parties became evident at an all-party meeting convened by Lok Sabha speaker Somnath Chatterjee when the leader of opposition, LK Advani questioned the status, timing and schedule of the current session of parliament.[65]
Karunanidhi had said he felt "let down" by the "lukewarm" response of the Centre and had demanded amendments in the resolution on Sri Lanka.[citation needed]
One of the amendments was to "declare that genocide and war crimes had been committed and inflicted on the Eelam Tamils by the Sri Lankan Army and the administrators".
The second one was "establishment of a credible and independent international commission of investigation in a time-bound manner into the allegations of war crimes, crimes against humanity, violations of international human rights law, violations of international humanitarian law and crime of genocide against the Tamils". Karunanidhi said Parliament should adopt the resolution incorporating these two amendments.[66]
The UPA has also been criticised for its alleged involvement in a number of scams such as the Commonwealth Games Scam of 2010, the 2G spectrum case, and the Coalgate scam. Apart from the above-mentioned scams, the UPA has been under intense fire for the alleged doles handed out to the son-in-law of the Gandhi family, Robert Vadra, by different state governments run by the UPA.[67]
See also
- National Democratic Alliance
- National Advisory Council
- Coalition government
- Third Front (India)
References
^ "No decision yet on Sonia Gandhi continuing as UPA chairperson: Veerappa Moily". The Times of India. 26 December 2017. Retrieved 26 December 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "Members: Lok Sabha". loksabha.nic.in. Lok Sabha Secretariat. Retrieved 28 September 2018.
^ "United Progressive Alliance, UPA, UPA Performance General Election 2009, UPA Tally, UPA in Lok Sabha Elections 2009, India Elections 2009, General Elections, Election Manifesto, India Election News, India Elections Results, Indian Election Schedule, 15th Lok Sabha Elections, General Elections 2009, State Assembly Elections, State Assembly Elections Schedule, State Assembly Election Results". electionaffairs.com. Archived from the original on 5 February 2012.
^ Small parties, independents in great demand.
^ Originally the SP had 39 MPs. 6 MPs defied party whip and have been expelled from the party. Archived 26 July 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Lok Sabha members Archived 31 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
^ "Congress pins hopes on Jyoti Basu". The Times of India.
[dead link]
^ Madhu Koda to be next Jharkhand CM. Retrieved 26 March 2007.
^ "Indian government survives vote". BBC News. 22 July 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
^ "Cash-for-votes scam: The deadly secrets of sting Singh : Cover Story - India Today". intoday.in.
^ "Cash For Vote Scam - Amar Singh - Supreme Court - Sudheendra Kulkarni - Swamajwadi Party - BJP". www.oneindia.com.
^ "Cash-for-vote scam 2008: Court orders further probe". indianexpress.com.
^ https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/united-progressive-alliance
^ https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/looking-ahead-at-2019-congress-ncp-form-alliance-for-mlc-polls-in-maharashtra-1846826
^ https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/post-victory-in-bhandara-gondiya-congress-ncp-alliance-may-flourish/story-4o4nVCJbSqyuFelGG955UL.html
^ https://www.business-standard.com/article/opinion/lok-sabha-elections-grand-alliance-of-rjd-and-congress-under-strain-118021700685_1.html
^ https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/ranchi/congress-jmm-seal-pre-poll-pact-in-jharkhand/articleshow/63190239.cms
^ https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/ajit-singhs-rld-to-join-upa/article2704214.ece/amp/
^ Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly
^ Arunachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly
^ Assam Legislative Assembly
^ Bihar Legislative Assembly
^ Chhattisgarh Legislative Assembly
^ Goa Legislative Assembly
^ Gujarat Legislative Assembly
^ Haryana Legislative Assembly
^ Himachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly
^ Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly
^ Jharkhand Legislative Assembly
^ Karnataka Legislative Assembly
^ Kerala Legislature
^ Madhya Pradesh Legislative Assembly
^ Maharashtra Legislative Assembly
^ Manipur Legislative Assembly
^ Meghalaya Legislative Assembly
^ Mizoram Legislative Assembly
^ Nagaland Legislative Assembly
^ Odisha Legislative Assembly
^ Punjab Legislative Assembly
^ Rajasthan Legislative Assembly
^ Sikkim Legislative Assembly
^ Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly
^ Telangana Legislative Assembly
^ Tripura Legislative Assembly
^ Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly
^ Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly
^ West Bengal Legislative Assembly
^ Delhi Legislative Assembly
^ Puducherry Legislative Assembly
^ TRS withdraws support to the UPA.
^ ab Vaiko withdraws support. Retrieved 26 March 2007.
^ abc "Left pulls out, will meet President Patil on Wednesday". expressindia.com. Archived from the original on 12 October 2012.
^ PDP withdraws from UPA, The Indian Express. 5 January 2009
^ ab "Majlis-e-Ittehadul Muslimeen withdraws support to Andhra Pradesh government and UPA". The Times of India. 13 November 2012.
^ ab "MIM withdraws support to UPA, Congress in Andhra Pradesh". dna.
^ ab "Rupee falls after TMC pulls out from government". Monetcontrol.com. Retrieved 20 September 2012.
^ ab "Mamata's party ready to meet President tomorrow to officially quit UPA". NDTV. Retrieved 20 September 2012.
^ Nitish Kumar hails SJD's merger with JD-U in Kerala : South, News - India Today
^ SJD Merges with Sharad Yadav's Janata Dal (United) - The New Indian Express
^ "Secular govt a priority: Basu." Rediff Election Bureau 13 May 2004.
^ TRS withdraws support to the UPA. Retrieved 26 March 2007.
^ PDP withdraws from UPA, The Indian Express. 5 January 2009
^ http://indianexpress.com/article/india/politics/dmk-congress-forge-alliance-ahead-of-tamil-nadu-assembly-elections
^ "We have documentary proof of 'cash for vote' scam: BJP". Express India. Archived from the original on 7 August 2008.
^ Political Bureau. "Left joins BJP to sing chorus against UPA". The Financial Express.
^ "DMK pulls out of UPA govt over Sri Lanka Tamils issue – The Times of India". The Times of India.
^ "CAG raps Haryana govt. for showing undue favours to Robert vadra". The Economic Times.
External links
- Common Minimum Programme of the UPA.
- Arora, Balveer and Tawa Lama Rewal, Stéphanie. "Introduction: Contextualizing and Interpreting the 15th Lok Sabha Elections". South Asia Multidisciplinary Academic Journal, 3, 2009