Arabs

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP | عَرَب ('arab) | |
|---|---|
| Total population | |
c. 450 million (2011 est.)[1] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
Arab League 430,000,000[2][3] | |
| Significant Arab diaspora (including partial ancestry) | |
| Brazil | 12,000,000[4][a] |
| France | 6,000,000[6] |
| Indonesia | 5,000,000[7] |
| Turkey | 5,000,000[b][8][9][10][11] |
| United States | 3,500,000[12] |
| Argentina | 1,300,000–3,500,000[13] |
Israel (native) | 1,700,000[14] |
| Venezuela | 1,600,000[15] |
| Colombia | 1,500,000[16] |
Iran (native) | 1,500,000[17] |
Chad (native) | 1,493,410[18] |
| Mexico | 1,100,000[19] |
| Germany | 1,000,000+[20][21] |
| Chile | 700,000[22] |
| Italy | 680,000[23] |
| United Kingdom | 366,769[24] |
| Canada | 380,620 (2011 Census)[25] |
| Netherlands | 180,000[26] |
| Australia | 350,000[27] |
| Ecuador | 100,000–250,000[28] |
| Honduras | 150,000–200,000[29] |
| Languages | |
Arabic | |
| Religion | |
Predominantly: Islam Historically: Arabian mythology | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
Other Afroasiatic-speaking peoples, especially Semitic peoples such as Assyrians and Jews[30][31][32][33][30][34][35] | |
a Arab ethnicity should not be confused with non-Arab ethnicities that are also native to the Arab world.[35] b Not all Arabs are Muslims and not all Muslims are Arabs. An Arab can follow any religion or irreligion. cArab identity is defined independently of religious identity. | |
Arabs (/ˈærəbz/;[37]Arabic: عَرَب ISO 233 ‘arab, Arabic pronunciation [ˈʕarab] (![]() listen)) are a population inhabiting the Arab world. They primarily live in the Arab states in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and western Indian Ocean islands.[38] They also form a significant diaspora, with Arab communities established around the world.[39]
listen)) are a population inhabiting the Arab world. They primarily live in the Arab states in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and western Indian Ocean islands.[38] They also form a significant diaspora, with Arab communities established around the world.[39]
The first mention of Arabs is from the mid-ninth century BCE as a tribal people in eastern and southern Syria, and the north of the Arabian Peninsula.[40] The Arabs appear to have been under the vassalage of the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–612 BCE), and the succeeding Neo-Babylonian (626–539 BCE), Achaemenid (539–332 BCE), Seleucid and Parthian empires.[41]Arab tribes, most notably the Ghassanids and Lakhmids, begin to appear in the southern Syrian Desert from the mid 3rd century CE onward, during the mid to later stages of the Roman and Sasanian empires.[42] Tradition holds that Arabs descend from Ishmael, the son of Abraham.[43] The Arabian Desert is the birthplace of "Arab",[44] as well other Arab groups that spread in the land and existed for millennia.[45]
Before the expansion of the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), "Arab" referred to any of the largely nomadic and settled Semitic people from the Arabian Peninsula, Syrian Desert, North and Lower Mesopotamia.[46] Today, "Arab" refers to a large number of people whose native regions form the Arab world due to the spread of Arabs and the Arabic language throughout the region during the early Muslim conquests of the 7th and 8th centuries and the subsequent Arabisation of indigenous populations.[47] The Arabs forged the Rashidun (632–661), Umayyad (661–750), Abbasid (750–1517) and the Fatimid (901–1071) caliphates, whose borders reached southern France in the west, China in the east, Anatolia in the north, and the Sudan in the south. This was one of the largest land empires in history.[48] In the early 20th century, the First World War signalled the end of the Ottoman Empire; which had ruled much of the Arab world since conquering the Mamluk Sultanate in 1517.[49] This resulted in the defeat and dissolution of the empire and the partition of its territories, forming the modern Arab states.[50] Following the adoption of the Alexandria Protocol in 1944, the Arab League was founded on 22 March 1945.[51] The Charter of the Arab League endorsed the principle of an Arab homeland whilst respecting the individual sovereignty of its member states.[52]
Today, Arabs primarily inhabit the 22 Arab states within the Arab League: Algeria, Bahrain, Comoros, Djibouti, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates and Yemen. The Arab world stretches around 13 million km2, from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east, and from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Horn of Africa and the Indian Ocean in the southeast. Beyond the boundaries of the League of Arab States, Arabs can also be found in the global diaspora.[38] The ties that bind Arabs are ethnic, linguistic, cultural, historical, identical, nationalist, geographical and political.[53] The Arabs have their own customs, language, architecture, art, literature, music, dance, media, cuisine, dress, society, sports and mythology.[54] The total number of Arabs are an estimated 450 million.[1]
Arabs are a diverse group in terms of religious affiliations and practices. In the pre-Islamic era, most Arabs followed polytheistic religions. Some tribes had adopted Christianity or Judaism, and a few individuals, the hanifs, apparently observed monotheism.[55] Today, Arabs are mostly adherents of Islam, with sizable Christian minorities. [56]Arab Muslims primarily belong to the Sunni, Shiite, Ibadi, and Alawite denominations. Arab Christians generally follow one of the Eastern Christian Churches, such as the Greek Orthodox or Greek Catholic churches.[57] Other smaller minority religions are also followed, such as the Bahá'í Faith and Druze.
Arabs have greatly influenced and contributed to diverse fields, notably the arts and architecture, language, philosophy, mythology, ethics, literature, politics, business, music, dance, cinema, medicine, science and technology[58] in the ancient and modern history. Arab people are generally known for their generosity and hospitality[59] as well as their beliefs and family values.[60]
Contents
1 Etymology
2 History
2.1 Antiquity
2.1.1 Origins and early history
2.1.2 Classical kingdoms
2.1.3 Late kingdoms
2.2 Medieval period
2.2.1 Arab caliphates
2.2.1.1 Rashidun era (632–661)
2.2.1.2 Umayyad era (661–750 & 756–1031)
2.2.1.3 Abbassid era (750–1258 & 1261–1517)
2.2.1.4 Fatimid Caliphate (909–1171)
2.2.2 Ottoman Empire
2.3 Modern period
3 Identity
4 Subgroups
5 Demographics
5.1 Arab world
5.2 Arab diaspora
6 Religion
7 Culture
7.1 Language
7.2 Mythology
7.3 Literature
7.4 Gastronomy
7.5 Art
7.6 Architecture
7.7 Music
7.8 Spirituality
7.9 Philosophy
7.10 Science
7.11 Wedding and marriage
8 Genetics
9 See also
10 References
11 Further reading
12 External links
Etymology

Arabic epitaph of Imru' al-Qais, son of 'Amr, king of all the Arabs", inscribed in Nabataean script. Basalt, dated in 7 Kislul, 223, viz. 7 December 328 CE. Found at Nemara in the Hauran (Southern Syria).
The earliest documented use of the word "Arab" to refer to a people appears in the Kurkh Monoliths, an Akkadian language record of the ninth century BCE Assyrian conquest of Aram, which referred to Bedouins of the Arabian Peninsula under King Gindibu, who fought as part of a coalition opposed to Assyria.[61] Listed among the booty captured by the army of king Shalmaneser III of Assyria in the Battle of Qarqar are 1000 camels of "Gi-in-di-bu'u the ar-ba-a-a" or "[the man] Gindibu belonging to the Arab (ar-ba-a-a being an adjectival nisba of the noun ʿarab[61]). The related word ʾaʿrāb is still used to refer to Bedouins today, in contrast to ʿarab which refers to Arabs in general.[62]
The oldest surviving indication of an Arab national identity is an inscription made in an archaic form of Arabic in 328 using the Nabataean alphabet, which refers to Imru' al-Qays ibn 'Amr as "King of all the Arabs".[63][64]Herodotus refers to the Arabs in the Sinai, southern Palestine, and the frankincense region (Southern Arabia). Other ancient Greek historians like Agatharchides, Diodorus Siculus and Strabo mention Arabs living in Mesopotamia (along the Euphrates), in Egypt (the Sinai and the Red Sea), southern Jordan (the Nabataeans), the Syrian steppe and in eastern Arabia (the people of Gerrha). Inscriptions dating to the 6th century BCE in Yemen include the term "Arab".[65]
The most popular Arab account holds that the word "Arab" came from an eponymous father called Ya'rub who was supposedly the first to speak Arabic. Abu Muhammad al-Hasan al-Hamdani had another view; he states that Arabs were called Gharab ("West") by Mesopotamians because Bedouins originally resided to the west of Mesopotamia; the term was then corrupted into "Arab".
Yet another view is held by al-Masudi that the word "Arabs" was initially applied to the Ishmaelites of the "Arabah" valley. In Biblical etymology, "Arab" (in Hebrew Arvi ) comes both from the desert origin of the Bedouins it originally described (Arava means wilderness).
The root ʿ-r-b has several additional meanings in Semitic languages—including "west/sunset," "desert," "mingle," "mixed," "merchant," and "raven"—and are "comprehensible" with all of these having varying degrees of relevance to the emergence of the name. It is also possible that some forms were metathetical from ʿ-B-R "moving around" (Arabic ʿ-B-R "traverse"), and hence, it is alleged, "nomadic."[66]
History
Antiquity
| Historical Arab states and dynasties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ancient Arab States
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arab Empires
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Eastern Dynasties
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Western Dynasties
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arabian Peninsula
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Current monarchies
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pre-Islamic Arabia refers to the Arabian Peninsula prior to the rise of Islam in the 630s. The study of Pre-Islamic Arabia is important to Islamic studies as it provides the context for the development of Islam. Some of the settled communities in the Arabian Peninsula developed into distinctive civilizations. Sources for these civilizations are not extensive, and are limited to archaeological evidence, accounts written outside of Arabia, and Arab oral traditions later recorded by Islamic scholars. Among the most prominent civilizations was Dilmun, which arose around the 4th millennium BCE and lasted to 538 BCE, and Thamud, which arose around the 1st millennium BCE and lasted to about 300 CE. Additionally, from the beginning of the first millennium BCE, Southern Arabia was the home to a number of kingdoms, such as the Sabaean kingdom (Arabic: سَـبَـأ, translit. Saba',[67] possibly Sheba),[68] and the coastal areas of Eastern Arabia were controlled by the Parthian and Sassanians from 300 BCE.
Origins and early history
According to Arab-Islamic-Jewish traditions, Ishmael was father of the Arabs, to be the ancestor of the Ishmaelites.[69]

Traditional Qahtanite genealogy
The first written attestation of the ethnonym Arab occurs in an Assyrian inscription of 853 BCE, where Shalmaneser III lists a King Gindibu of mâtu arbâi (Arab land) as among the people he defeated at the Battle of Qarqar. Some of the names given in these texts are Aramaic, while others are the first attestations of Ancient North Arabian dialects. In fact several different ethnonyms are found in Assyrian texts that are conventionally translated "Arab": Arabi, Arubu, Aribi and Urbi. Many of the Qedarite queens were also described as queens of the aribi. The Hebrew Bible occasionally refers to Aravi peoples (or variants thereof), translated as "Arab" or "Arabian." The scope of the term at that early stage is unclear, but it seems to have referred to various desert-dwelling Semitic tribes in the Syrian Desert and Arabia.[citation needed] Arab tribes came into conflict with the Assyrians during the reign of the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal, and he records military victories against the powerful Qedar tribe among others.
Old Arabic diverges from Central Semitic by the beginning of the 1st millennium BCE.[citation needed]

Nabataean trade routes in Pre-Islamic Arabia.
Medieval Arab genealogists divided Arabs into three groups:
- "Ancient Arabs", tribes that had vanished or been destroyed, such as ʿĀd and Thamud, often mentioned in the Qur'an as examples of God's power to vanquish those who fought his prophets.
- "Pure Arabs" of South Arabia, descending from Qahtan. The Qahtanites (Qahtanis) are said to have migrated from the land of Yemen following the destruction of the Ma'rib Dam (sadd Ma'rib).
- The "Arabized Arabs" (mustaʿribah) of Central Arabia (Najd) and North Arabia, descending from Ishmael the elder son of Abraham, through Adnan (hence, Adnanites). The Book of Genesis narrates that God promised Hagar to beget from Ishmael twelve princes and turn him to a great nation.(Genesis 17:20) The Book of Jubilees claims that the sons of Ishmael intermingled with the 6 sons of Keturah, from Abraham, and their descendants were called Arabs and Ishmaelites:
.mw-parser-output .templatequoteoverflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequoteciteline-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0
And Ishmael and his sons, and the sons of Keturah and their sons, went together and dwelt from Paran to the entering in of Babylon in all the land towards the East facing the desert. And these mingled with each other, and their name was called Arabs, and Ishmaelites.
— Book of Jubilees 20:13

Assyrian horsemen pursue defeated Arabs
Assyrian and Babylonian Royal Inscriptions and North Arabian inscriptions from 9th to 6th century BCE, mention the king of Qedar as king of the Arabs and King of the Ishmaelites.[70][71][72][73]
Of the names of the sons of Ishmael the names "Nabat, Kedar, Abdeel, Dumah, Massa, and Teman" were mentioned in the Assyrian Royal Inscriptions as tribes of the Ishmaelites. Jesur was mentioned in Greek inscriptions in the 1st century BCE.[74]

Life-size bronze bust sculpture of Ibn Khaldun.[75]
Ibn Khaldun's Muqaddima distinguishes between sedentary Arabian Muslims who used to be nomadic, and Bedouin nomadic Arabs of the desert. He used the term "formerly nomadic" Arabs and refers to sedentary Muslims by the region or city they lived in, as in Yemenis.[76] The Christians of Italy and the Crusaders preferred the term Saracens for all the Arabs and Muslims of that time.[77] The Christians of Iberia used the term Moor to describe all the Arabs and Muslims of that time.
Muslims of Medina referred to the nomadic tribes of the deserts as the A'raab, and considered themselves sedentary, but were aware of their close racial bonds. The term "A'raab" mirrors the term Assyrians used to describe the closely related nomads they defeated in Syria. The Qur'an does not use the word ʿarab, only the nisba adjective ʿarabiy. The Qur'an calls itself ʿarabiy, "Arabic", and Mubin, "clear". The two qualities are connected for example in ayat 43.2–3, "By the clear Book: We have made it an Arabic recitation in order that you may understand". The Qur'an became regarded as the prime example of the al-ʿarabiyya, the language of the Arabs. The term ʾiʿrāb has the same root and refers to a particularly clear and correct mode of speech. The plural noun ʾaʿrāb refers to the Bedouin tribes of the desert who resisted Muhammad, for example in at-Tawba 97,
al-ʾaʿrābu ʾašaddu kufrān wanifāqān "the Bedouin are the worst in disbelief and hypocrisy".
Based on this, in early Islamic terminology, ʿarabiy referred to the language, and ʾaʿrāb to the Arab Bedouins, carrying a negative connotation due to the Qur'anic verdict just cited. But after the Islamic conquest of the eighth century, the language of the nomadic Arabs became regarded as the most pure by the grammarians following Abi Ishaq, and the term kalam al-ʿArab, "language of the Arabs", denoted the uncontaminated language of the Bedouins.
Classical kingdoms

Façade of Al Khazneh in Petra, Jordan, built by the Nabateans.
Proto-Arabic, or Ancient North Arabian, texts give a clearer picture of the Arabs' emergence. The earliest are written in variants of epigraphic south Arabian musnad script, including the 8th century BCE Hasaean inscriptions of eastern Saudi Arabia, the 6th century BCE Lihyanite texts of southeastern Saudi Arabia and the Thamudic texts found throughout the Arabian Peninsula and Sinai (not in reality connected with Thamud).
The Nabataeans were nomadic Arabs who moved into territory vacated by the Edomites – Semites who settled the region centuries before them. Their early inscriptions were in Aramaic, but gradually switched to Arabic, and since they had writing, it was they who made the first inscriptions in Arabic. The Nabataean alphabet was adopted by Arabs to the south, and evolved into modern Arabic script around the 4th century. This is attested by Safaitic inscriptions (beginning in the 1st century BCE) and the many Arabic personal names in Nabataean inscriptions. From about the 2nd century BCE, a few inscriptions from Qaryat al-Faw reveal a dialect no longer considered proto-Arabic, but pre-classical Arabic. Five Syriac inscriptions mentioning Arabs have been found at Sumatar Harabesi, one of which dates to the 2nd century CE.

The ruins of Palmyra. The Palmyrenes were a mix of Arabs, Amorites and Arameans.
Arabs arrived in the Palmyra in the late first millennium BCE.[78] The soldiers of the sheikh Zabdibel, who aided the Seleucids in the battle of Raphia (217 BCE), were described as Arabs; Zabdibel and his men were not actually identified as Palmyrenes in the texts, but the name "Zabdibel" is a Palmyrene name leading to the conclusion that the sheikh hailed from Palmyra.[79] Palmyra was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate after its 634 capture by the Arab general Khalid ibn al-Walid, who took the city on his way to Damascus; an 18-day march by his army through the Syrian Desert from Mesopotamia.[80] By then Palmyra was limited to the Diocletian camp.[81] After the conquest, the city became part of Homs Province.[82]

Fragment of a wall painting showing a Kindite king, 1st century CE
Palmyra prospered as part of the Umayyad Caliphate, and its population grew.[83] It was a key stop on the East-West trade route, with a large souq (Arabic: سُـوق, market), built by the Umayyads,[83][84] who also commissioned part of the Temple of Bel as a mosque.[84] During this period, Palmyra was a stronghold of the Banu Kalb tribe.[85] After being defeated by Marwan II during a civil war in the caliphate, Umayyad contender Sulayman ibn Hisham fled to the Banu Kalb in Palmyra, but eventually pledged allegiance to Marwan in 744; Palmyra continued to oppose Marwan until the surrender of the Banu Kalb leader al-Abrash al-Kalbi in 745.[86] That year, Marwan ordered the city's walls demolished.[81][87] In 750 a revolt, led by Majza'a ibn al-Kawthar and Umayyad pretender Abu Muhammad al-Sufyani, against the new Abbasid Caliphate swept across Syria;[88] the tribes in Palmyra supported the rebels.[89] After his defeat Abu Muhammad took refuge in the city, which withstood an Abbasid assault long enough to allow him to escape.[89]
Late kingdoms

The Near East in 565, showing the Lakhmids and their neighbors
The Ghassanids, Lakhmids and Kindites were the last major migration of pre-Islamic Arabs out of Yemen to the north. The Ghassanids increased the Semitic presence in the then Hellenized Syria, the majority of Semites were Aramaic peoples. They mainly settled in the Hauran region and spread to modern Lebanon, Palestine and East Jordan.

The imperial province of Arabia Petraea in 117–138 CE
Greeks and Romans referred to all the nomadic population of the desert in the Near East as Arabi. The Romans called Yemen "Arabia Felix".[90] The Romans called the vassal nomadic states within the Roman Empire Arabia Petraea, after the city of Petra, and called unconquered deserts bordering the empire to the south and east Arabia Magna.
The Lakhmids as a dynasty inherited their power from the Tanukhids, the mid Tigris region around their capital Al-Hira. They ended up allying with the Sassanids against the Ghassanids and the Byzantine Empire. The Lakhmids contested control of the Central Arabian tribes with the Kindites with the Lakhmids eventually destroying Kinda in 540 after the fall of their main ally Himyar. The Persian Sassanids dissolved the Lakhmid dynasty in 602, being under puppet kings, then under their direct control.[91]
The Kindites migrated from Yemen along with the Ghassanids and Lakhmids, but were turned back in Bahrain by the Abdul Qais Rabi'a tribe. They returned to Yemen and allied themselves with the Himyarites who installed them as a vassal kingdom that ruled Central Arabia from "Qaryah Dhat Kahl" (the present-day called Qaryat al-Faw). They ruled much of the Northern/Central Arabian peninsula, until they were destroyed by the Lakhmid king Al-Mundhir, and his son 'Amr.
Medieval period

Age of the Caliphs
Expansion under Muhammad, 622–632/A.H. 1–11
Expansion during the Rashidun Caliphate, 632–661/A.H. 11–40
Expansion during the Umayyad Caliphate, 661–750/A.H. 40–129
Arab caliphates
Rashidun era (632–661)
After the death of Muhammad in 632, Rashidun armies launched campaigns of conquest, establishing the Caliphate, or Islamic Empire, one of the largest empires in history. It was larger and lasted longer than the previous Arab empire of Queen Mawia or the Aramean-Arab Palmyrene Empire. The Rashidun state was a completely new state and unlike the Arab kingdoms of its century such as the Himyarite, Lakhmids or Ghassanids.
Umayyad era (661–750 & 756–1031)

The Great Mosque of Kairouan in Kairouan, Tunisia was founded in 670 by the Arab general Uqba ibn Nafi; it is the oldest mosque in the Maghreb[92] and represents an architectural testimony of the Arab conquest of North Africa

The Umayyad Mosque in Damascus, built in 715, is one of the oldest, largest and best preserved mosques in the world
In 661, the Rashidun Caliphate fell into the hands of the Umayyad dynasty and Damascus was established as the empire's capital. The Umayyads were proud of their Arab identity and sponsored the poetry and culture of pre-Islamic Arabia. They established garrison towns at Ramla, Raqqa, Basra, Kufa, Mosul and Samarra, all of which developed into major cities.[93]
Caliph Abd al-Malik established Arabic as the Caliphate's official language in 686.[94] This reform greatly influenced the conquered non-Arab peoples and fueled the Arabization of the region. However, the Arabs' higher status among non-Arab Muslim converts and the latter's obligation to pay heavy taxes caused resentment. Caliph Umar II strove to resolve the conflict when he came to power in 717. He rectified the disparity, demanding that all Muslims be treated as equals, but his intended reforms did not take effect, as he died after only three years of rule. By now, discontent with the Umayyads swept the region and an uprising occurred in which the Abbasids came to power and moved the capital to Baghdad.

The Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem, constructed during the reign of Abd al Malik
Umayyads expanded their Empire westwards capturing North Africa from the Byzantines. Before the Arab conquest, North Africa was conquered or settled by various people including Punics, Vandals and Romans. After the Abbasid Revolution, the Umayyads lost most of their territories with the exception of Iberia. Their last holding became known as the Emirate of Córdoba. It wasn't until the rule of the grandson of the founder of this new emirate that the state entered a new phase as the Caliphate of Córdoba. This new state was characterized by an expansion of trade, culture and knowledge, and saw the construction of masterpieces of al-Andalus architecture and the library of Al-Ḥakam II which housed over 400,000 volumes. With the collapse of the Umayyad state in 1031 CE, Islamic Spain was divided into small kingdoms.
Abbassid era (750–1258 & 1261–1517)

Mustansiriya University in Baghdad

Scholars at an Abbasid library in Baghdad. Maqamat of al-Hariri Illustration, 123.
The Abbasids were the descendants of Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib, one of the youngest uncles of Muhammad and of the same Banu Hashim clan. The Abbasids led a revolt against the Umayyads and defeated them in the Battle of the Zab effectively ending their rule in all parts of the Empire with the exception of al-Andalus. In 762, the second Abbasid Caliph al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad and declared it the capital of the Caliphate. Unlike the Umayyads, the Abbasids had the support of non-Arab subjects.[93]
The Islamic Golden Age was inaugurated by the middle of the 8th century by the ascension of the Abbasid Caliphate and the transfer of the capital from Damascus to the newly founded city of Baghdad. The Abbassids were influenced by the Qur'anic injunctions and hadith such as "The ink of the scholar is more holy than the blood of martyrs" stressing the value of knowledge. During this period the Muslim world became an intellectual centre for science, philosophy, medicine and education as the Abbasids championed the cause of knowledge and established the "House of Wisdom" (Arabic: بيت الحكمة) in Baghdad. Rival dynasties such as the Fatimids of Egypt and the Umayyads of al-Andalus were also major intellectual centres with cities such as Cairo and Córdoba rivaling Baghdad.[95]

Harun al-Rashid receiving a delegation sent by Charlemagne
The Abbasids ruled for 200 years before they lost their central control when Wilayas began to fracture in the 10th century; afterwards, in the 1190s, there was a revival of their power, which was ended by the Mongols, who conquered Baghdad in 1258 and killed the Caliph Al-Musta'sim. Members of the Abbasid royal family escaped the massacre and resorted to Cairo, which had broken from the Abbasid rule two years earlier; the Mamluk generals taking the political side of the kingdom while Abbasid Caliphs were engaged in civil activities and continued patronizing science, arts and literature.
Fatimid Caliphate (909–1171)

Al-Azhar Mosque, commissioned by the Fatimid Caliph Al-Mu'izz for the newly established capital city of Cairo in 969
The Fatimid caliphate was founded by al-Mahdi Billah, a descendant of Fatimah, the daughter of Muhammad, in the early 10th century. Egypt was the political, cultural, and religious centre of the Fatimid empire. The Fatimid state took shape among the Kutama Berbers, in the West of the North African littoral, in Algeria, in 909 conquering Raqqada, the Aghlabid capital. In 921 the Fatimids established the Tunisian city of Mahdia as their new capital. In 948 they shifted their capital to Al-Mansuriya, near Kairouan in Tunisia, and in 969 they conquered Egypt and established Cairo as the capital of their caliphate.
Intellectual life in Egypt during the Fatimid period achieved great progress and activity, due to many scholars who lived in or came to Egypt, as well as the number of books available. Fatimid Caliphs gave prominent positions to scholars in their courts, encouraged students, and established libraries in their palaces, so that scholars might expand their knowledge and reap benefits from the work of their predecessors.[96] The Fatimids were also known for their exquisite arts. Many traces of Fatimid architecture exist in Cairo today; the most defining examples include Al-Hakim Mosque and the Al-Azhar University.

Arabesque pattern behind hunters on ivory plaque, 11th–12th century, Egypt
It was not until the 11th century that the Maghreb saw a large influx of ethnic Arabs. Starting with the 11th century, the Arab bedouin Banu Hilal tribes migrated to the West. Having been sent by the Fatimids to punish the Berber Zirids for abandoning Shias, they travelled westwards. The Banu Hilal quickly defeated the Zirids and deeply weakened the neighboring Hammadids. According to some modern historians. their influx was a major factor in the arabization of the Maghreb.[97][98] Although Berbers ruled the region until the 16th century (under such powerful dynasties as the Almoravids, the Almohads, Hafsids, etc.), the arrival of these tribes eventually helped Arabize much of it ethnically, in addition to the linguistic and political impact on local non-Arabs.[citation needed]
Ottoman Empire

Soldiers of the Arab Army in the Arabian Desert carrying the Flag of the Arab Revolt
From 1517 to 1918, much of the Arab world was under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans defeated the Mamluk Sultanate in Cairo, and ended the Abbasid Caliphate. Arabs did not feel the change of administration because the Ottomans modeled their rule after the previous Arab administration systems.[citation needed]
In 1911, Arab intellectuals and politicians from throughout the Levant formed al-Fatat ("the Young Arab Society"), a small Arab nationalist club, in Paris. Its stated aim was "raising the level of the Arab nation to the level of modern nations." In the first few years of its existence, al-Fatat called for greater autonomy within a unified Ottoman state rather than Arab independence from the empire. Al-Fatat hosted the Arab Congress of 1913 in Paris, the purpose of which was to discuss desired reforms with other dissenting individuals from the Arab world. However, as the Ottoman authorities cracked down on the organization's activities and members, al-Fatat went underground and demanded the complete independence and unity of the Arab provinces.[99]
After World War I, when the Ottoman Empire was overthrown by the British Empire, former Ottoman colonies were divided up between the British and French as League of Nations mandates.
Modern period
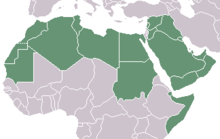
A map of the Arab world
Arabs in modern times live in the Arab world, which comprises 22 countries in Western Asia, North Africa, and parts of the Horn of Africa. They are all modern states and became significant as distinct political entities after the fall and defeat and dissolution of the Ottoman Empire (1908–1922).
Identity
Arab identity is defined independently of religious identity, and pre-dates the spread of Islam, with historically attested Arab Christian kingdoms and Arab Jewish tribes. Today, however, most Arabs are Muslim, with a minority adhering to other faiths, largely Christianity, but also Druze and Baha'i.[100][101]
Paternal descent plays a strong part in the role of citizenship of an individual and maternal descent also plays an issue. Paternal descent is considered the main source of affiliation in the Arab world when it comes to membership into a kin group or clan.[102]

The Near East in 565, showing the Ghassanids, Lakhmids, Kindah and Hejaz
Today, the main unifying characteristic among Arabs is Arabic, a Central Semitic language from the Afroasiatic language family. Modern Standard Arabic serves as the standardized and literary variety of Arabic used in writing. The Arabs are first mentioned in the mid-ninth century BCE as a tribal people dwelling in the central Arabian Peninsula subjugated by Upper Mesopotamia-based state of Assyria. The Arabs appear to have remained largely under the vassalage of the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–605 BCE), and then the succeeding Neo-Babylonian Empire (605–539 BCE), Persian Achaemenid Empire (539–332 BCE), Greek Macedonian/Seleucid Empire and Parthian Empire.
Arab tribes, most notably the Ghassanids and Lakhmids begin to appear in the south Syrian deserts and southern Jordan from the mid 3rd century CE onwards, during the mid to later stages of the Roman Empire and Sasanian Empire. Also, before them the Nabataeans of Jordan and arguably the Emessans,[103]Edessans,[104] and Hatrans[105] all appear to have been an Aramaic speaking ethnic Arabs who came to rule much of the pre-Islamic fertile crescent often as vassals of the two rival empires, the Sasanian (Persian) and the Byzantine (Eastern Roman).[106] Thus, although a more limited diffusion of Arab culture and language was felt in some areas by these migrant minority Arabs in pre-Islamic times through Arabic-speaking Christian kingdoms and Jewish tribes, it was only after the rise of Islam in the mid-7th century that Arab culture, people and language began their wholesale spread from the central Arabian Peninsula (including the south Syrian desert) through conquest and trade.
Subgroups
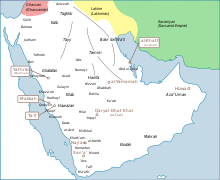
Approximate locations of certain tribes of Arabia, including those descended from Adnan, Hawazin and Quraysh at the dawn of Islam, 600 CE
Arabs in the narrow sense are the indigenous Arabians who trace their roots back to the tribes of Arabia and their immediate descendant groups in the Levant and North Africa. Within the people of the Arabian Peninsula, distinction is made between:
"Perishing Arabs" (Arabic: الـعـرب الـبـائـدة) are ancient tribes of whose history little is known. They include ʿĀd (Arabic: عَـاد),[107]Thamûd (Arabic: ثَـمُـود,[108] Tasm, Jadis, Imlaq and others. Jadis and Tasm perished because of genocide. 'Aad and Thamud perished because of their decadence, as recorded in the Qur'an. Archaeologists have recently uncovered inscriptions that contain references to Iram dhāṫ al-'Imād (Arabic: إِرَم ذَات الـعِـمَـاد, Iram of the Pillars),[107] which was a major city of the 'Aad. Imlaq is the singular form of 'Amaleeq and is probably synonymous to the biblical Amalek. "Pure Arabs" (Arabic: الـعـرب الـعـاربـة) or Qahtanites from Yemen, taken to be descended from Ya'rub ibn Yashjub ibn Qahtan and further from Hud. "Arabized Arabs" (Arabic: الـعـرب الـمـسـتـعـربـة) or Adnanites, taken to be the descendants of Ishmael son of Abraham.
Arabians are most prevalent in the Arabian Peninsula, but are also found in large numbers in Mesopotamia (Arab tribes in Iraq), the Levant and Sinai (Negev Bedouin, Tarabin bedouin), as well as the Maghreb (Eastern Libya, South Tunisia and South Algeria) and the Sudan region.

Arabian tribes before the spread of Islam
This traditional division of the Arabs of Arabia may have arisen at the time of the First Fitna. Of the Arabian tribes that interacted with Muhammad, the most prominent was the Quraysh. The Quraysh subclan, the Banu Hashim, was the clan of Muhammad. During the early Muslim conquests and the Islamic Golden Age, the political rulers of Islam were exclusively members of the Quraysh.
The Arab presence in Iran did not begin with the Arab conquest of Persia in 633 CE. For centuries, Iranian rulers had maintained contacts with Arabs outside their borders, dealt with Arab subjects and client states (such as those of Iraq and Yemen), and settled Arab tribesmen in various parts of the Iranian plateau. It follows that the "Arab" conquests and settlements were by no means the exclusive work of Arabs from the Hejaz and the tribesmen of inner Arabia. The Arab infiltration into Iran began before the Muslim conquests and continued as a result of the joint exertions of the civilized Arabs (ahl al-madar) as well as the desert Arabs (ahl al-wabar).[109] The largest group of Iranian Arabs are the Ahwazi Arabs, including Banu Ka'b, Bani Turuf and the Musha'sha'iyyah sect. Smaller groups are the Khamseh nomads in Fars Province and the Arabs in Khorasan.

Post-card of Emir Mejhem ibn Meheid, chief of the Anaza tribe near Aleppo with his sons after being decorated with the Croix de Légion d'honneur on 20 September 1920
The Arabs of the Levant are traditionally divided into Qays and Yaman tribes. This tribal division is likewise taken to date to the Umayyad period.
The Yemen trace their origin to South Arabia or Yemen; they include Banu Kalb, Kindah, Ghassanids, and Lakhmids.[110] Since the 1834 Peasants' revolt in Palestine, the Arabic-speaking population of Palestine has shed its formerly tribal structure and emerged as the Palestinians[citation needed].
Native Jordanians are either descended from Bedouins (of which, 6% live a nomadic lifestyle),[111] or from the many deeply rooted non bedouin communities across the country, most notably Al-Salt city west of Amman which was at the time of Emirate the largest urban settlement east of the Jordan River. Along with indigenous communities in Al Husn, Aqaba, Irbid, Al Karak, Madaba, Jerash, Ajloun, Fuheis and Pella.[112] In Jordan, there is no official census data for how many inhabitants have Palestinian roots but they are estimated to constitute half of the population,[113][114] which in 2008 amounted to about 3 million.[114] Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics put their number at 3.24 million in 2009.[115]

Old Bedouin man and his wife in Egypt, 1918
The Bedouins of western Egypt and eastern Libya are traditionally divided into Saʿada and Murabtin, the Saʿada having higher social status. This may derive from a historical feudal system in which the Murabtin were vassals to the Saʿada
In Sudan, there are numerous Arabic-speaking tribes, including the Shaigya, Ja'alin and Shukria, who are ancestrally related to the Nubians. These groups are collectively known as Sudanese Arabs. In addition, there are other Afroasiatic-speaking populations, such as Copts and Beja.

Commander and Amir of Mascara, Banu Hilal
The medieval Arab slave trade in the Sudan drove a wedge between the Arabic-speaking groups and the indigenous Nilotic populations. Slavery substantially persists today along these lines.[116] It has contributed to ethnic conflict in the region, such as the Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile, Northern Mali conflict, or the Boko Haram insurgency.
The Arabs of the Maghreb are descendants of Arabian tribes of Banu Hilal, the Banu Sulaym and the Maqil native of Middle East[117] and of other tribes native to Saudi Arabia, Yemen and Iraq. Arabs and Arabic-speakers inhabit plains and cities. The Banu Hilal spent almost a century in Egypt before moving to Libya, Tunisia and Algeria, and another century later some moved to Morocco, it is logical to think that they are mixed with inhabitants of Egypt and with Libya.[118]
Demographics
The total number of Arabic speakers living in the Arab nations is estimated at 366 million by the CIA Factbook (as of 2014). The estimated number of Arabs in countries outside the Arab League is estimated at 17.5 million, yielding a total of close to 384 million.
Arab world

Population density of the Arab world in 2008
According to the Charter of the Arab League (also known as the Pact of the League of Arab States), the League of Arab States is composed of independent Arab states that are signatories to the Charter.[119]
Although all Arab states have Arabic as an official language, there are many non-Arabic-speaking populations native to the Arab world. Among these are Berbers, Toubou, Nubians, Jews, Kurds, Armenians.[35] Additionally, many Arab countries in the Persian Gulf have sizable non-Arab immigrant populations (10–30%). Iraq, Bahrain, Kuwait, Qatar, United Arab Emirates and Oman have a Persian speaking minority. The same countries also have Hindi-Urdu speakers and Filipinos as sizable minority. Balochi speakers are a good size minority in Oman. Additionally, countries like Bahrain, UAE, Oman and Kuwait have significant non-Arab and non-Muslim minorities (10–20%) like Hindus and Christians from India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and the Philippines.
The table below shows the distribution of populations in the Arab world, as well as the official language(s) within the various Arab states.[120]
| Arab state | Population | Official language(s) |
|---|---|---|
| 38,700,000[121] | Arabic co-official language with Berber | |
| 1,314,089[122] | Arabic official language | |
| 780,971[123] | Arabic co-official language with Comorian and French | |
| 810,179[124] | Arabic co-official language with French | |
| 94,526,231[125] | Arabic official language | |
| 32,585,692[126] | Arabic co-official language with Kurdish | |
| 9,531,712[127] | Arabic official language | |
| 4,156,306[128] | Arabic official language | |
| 5,882,562[129] | Arabic official language | |
| 6,244,174[130] | Arabic official language | |
| 3,516,806[131] | Arabic official language | |
| 32,987,206[132] | Arabic co-official language with Berber | |
| 3,219,775[133] | Arabic official language | |
| 4,550,368[134] | Arabic official language | |
| 2,123,160[135] | Arabic official language | |
| 27,345,986[136] | Arabic official language | |
| 10,428,043[137] | Arabic co-official language with Somali | |
| 35,482,233[138] | Arabic co-official language with English | |
| 17,951,639[139] | Arabic official language | |
| 10,937,521[140] | Arabic official language | |
| 10,102,678[141] | Arabic official language | |
| 26,052,966[142] | Arabic official language |
Arab diaspora

Syrian immigrants in New York City, as depicted in 1895
Arab diaspora refers to descendants of the Arab immigrants who, voluntarily or as refugees, emigrated from their native lands in non-Arab countries, primarily in East Africa, South America, Europe, North America, Australia and parts of South Asia, Southeast Asia, the Caribbean, and West Africa. According to the International Organization for Migration, there are 13 million first-generation Arab migrants in the world, of which 5.8 million reside in Arab countries. Arab expatriates contribute to the circulation of financial and human capital in the region and thus significantly promote regional development. In 2009, Arab countries received a total of 35.1 billion USD in remittance in-flows and remittances sent to Jordan, Egypt and Lebanon from other Arab countries are 40 to 190 per cent higher than trade revenues between these and other Arab countries.[143] The 250,000 strong Lebanese community in West Africa is the largest non-African group in the region.[144][145] Arab traders have long operated in Southeast Asia and along the East Africa's Swahili coast. Zanzibar was once ruled by Omani Arabs.[146] Most of the prominent Indonesians, Malaysians, and Singaporeans of Arab descent are Hadhrami people with origins in southern Yemen in the Hadramawt coastal region.[147]

Amel Bent, a French-born Maghrebi pop singer
There are millions of Arabs living in Europe mostly concentrated in France (about 6,000,000 in 2005[6]). Most Arabs in France are from the Maghreb but some also come from the Mashreq areas of the Arab world. Arabs in France form the second largest ethnic group after French people of French origin.[148]Spain (about 800,000[149][150] to 1,600,000 – 1,800,000[151][152][153][154]), there have been Arabs in Spain since the early 8th century when the Umayyad conquest of Hispania created the state of Al-Andalus.[155][156][157]Germany (over 1,000,000[158]), Italy (about 680,000[23]), United Kingdom (366,769[159] to 500,000[160]). Greece (250,000 to 750,000[161]), In addition, Greece has people from Arab countries who have the status of refugees (e.g. refugees of the Syrian civil war) or illegal immigrants trying to immigrate to Western Europe.[162]Sweden (210,400[163]). Netherlands (180,000[164]). Denmark (121,000). And in other European countries, such as Norway, Austria, Bulgaria, Switzerland, Republic of Macedonia, Romania and Serbia.[165] As of late 2015, Turkey had a population of 78.7 million, with Syrian refugees accounting for 3.1% of that figure based on conservative estimates. Demographic trends indicate that the country already had from 1,500,000[166] to more than 2,000,000,[10] so Turkey's Arab constituency now numbers anywhere from 4.5 to 5.1% of the population. In other words, nearly 4–5 million Arab inhabitants.[9][10]

The Arab American National Museum in Dearborn, Michigan, the United States of America
Arab immigration to the United States began in sizable numbers during the 1880s. Today, it is estimated that nearly 3.7 million Americans trace their roots to an Arab country.[167][168][169]Arab Americans are found in every state, but more than two thirds of them live in just ten states: California, Michigan, New York, Florida, Texas, New Jersey, Illinois, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Virginia. Metropolitan Los Angeles, Detroit, and New York City are home to one-third of the population.[168][170] Contrary to popular assumptions or stereotypes, the majority of Arab Americans are native-born, and nearly 82% of Arabs in the U.S. are citizens.[171][172][172][173][174] Arabs immigrants began to arrive in Canada in small numbers in 1882. Their immigration was relatively limited until 1945, after which time it increased progressively, particularly in the 1960s and thereafter.[175] According to the website "Who are Arab Canadians," Montreal, the Canadian city with the largest Arab population, has approximately 267,000 Arab inhabitants.[176]

Michel Temer, the 37th and current President of Brazil, is of Lebanese descent.[177][178][179]
Latin America has the largest Arab population outside of the Arab World.[180] Latin America is home to anywhere from 17–25 to 30 million people of Arab descent,[181] which is more than any other diaspora region in the world.[182][183] The Brazilian and Lebanese governments claim there are 7 million Brazilians of Lebanese descent.[184][185] Also, the Brazilian government claims there are 4 million Brazilians of Syrian descent.[184] According to research conducted by IBGE in 2008, covering only the states of Amazonas, Paraíba, São Paulo, Rio Grande do Sul, Mato Grosso and Distrito Federal, 0.9% of white Brazilian respondents said they had family origins in the Middle East.[186][187][188][189][190] Other large Arab communities includes Argentina (about 4,500,000[191][192][193]) The interethnic marriage in the Arab community, regardless of religious affiliation, is very high; most community members have only one parent who has Arab ethnicity.[194]Venezuela (over 1,600,000[15][195][196]), Colombia (over 1,600,000[16] to 3,200,000[197][198][199]), Mexico (over 1,100,000[19]), Chile (over 800,000[200][201][202][203]), and Central America, particularly El Salvador, and Honduras (between 150,000 and 200,000).[204][205][206] is the fourth largest in the world after those in Israel, Lebanon, and Jordan. Arab Haitians (a large number of whom live in the capital) are more often than not, concentrated in financial areas where the majority of them establish businesses.[207][207][207]
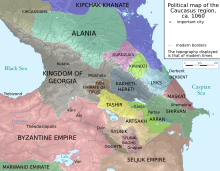
Georgia and the Caucasus in 1060, during the final decline of the emirate
In 1728, a Russian officer described a group of Arab nomads who populated the Caspian shores of Mughan (in present-day Azerbaijan) and spoke a mixed Turkic-Arabic language.[208] It is believed that these groups migrated to the Caucasus in the 16th century.[209] The 1888 edition of Encyclopædia Britannica also mentioned a certain number of Arabs populating the Baku Governorate of the Russian Empire.[210] They retained an Arabic dialect at least into the mid-19th century,[211] there are nearly 30 settlements still holding the name Arab (for example, Arabgadim, Arabojaghy, Arab-Yengija, etc.). From the time of the Arab conquest of the Caucasus, continuous small-scale Arab migration from various parts of the Arab world occurred in Dagestan. The majority of these lived in the village of Darvag, to the north-west of Derbent. The latest of these accounts dates to the 1930s.[209] Most Arab communities in southern Dagestan underwent linguistic Turkicisation, thus nowadays Darvag is a majority-Azeri village.[212][213] According to the History of Ibn Khaldun, the Arabs that were once in Central Asia have been either killed or have fled the Tatar invasion of the region, leaving only the locals.[214] However, today many people in Central Asia identify as Arabs. Most Arabs of Central Asia are fully integrated into local populations, and sometimes call themselves the same as locals (for example, Tajiks, Uzbeks) but they use special titles to show their Arab origin such as Sayyid, Khoja or Siddiqui.[215]

Kechimalai Mosque, Beruwala. One of the oldest mosques in Sri Lanka. It is believed to be the site where the first Arabs landed in Sri Lanka.
There are only two communities in India which self-identify as Arabs, the Chaush of the Deccan region and the Chavuse of Gujarat.[216][217] These groups are largely descended from Hadhrami migrants who settled in these two regions in the 18th century. However, neither community still speaks Arabic, although the Chaush have seen re-immigration to the Arab States of the Persian Gulf and thus a re-adoption of Arabic.[218] In South Asia, where Arab ancestry is considered prestigious, many communities have origin myths that claim Arab ancestry. These include the Mappilla of Kerala and the Labbai of Tamil Nadu.[219] Among North Indian and Pakistani Arabs, there are groups who claim the status of Sayyid and have origin myths that allege descent from Muhammad.[220] The South Asian Iraqi biradri may be considered Arabs because records of their ancestors who migrated from Iraq exist in historical documents. There are about 5,000,000 Native Indonesians with Arab ancestry.[221]Arab Indonesians are mainly of Hadrami descent.[222][222] The Sri Lankan Moors are the third largest ethnic group in Sri Lanka, comprising 9.23% of the country's total population.[223] Some sources trace the ancestry of the Sri Lankan Moors to Arab traders who settled in Sri Lanka at some time between the 8th and 15th centuries.[224][225][226]

Baggara belt
Afro-Arabs are individuals and groups from Africa who are of partial Arab descent. Most Afro-Arabs inhabit the Swahili Coast in the African Great Lakes region, although some can also be found in parts of the Arab world.[227][228] Large numbers of Arabs migrated to West Africa, particularly Côte d'Ivoire (home to over 100,000 Lebanese),[229]Senegal (roughly 30,000 Lebanese),[230]Sierra Leone (roughly 10,000 Lebanese today; about 30,000 prior to the outbreak of civil war in 1991), Liberia, and Nigeria.[231] Since the end of the civil war in 2002, Lebanese traders have become re-established in Sierra Leone.[232][233][234][235] The Arabs of Chad occupy northern Cameroon and Nigeria (where they are sometimes known as Shuwa), and extend as a belt across Chad and into Sudan, where they are called the Baggara grouping of Arab ethnic groups inhabiting the portion of Africa's Sahel. The Chadian Arabs are (2,391,000 to 2,500,000[236]), Nigeria (289,000[237]), Cameroon (171,000), Niger (150,000[238]), and the Central African Republic (107,000).[239]
Religion

Bas-relief: Nemesis, Allāt and the dedicator
Arabs are mostly Muslims with a Sunni majority and a Shia minority, one exception being the Ibadis, who predominate in Oman.[240]Arab Christians generally follow Eastern Churches such as the Greek Orthodox and Greek Catholic churches, though a minority of Protestant Church followers also exists.[241] There are also Arab communities consisting of Druze and Baha'is.[242][243]
Before the coming of Islam, most Arabs followed a pagan religion with a number of deities, including Hubal,[244]Wadd, Allāt,[245]Manat, and Uzza. A few individuals, the hanifs, had apparently rejected polytheism in favor of monotheism unaffiliated with any particular religion. Some tribes had converted to Christianity or Judaism. The most prominent Arab Christian kingdoms were the Ghassanid and Lakhmid kingdoms.[246] When the Himyarite king converted to Judaism in the late 4th century,[247] the elites of the other prominent Arab kingdom, the Kindites, being Himyirite vassals, apparently also converted (at least partly). With the expansion of Islam, polytheistic Arabs were rapidly Islamized, and polytheistic traditions gradually disappeared.[248][249]

The holiest place in Islam, the Kaaba in Al-Haram Mosque, is located in Mecca, the Hejazi region of Saudi Arabia
Today, Sunni Islam dominates in most areas, overwhelmingly so in North Africa and the Horn of Africa. Shia Islam is dominant among the Arab population in Bahrain and southern Iraq while northern Iraq is mostly Sunni. Substantial Shia populations exist in Lebanon, Yemen, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia,[250] northern Syria and Al-Batinah Region in Oman. There are small numbers of Ibadi and non-denominational Muslims too.[240] The Druze community is concentrated in Lebanon, Syria, Israel and Jordan. Many Druze claim independence from other major religions in the area and consider their religion more of a philosophy. Their books of worship are called Kitab Al Hikma (Epistles of Wisdom). They believe in reincarnation and pray to five messengers from God. In Israel, the Druze have a status aparte from the general Arab population, treated as a separate ethno-religious community.

A Greek Orthodox Church during a snow storm in Amman, Jordan
Christianity had a prominent presence In pre-Islamic Arabia among several Arab communities, including the Bahrani people of Eastern Arabia, the Christian community of Najran, in parts of Yemen, and among certain northern Arabian tribes such as the Ghassanids, Lakhmids, Taghlib, Banu Amela, Banu Judham, Tanukhids and Tayy. In the early Christian centuries, Arabia was sometimes known as Arabia heretica, due to its being "well known as a breeding-ground for heterodox interpretations of Christianity."[251] Christians make up 5.5% of the population of Western Asia and North Africa.[252] A sizeable share of those are Arab Christians proper, and affiliated Arabic-speaking populations of Copts and Maronites. In Lebanon, Christians number about 40.5% of the population.[129] In Syria, Christians make up 10% of the population.[139] In West Bank and in Gaza Strip, Christians make up 8% and 0.7% of the populations, respectively.[253][254] In Egypt, Coptic Christians number about 10% of the population. In Iraq, Christians constitute 0.1% of the population.[255] In Israel, Arab Christians constitute 2.1% (roughly 9% of the Arab population).[256] Arab Christians make up 8% of the population of Jordan.[257] Most North and South American Arabs are Christian,[258] so are about half of the Arabs in Australia who come particularly from Lebanon, Syria and Palestine. One well known member of this religious and ethnic community is Saint Abo, martyr and the patron saint of Tbilisi, Georgia.[259] Arab Christians also live in holy Christian cities such as Nazareth, Bethlehem and the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem and many other villages with holy Christian sites.
Culture

An Abbasid-era Arabic manuscript
| Part of a series on |
| Arab culture |
|---|
 |
Architecture Styles
Features
Types
|
art Styles
Types
Features
|
Gastronomy
|
Dress Headwear
Clothing
|
Music Theory
Genres
Art music
Folk
|
Dance
|
Literature Language
Prose
Islamic
Poetry
Genres
Forms
Arabic prosody
|
Science
|
Philosophy
Concepts
Texts
|
Mythology
Fictional Arab people
|
Spirituality North Arabian deities
South Arabian deities
|
Arabic culture is the culture of Arab people, from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east, and from the Mediterranean Sea. Language, literature, gastronomy, art, architecture, music, spirituality, philosophy, mysticism (etc.) are all part of the cultural heritage of the Arabs.[260]
Arabs share basic beliefs and values that cross national and social class boundaries. Social attitudes have remained constant because Arab society is more conservative and demands conformity from its members.[261]
Language

Arabic calligraphy
Another important and unifying characteristic of Arabs is a common language. Arabic is a Semitic language of the Afro-Asiatic Family.[262] Evidence of its first use appears in accounts of wars in 853 BCE. It also became widely used in trade and commerce. Arabic also is a liturgical language of 1.7 billion Muslims.[263][264]
Arabic is one of six official languages of the United Nations.[265] It is revered as the language that God chose to reveal the Quran.[266][267]
Arabic has developed into at least two distinct forms. Classical Arabic is the form of the Arabic language used in literary texts from Umayyad and Abbasid times (7th to 9th centuries). It is based on the medieval dialects of Arab tribes. Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is the direct descendant used today throughout the Arab world in writing and in formal speaking, for example, prepared speeches, some radio broadcasts, and non-entertainment content,[268] while the lexis and stylistics of Modern Standard Arabic are different from Classical Arabic. Colloquial Arabic, an informal spoken language, varies by dialect from region to region; various forms of the language are in use today and provide an important force for Arab cohesion.[269]
Mythology

Aladdin flying away with two people, from the Arabian Nights, c. 1900
Arabic mythology comprises the ancient beliefs of the Arabs.[270] Prior to Islam the Kaaba of Mecca was covered in symbols representing the myriad demons, djinn, demigods, or simply tribal gods and other assorted deities which represented the polytheistic culture of pre-Islamic.[271][272] It has been inferred from this plurality an exceptionally broad context in which mythology could flourish. The most popular beasts and demons of Arabian mythology are Bahamut, Dandan, Falak, Ghoul, Hinn, Jinn, Karkadann, Marid, Nasnas, Qareen, Roc, Shadhavar, Werehyena and other assorted creatures which represented the profoundly polytheistic environment of pre-Islamic.[273]
The most obvious symbol of Arabian mythology is the Jinn or genie.[274] Jinns are supernatural beings of varying degrees of power. They possess free will (that is, they can choose to be good or evil) and come in two flavors. There are the Marids, usually described as the most powerful type of Jinn. These are the type of genie with the ability to grant wishes to humans. However, granting these wishes is not free. The Quran says that the jinn were created from "mārijin min nar" (smokeless fire or a mixture of fire; scholars explained, this is the part of the flame, which mixed with the blackness of fire).[275][276] They are not purely spiritual, but are also physical in nature, being able to interact in a tactile manner with people and objects and likewise be acted upon. The jinn, humans, and angels make up the known sapient creations of God.[277]
A ghoul is a monster or evil spirit in Arabic mythology, associated with graveyards and consuming human flesh,[278][279] demonic being believed to inhabit burial grounds and other deserted places. In ancient Arabic folklore, ghūls belonged to a diabolic class of jinn (spirits) and were said to be the offspring of Iblīs, the prince of darkness in Islam. They were capable of constantly changing form, but their presence was always recognizable by their unalterable sign—ass's hooves.[280] which describes the ghūl of Arabic folklore. The ghul is a devilish type of jinn believed to be sired by Iblis.[281]
Literature

A giraffe from the Kitāb al-Ḥayawān (Book of the Animals), an important scientific treatise by the 9th century Arab writer Al-Jahiz.[282]
Al-Jahiz (born 776, in Basra – December 868/January 869) was an Arab prose writer and author of works of literature, Mu'tazili theology, and politico-religious polemics. A leading scholar in the Abassid Caliphate, his canon includes two hundred books on various subjects, including Arabic grammar, zoology, poetry, lexicography, and rhetoric. Of his writings, only thirty books survive. Al-Jāḥiẓ was also one of the first Arabian writers to suggest a complete overhaul of the language's grammatical system, though this would not be undertaken until his fellow linguist Ibn Maḍāʾ took up the matter two hundred years later.[283]
There is a small remnant of pre-Islamic poetry, but Arabic literature predominantly emerges in the Middle Ages, during the Golden Age of Islam.[284]Literary Arabic is derived from Classical Arabic, based on the language of the Quran as it was analyzed by Arabic grammarians beginning in the 8th century.[285]

Illustration from Kitab al-Aghani (Book of Songs), by Abu al-Faraj al-Isfahani. The 14th-century historian Ibn Khaldun called the Book of Songs the register of the Arabs.[286]
A large portion of Arabic literature before the 20th century is in the form of poetry, and even prose from this period is either filled with snippets of poetry or is in the form of saj or rhymed prose.[287]
The ghazal or love poem had a long history being at times tender and chaste and at other times rather explicit.[288] In the Sufi tradition the love poem would take on a wider, mystical and religious importance. Arabic epic literature was much less common than poetry, and presumably originates in oral tradition, written down from the 14th century or so. Maqama or rhymed prose is intermediate between poetry and prose, and also between fiction and non-fiction.[289]Maqama was an incredibly popular form of Arabic literature, being one of the few forms which continued to be written during the decline of Arabic in the 17th and 18th centuries.[290]

Self portrait of renowned Lebanese poet/writer Khalil Gibran
Arabic literature and culture declined significantly after the 13th century, to the benefit of Turkish and Persian. A modern revival took place beginning in the 19th century, alongside resistance against Ottoman rule. The literary revival is known as al-Nahda in Arabic, and was centered in Egypt and Lebanon. Two distinct trends can be found in the nahda period of revival.[291] The first was a neo-classical movement which sought to rediscover the literary traditions of the past, and was influenced by traditional literary genres—such as the maqama—and works like One Thousand and One Nights. In contrast, a modernist movement began by translating Western modernist works—primarily novels—into Arabic.[292] A tradition of modern Arabic poetry was established by writers such as Francis Marrash, Ahmad Shawqi and Hafiz Ibrahim. Iraqi poet Badr Shakir al-Sayyab is considered to be the originator of free verse in Arabic poetry.[293][294][295]
Gastronomy

A large plate of Mezes in Petra, Jordan
Arabic cuisine is the cuisine of the Arab people.[296] The cuisines are often centuries old and resemble and culture of great trading in spices, herbs, and foods. The three main regions, also known as the Maghreb, the Mashriq, and the Khaleej have many similarities, but also many unique traditions. These kitchens have been influenced by the climate, cultivating possibilities, as well as trading possibilities. The kitchens of the Maghreb and Levant are relatively young kitchens which were developed over the past centuries. The kitchen from the Khaleej region is a very old kitchen. The kitchens can be divided into the urban and rural kitchens.
Arab cuisine mostly follows one of three culinary traditions – from the Maghreb, the Levant or the Persian Gulf states. In the Maghreb countries (Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya) traditional main meals are tajines or dishes using couscous. In the Levant (Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon and Syria) main meals usually start with mezze – small dishes of dips and other items which are eaten with bread. This is typically followed by skewers of grilled lamb or chicken. Gulf cuisine, tends to be more highly spiced with more use of rice. Sometimes a lamb is roasted and served whole.[297]
One will find the following items on most dishes; Cinnamon, Fish (in coastal areas), Garlic, Lamb (or veal), Mild to hot sauces, Mint, Onion, Rice, Saffron, Sesame, Yogurt, Spices due to heavy trading between the two regions. Tea, Thyme (or oregano), Turmeric, Variety of fruits (primarily citrus), Variety of vegetables such as cucumbers, eggplants, lettuce, tomato, green pepper, green beans, zucchini and parsley.[297][298]
Art

Mosaic and arabesque on a wall of the Myrtle court in Alhambra, Granada.
Arabic art takes on many forms, though it is jewelry, textiles and architecture that are the most well-known. It is generally split up by different eras, among them being early Arabic, early medieval, late medieval, late Arabic, and finally, current Arabic. One thing to remember is that many times a particular style from one era may continue into the next with few changes, while some have a drastic transformation. This may seem like a strange grouping of art mediums, but they are all closely related.[299][300]

Arabic miniature dibicting Al-Harith from Maqamat of al-Hariri
Arabic writing is done from right to left, and was generally written in dark inks, with certain things embellished with special colored inks (red, green, gold). In early Arabic and early Medieval, writing was typically done on parchment made of animal skin. The ink showed up very well on it, and occasionally the parchment was dyed a separate color and brighter ink was used (this was only for special projects). The name given to the form of writing in early times was called Kufic script.[301]
Arabic miniatures are small paintings on paper, whether book illustrations or separate works of art. Arabic miniature art dates to the late 7th century. Arabs depended on such art not only to satisfy their artistic taste, but also for scientific explanations.
Arabesque is a form of artistic decoration consisting of "surface decorations based on rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing foliage, tendrils" or plain lines,[302] often combined with other elements. Another definition is "Foliate ornament, typically using leaves, derived from stylised half-palmettes, which were combined with spiralling stems".[303] It usually consists of a single design which can be 'tiled' or seamlessly repeated as many times as desired.[304][305]
Architecture

The Mosque-Cathedral of Cordóba, built by Abd al Rahman I in 987
Arabic Architecture has a deep diverse history, it dates to the dawn of the history in pre-Islamic Arabia and includes various styles from the Nabataean architecture to the old yet still used architecture in various regions of the Arab world. Each of it phases largely
an extension of the earlier phase, it left also heavy impact on the architecture of other nations. Arab Architecture also encompasses a wide range of both secular and religious styles from the foundation of Islam to the present day. Some parts of its religious architectures raised by Muslim Arabs were influenced by cultures of Roman, Byzantine and cultures of other lands which the Arab conquered in the 7th and 8th centuries.[306][307]
In Sicily, Arab-Norman architecture combined Occidental features, such as the Classical pillars and friezes, with typical Arabic decorations and calligraphy. The principal Islamic architectural types are: the Mosque, the Tomb, the Palace and the Fort. From these four types, the vocabulary of Islamic architecture is derived and used for other buildings such as public baths, fountains and domestic architecture.[308][309]
Music

Bayad plays the "Oud to The Lady," from the Bayad & Riyad, Arabic tale
Arabic music, while independent and flourishing in the 2010s, has a long history of interaction with many other regional musical styles and genres. It is an amalgam of the music of the Arab people in the Arabian Peninsula and the music of all the peoples that make up the Arab world today[310] Pre-Islamic Arab music was similar to that of Ancient Middle Eastern music. Most historians agree that there existed distinct forms of music in the Arabian peninsula in the pre-Islamic period between the 5th and 7th century CE. Arab poets of that "Jahili poets", meaning "the poets of the period of ignorance"—used to recite poems with a high notes.[311] It was believed that Jinns revealed poems to poets and music to musicians.[311][311] By the 11th century, Islamic Iberia had become a center for the manufacture of instruments. These goods spread gradually throughout France, influencing French troubadours, and eventually reaching the rest of Europe. The English words lute, rebec, and naker are derived from Arabic oud, rabab, and naqareh.[312][313]

Umm Kulthum was an internationally famous Egyptian singer.
A number of musical instruments used in classical music are believed to have been derived from Arabic musical instruments: the lute was derived from the Oud, the rebec (ancestor of violin) from the rebab, the guitar from qitara, which in turn was derived from the Persian Tar, naker from naqareh, adufe from al-duff, alboka from al-buq, anafil from al-nafir, exabeba from al-shabbaba (flute), atabal (bass drum) from al-tabl, atambal from al-tinbal,[314] the balaban, the castanet from kasatan, sonajas de azófar from sunuj al-sufr, the conical bore wind instruments,[315] the xelami from the sulami or fistula (flute or musical pipe),[316]
the shawm and dulzaina from the reed instruments zamr and al-zurna,[317] the gaita from the ghaita, rackett from iraqya or iraqiyya,[318]geige (violin) from ghichak,[319]
and the theorbo from the tarab.[320]
During the 1950s and the 1960s, Arabic music began to take on a more Western tone – artists Umm Kulthum and Abdel Halim Hafez along with composers Mohamed Abd al-Wahab and Baligh Hamdi pioneered the use of western instruments in Egyptian music. By the 1970s several other singers had followed suit and a strand of Arabic pop was born. Arabic pop usually consists of Western styled songs with Arabic instruments and lyrics. Melodies are often a mix between Eastern and Western. Beginning in the mid-1980s, Lydia Canaan, musical pioneer widely regarded as the first rock star of the Middle East[321][322][323][324][325][326][327][328]
Spirituality

Al-'Uzzá was one of the three chief goddesses of a pagan Arabian religion
Arab polytheism was the dominant religion in pre-Islamic Arabia. Gods and goddesses, including Hubal and the goddesses al-Lāt, Al-'Uzzá and Manāt, were worshipped at local shrines, such as the Kaaba in Mecca, whilst Arabs in the south, in what is today's Yemen, worshipped various gods, some of which represented the Sun or Moon. Different theories have been proposed regarding the role of Allah in Meccan religion.[55][329][330][331] Many of the physical descriptions of the pre-Islamic gods are traced to idols, especially near the Kaaba, which is said to have contained up to 360 of them.[332] Until about the fourth century, almost all Arabs practised polytheistic religions.[333] Although significant Jewish and Christian minorities developed, polytheism remained the dominant belief system in pre-Islamic Arabia.[55][334]
The religious beliefs and practices of the nomadic bedouin were distinct from those of the settled tribes of towns such as Mecca.[335] Nomadic religious belief systems and practices are believed to have included fetishism, totemism and veneration of the dead but were connected principally with immediate concerns and problems and did not consider larger philosophical questions such as the afterlife.[335] Settled urban Arabs, on the other hand, are thought to have believed in a more complex pantheon of deities.[335] While the Meccans and the other settled inhabitants of the Hejaz worshipped their gods at permanent shrines in towns and oases, the bedouin practised their religion on the move.[336]
Philosophy

Averroes, founder of the Averroism school of philosophy, was influential in the rise of secular thought in Western Europe.

Ibn Arabi, one of the most celebrated mystic-philosophers in Islamic history.
Arabic philosophy refers to philosophical thought in the Arab world. Schools of Arabic thought include Avicennism and Averroism. The first great Arab thinker is widely regarded to be al-Kindi (801–873 A.D.), a Neo-Platonic philosopher, mathematician and scientist who lived in Kufa and Baghdad (modern day Iraq). After being appointed by the Abbasid Caliphs to translate Greek scientific and philosophical texts into Arabic, he wrote a number of original treatises of his own on a range of subjects, from metaphysics and ethics to mathematics and pharmacology.[337]
Much of his philosophical output focuses on theological subjects such as the nature of God, the soul and prophetic knowledge.[338] Doctrines of the Arabic philosophers of the 9th–12th century who influenced medieval Scholasticism in Europe. The Arabic tradition combines Aristotelianism and Neoplatonism with other ideas introduced through Islam. Influential thinkers include the Persians al-Farabi and Avicenna. The Arabic philosophic literature was translated into Hebrew and Latin, this contributed to the development of modern European philosophy. The Arabic tradition was developed by Moses Maimonides and Ibn Khaldun.[339][340]
Science

Hevelius's Selenographia, showing Alhazen [sic] representing reason, and Galileo representing the senses. Alhazen has been described as the "world's first true scientist".[341]
Arabic science underwent considerable development during the 8th to 13th centuries CE, a source of knowledge that later spread throughout Europe and greatly influenced both medical practice and education. These scientific accomplishments occurred after Muhammad united the Arab tribes.[342]

Albategnius's Kitāb az-Zīj was one of the most influential books in medieval astronomy
Within a century after Muhammed's death (632 CE), an empire ruled by Arabs was established. It encompassed a large part of the planet, stretching from southern Europe to North Africa to Central Asia and on to India. In 711 CE, Arab Muslims invaded southern Spain; al-Andalus was a center of Arabic scientific accomplishment. Another center emerged in Baghdad from the Abbasids, who ruled part of the Islamic world during a historic period later characterized as the "Golden Age" (∼750 to 1258 CE).[343]

The Tabula Rogeriana, drawn by al-Idrisi for Roger II of Sicily in 1154, is one of the most advanced ancient world maps. Modern consolidation, created from the 70 double-page spreads of the original atlas.
This era can be identified as the years between 692 and 945,[344] and ended when the caliphate was marginalized by local Muslim rulers in Baghdad – its traditional seat of power. From 945 onward until the sacking of Baghdad by the Mongols in 1258, the Caliph continued on as a figurehead, with power devolving more to local amirs.[345] The pious scholars of Islam, men and women collectively known as the ulama, were the most influential element of society in the fields of Sharia law, speculative thought and theology.[346] Arabic scientific achievement is not as yet fully understood, but is very large.[347] These achievements encompass a wide range of subject areas, especially mathematics, astronomy, and medicine.[347] Other subjects of scientific inquiry included physics, alchemy and chemistry, cosmology, ophthalmology, geography and cartography, sociology, and psychology.[348][349]
Al-Battani (c. 858 – 929; born Harran, Bilad al-Sham) was an Arab astronomer, astrologer and mathematician of the Islamic Golden Age. His work is considered instrumental in the development of science and astronomy. One of Al-Battani's best-known achievements in astronomy was the determination of the solar year as being 365 days, 5 hours, 46 minutes and 24 seconds which is only 2 minutes and 22 seconds off.[350]
Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) used experimentation to obtain the results in his Book of Optics (1021), an important development in the history of the scientific method. He combined observations, experiments and rational arguments to support his intromission theory of vision, in which rays of light are emitted from objects rather than from the eyes. He used similar arguments to show that the ancient emission theory of vision supported by Ptolemy and Euclid (in which the eyes emit the rays of light used for seeing), and the ancient intromission theory supported by Aristotle (where objects emit physical particles to the eyes), were both wrong.[351]
Al-Zahrawi, regarded by many as the greatest surgeon of the middle ages.[352] His surgical treatise "De chirurgia" is the first illustrated surgical guide ever written. It remained the primary source for surgical procedures and instruments in Europe for the next 500 years.[353] The book helped lay the foundation to establish surgery as a scientific discipline independent from medicine, earning al-Zahrawi his name as one of the founders of this field.[354]
Other notable Arab contributions include among other things: establishing the science of chemistry by Jābir ibn Hayyān,[355][356][357] establishing the science of cryptology and cryptanalysis by al-Kindi,[358][359][360] the development of analytic geometry by Ibn al-Haytham,[361][362] the discovery of the pulmonary circulation by Ibn al-Nafis,[363][364] the discovery of the itch mite parasite by Ibn Zuhr,[365] the first use of irrational numbers as an algebraic objects by Abū Kāmil,[366] the first use of the positional decimal fractions by al-Uqlidisi,[367][368] the development of the Arabic numerals and an early algebraic symbolism in the Maghreb,[369][370] the Thabit number and Thābit theorem by Thābit ibn Qurra,[371] the discovery of several new trigonometric identities by Ibn Yunus and al-Battani,[372][373] the mathematical proof for Ceva's theorem by Ibn Hűd,[374] the first accurate lunar model by Ibn al-Shatir,[375] the invention of the torquetum by Jabir ibn Aflah,[376] the invention of the universal astrolabe and the equatorium by al-Zarqali,[377][378] the first description of the crankshaft by al-Jazari,[379][380] the anticipation of the inertia concept by Averroes,[381] the discovery of the physical reaction by Avempace,[382] the identification of more than 200 new plants by Ibn al-Baitar[383] the Arab Agricultural Revolution, and the Tabula Rogeriana, which was the most accurate world map in pre-modern times by al-Idrisi.[384]
The birth of the University institution can be traced to this development, as several universities and educational institutions of the Arab world such as the University of Al Quaraouiyine, Al Azhar University, and Al Zaytuna University are considered to be the oldest in the world. Founded by Fatima al Fihri in 859, the University of Al Quaraouiyine in Fez is the oldest existing, continually operating and the first degree awarding educational institution in the world according to UNESCO and Guinness World Records[385][386] and is sometimes referred to as the oldest university.[387]
There are many scientific Arabic loanwords in Western European languages, including English, mostly via Old French.[388] This includes traditional star names such as Aldebaran, scientific terms like alchemy (whence also chemistry), algebra, algorithm, alcohol, alkali, cipher, zenith, etc.
Under Ottoman rule, cultural life and science in the Arab world declined. In the 20th and 21st centuries, Arabs who have won important science prizes include Ahmed Zewail and Elias Corey (Nobel Prize), Michael DeBakey and Alim Benabid (Lasker Award), Omar M. Yaghi (Wolf Prize), Huda Zoghbi (Shaw Prize), Zaha Hadid (Pritzker Prize), and Michael Atiyah both (Fields Medal) and (Abel Prize). Rachid Yazami was one of the co-inventors of the lithium-ion battery,[389] and Tony Fadell was important in the development of the iPod and the iPhone.[390]
Wedding and marriage

Henna tattoo in Morocco
Arabic weddings have changed greatly in the past 100 years. Original traditional Arabic weddings are supposed to be very similar to modern-day Bedouin weddings and rural weddings, and they are in some cases unique from one region to another, even within the same country. The practice of marrying of relatives is a common feature of Arab culture.[391]
In the Arab world today between 40% and 50% of all marriages are consanguineous or between close family members, though these figures may vary among Arab nations.[392][393] In Egypt, around 40% of the population marry a cousin. A 1992 survey in Jordan found that 32% were married to a first cousin; a further 17.3% were married to more distant relatives.[394] 67% of marriages in Saudi Arabia are between close relatives as are 54% of all marriages in Kuwait, whereas 18% of all Lebanese were between blood relatives.[395][395] Due to the actions of Muhammad and the Rightly Guided Caliphs, marriage between cousins is explicitly allowed in Islam and the Qur'an itself does not discourage or forbid the practice.[396] Nevertheless, opinions vary on whether the phenomenon should be seen as exclusively based on Islamic practices as a 1992 study among Arabs in Jordan did not show significant differences between Christian Arabs or Muslim Arabs when comparing the occurrence of consanguinity.[395]
Genetics
E1b1b is the most frequent paternal clade among the populations in the western part of the Arab world (Maghreb, Nile Valley, and the Horn of Africa), whereas haplogroup J is the most frequent paternal clade toward the east (Arabian peninsula and Near East). Other less common haplogroups are R1a, R1b, G, I, L and T.[397][398][399][400][401][402][403][404][405][406][407][408][409]
@media all and (max-width:720px).mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinnerwidth:100%!important;max-width:none!important.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsinglefloat:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center



Listed here are the human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups in Arabian Peninsula, Mashriq or Levant, Maghreb and Nile Valley.[410][411][412][413][414][415][416]Yemeni Arabs J (82.3%), E1b1b (12.9%) and E1b1a (3.2%).[417][418]Saudi Arabs J1 (58%), E1b1b (7.6%), E1b1a (7.6%), R1a (5.1%), T (5.1%), G (3.2%) and L (1.9%).[419][420]Emirati Arabs J (45.1%), E1b1b (11.6%), R1a (7.3%), E1b1a (5.5%), T (4.9%), R1b (4.3%) and L (3%).[417]Omani Arabs J (47.9%), E1b1b (15.7%), R1a (9.1%), T (8.3%), E1b1a (7.4%), R1b (1.7%), G (1.7%) and L (0.8%).[421]Qatari Arabs J (66.7%), R1a (6.9%), E1b1b (5.6%), E1b1a (2.8%), G (2.8%) and L (2.8%).[422][423]Lebanese Arabs J (45.2%), E1b1b (25.8%), R1a (9.7%), R1b (6.4%), G, I and I (3.2%), (3.2%), (3.2%).[424]Syrian Arabs J (58.3%),[425][426]E1b1b (12.0%), I (5.0%), R1a (10.0%) and R1b 15.0%.[424][426]Palestinian Arabs J (55.2%), E1b1b (20.3%), R1b (8.4%), I (6.3%), G (7%), R1a and T (1.4%), (1.4%).[427][428]Jordanian Arabs J (43.8%), E1b1b (26%), R1b (17.8%), G (4.1%), I (3.4%) and R1a (1.4%).[429]Iraqi Arabs J (50.6%), E1b1b (10.8%), R1b (10.8%), R1a (6.9%) and T (5.9%).[430][431]Egyptian Arabs E1b1b (36.7%) and J (32%), G (8.8%), T (8.2% R1b (4.1%), E1b1a (2.8%) and I (0.7%).[412][432]Sudanese Arabs J (47.1%), E1b1b (16.3%), R1b (15.7%) and I (3.13%).[433][434]Moroccan Arabs E1b1b (75.5%) and J1 (20.4%).[435][436]Tunisian Arabs E1b1b (49.3%), J1 (35.8%), R1b (6.8%) and E1b1a (1.4%).[437]Algerian Arabs E1b1b (54%), J1 (35%), R1b (13%).[437]Libyan Arabs E1b1b (35.88%), J (30.53%), E1b1a (8.78%), G (4.20%), R1a/R1b (3.43%) and E (1.53%).[438][439]
The mtDNA haplogroup J has been observed at notable frequencies among overall populations in the Arab world.[440][441] The maternal clade R0 reaches its highest frequency in the Arabian peninsula,[442] while K and T(specifically subclade T2) is more common in the Levant.[440] In the Nile Valley and Horn of Africa, haplogroups N1 and M1;[442] in the Maghreb, haplogroups H1 and U6 are more significant.[443]
There are four principal West Eurasian autosomal DNA components that characterize the populations in the Arab world: the Arabian, Levantine, Coptic and Maghrebi components.
The Arabian component is the main autosomal element in the Persian Gulf region. It is most closely associated with local Arabic-speaking populations.[415] The Arabian component is also found at significant frequencies in parts of the Levant and Northeast Africa.[415][444] The geographical distribution pattern of this component correlates with the pattern of the Islamic expansion, but its presence in Lebanese Christians, Sephardi and Ashkenazi Jews, Cypriots and Armenians might suggest that its spread to the Levant could also represent an earlier event.[415]
The Levantine component is the main autosomal element in the Near East and Caucasus. It peaks among Druze populations in the Levant. The Levantine component diverged from the Arabian component about 15,500–23,700 ypb.[415]
The Coptic component is the main autosomal element in Northeast Africa. It peaks among Egyptian Copts in Sudan, and is also found at high frequencies among other Afro-Asiatic-speaking populations in the Nile Valley and the Horn of Africa.[445]The Coptic component is roughly equivalent with the Ethio-Somali component.[446]
The Maghrebi component is the main autosomal element in the Maghreb. It peaks among the non-Arabized Berber populations in the region.[444] The Maghrebi component diverged from the Coptic/Ethio-Somali, Arabian and Levantine components prior to the Holocene.[444][446]
See also
- Arab Union
- Arab world
- Lists of Arab companies
- North African Arabs
References
- Notes
^ A 2008 IBGE study indicates that residents of Middle Eastern origin (Oriente médio) were distributed in the regions of Amazonas (0.3%), Paraíba (0.0%), São Paulo (0.5%), Rio Grande do Sul (0.5%), Mato Grosso (0.1%), and the Federal District (0.0%).[5]
^ Including recent Syrian refugees
^ ab Margaret Kleffner Nydell Understanding Arabs: A Guide For Modern Times, Intercultural Press, 2005, ISBN 1931930252, page xxiii, 14
^ total population 450 million, CIA Factbook estimates an Arab population of 450 million, see article text.
^ "World Arabic Language Day | United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization". Unesco.org. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "Arabs Love Brazil. They Are 7% of the Country". Brazzil. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
^ Características étnico-raciais da população: classificações e identidades (PDF). IBGE. 2013. p. 127. ISBN 9788524042447. Retrieved 20 June 2017.
^ ab By (29 January 2008). "French-Arabs battle stereotypes – Entertainment News, French Cinema, Media". Variety. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
^ "Hadramaut dan Para Kapiten Arab". 20 August 2009.
^ Kaya, Ibrahim (2009). "The Iraqi Refugee Crisis and Turkey: a Legal Outlook". cadmus.eui.eu. Retrieved 11 May 2017.
^ ab "The Impact of Syrian Refugees on Turkey". Washingtoninstitute.org. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ abc "Turkey's demographic challenge". Aljazeera.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "UNHCR Syria Regional Refugee Response/ Turkey". UNHCR. 31 December 2015. Retrieved 11 May 2017.
^ "The Arab American Institute". Aaiusa.org. Archived from the original on 1 June 2006. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
^ "Inmigración sirio-libanesa en Argentina". 20 June 2010. Archived from the original on 20 June 2010.
^ "65th Independence Day - More than 8 Million Residents in the State of Israel" (PDF). Cbs.gov.il. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ ab Margolis, Mac (15 September 2013). "Abdel el-Zabayar: From Parliament to the Frontlines". The Daily Beast.
^ ab "Las mil y una historias" (in Spanish). semana.com. 2004. There is an estimated population of 1,500,000 Arabs in Colombia.
^ "Iran". Archived from the original on 3 February 2012. Retrieved 3 August 2013.
^ "Chad". Archived from the original on 24 April 2013. Retrieved 3 August 2013.
^ ab Ben Cahoon. "World Statesmen.org". World Statesmen.org. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
^ Mediendienst Integration. "Syrische Flüchtlinge". Retrieved 8 June 2016.
^ "Men of Arab descent not finding Germany as welcoming as they used to". Public Radio International.
^ (in Spanish) En Chile viven unas 700.000 personas de origen árabe y de ellas 500.000 son descendientes de emigrantes palestinos que llegaron a comienzos del siglo pasado y que constituyen la comunidad de ese origen más grande fuera del mundo árabe.
^ ab Dati ISTAT 2016, counting only immigrants from the Arab world. "Cittadini stranieri in Italia – 2016". tuttitalia.it.
^ "REPORT ON THE 2011 CENSUS – MAY 2013 – Arabs and Arab League Population in the UK". National Association of British Arabs. Archived from the original on 29 May 2014. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
^ Statistics Canada. "2011 National Household Survey: Data tables". Retrieved 11 February 2014.
^ "Dutch media perceived as much more biased than Arabic media – Media & Citizenship Report conducted by University of Utrecht" (PDF), Utrecht University, 10 September 2010, retrieved 29 November 2010 [dead link]
^ "Monash University Research Repository" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 24 March 2015.
^ "revistas.ucm.es/index.php/ANQE/article/viewFile/ANQE9797110057A/3864". Missing or empty|url=(help)
^ Larry Luxner (2001). "The Arabs of Honduras". Saudi Aramco World. Retrieved 11 February 2016.
^ ab Shen, P; Lavi, T; Kivisild, T; Chou, V; Sengun, D; Gefel, D; Shpirer, I; Woolf, E; Hillel, J (2004). "Reconstruction of patrilineages and matrilineages of Samaritans and other Israeli populations from Y-chromosome and mitochondrial DNA sequence variation" (PDF). Human Mutation. 24 (3): 248–60. doi:10.1002/humu.20077. PMID 15300852.
^ Wade, Nicholas (9 June 2010). "Studies Show Jews' Genetic Similarity". New York Times.
^ Nebel, Almut; Filon, Dvora; Weiss, Deborah A.; Weale, Michael; Faerman, Marina; Oppenheim, Ariella; Thomas, Mark G. (2000). "High-resolution Y chromosome haplotypes of Israeli and Palestinian Arabs reveal geographic substructure and substantial overlap with haplotypes of Jews" (PDF). Human Genetics. 107 (6): 630–41. doi:10.1007/s004390000426. PMID 11153918.
^ "Jews Are The Genetic Brothers Of Palestinians, Syrians, And Lebanese". Sciencedaily.com. 9 May 2000. Retrieved 12 April 2013.
^ Atzmon, G; Hao, L; Pe'Er, I; Velez, C; Pearlman, A; Palamara, PF; Morrow, B; Friedman, E; Oddoux, C (2010). "Abraham's Children in the Genome Era: Major Jewish Diaspora Populations Comprise Distinct Genetic Clusters with Shared Middle Eastern Ancestry". American Journal of Human Genetics. 86 (6): 850–59. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.04.015. PMC 3032072 . PMID 20560205.
. PMID 20560205.
^ abc Ghazi O. Tadmouri; Konduru S. Sastry; Lotfi Chouchane (2014). "Arab gene geography: From population diversities to personalized medical genomics". Global Cardiology Science and Practice. 2014 (4): 394–408. doi:10.5339/gcsp.2014.54. PMC 4355514 . PMID 25780794. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
. PMID 25780794. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
^ Serge D. Elie, "Hadiboh: From Peripheral Village to Emerging City", Chroniques Yéménites: "In the middle, were the Arabs who originated from different parts of the mainland (e.g., prominent Mahrî tribes10, and individuals from Hadramawt, and Aden)". Footnote 10: "Their neighbors in the West scarcely regarded them as Arabs, though they themselves consider they are of the pure stock of Himyar."
^ "Arabs - Wiktionary". en.wiktionary.org.
^ ab Frishkopf, edited by Michael (2010). Music and media in the Arab world (1st ed.). Cairo: The American University in Cairo Press. ISBN 9774162935. CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ Bureš, Jaroslav (2008). Main characteristic and development trends of migration in the Arab world. Prague: Institute of International Relations. ISBN 8086506711.
^ Myers, E. A. (2010-02-11). The Ituraeans and the Roman Near East: Reassessing the Sources. Cambridge University Press. p. 18. ISBN 9781139484817.
^
Bowman, Alan K.; Champlin, Edward; Lintott, Andrew (1996-02-08). The Cambridge Ancient History. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521264303.
Jan, Retsö,. "Arabs (historical)".
"The origin of the word "Arab"". Ismaili.net. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^
"LAKHMIDS – Encyclopaedia Iranica". Iranicaonline.org. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
Bowersock, G.W.; Brown, Peter; editors, Oleg Grabar, (1999). Late antiquity : a guide to the postclassical world (2. print. ed.). Cambridge, Mass.: Belknap Press of Harvard Univ. Press. ISBN 0674511735.
Cameron, Averil (2015-04-29). The Mediterranean World in Late Antiquity: AD 395–700. Routledge. ISBN 9781136673054.
^ Fredrick E. Greenspahn (2005). "Ishmael". In Lindsay Jones. Encyclopedia of Religion. 7. Macmillan Reference USA. pp. 4551–4552. ISBN 9780028657400.ISHMAEL, or, in Hebrew, Yishmaʿeʾl; eldest son of Abraham. Ishmael's mother was Hagar, an Egyptian slave girl whom Sarah gave to Abraham because of her own infertility; in accordance with Mesopotamian law, the offspring of such a union would be credited to Sarah (Gn. 16:2). The name Yishmaʿeʾl is known from various ancient Semitic cultures and means "God has hearkened," suggesting that a child so named was regarded as the fulfillment of a divine promise. Ishmael was circumcised at the age of thirteen by Abraham and expelled with his mother at the instigation of Sarah, who wanted to ensure that Isaac would be Abraham's heir (Gn. 21). In the New Testament, Paul uses this incident to symbolize the relationship between Judaism, the older but now rejected tradition, and Christianity (Gal. 4:21–31). In the Genesis account, God blessed Ishmael, promising that he would be the founder of a great nation and a "wild ass of a man" always at odds with others (Gn. 16:12). He is credited with twelve sons, described as "princes according to their tribes" (Gn. 25:16), representing perhaps an ancient confederacy. The Ishmaelites, vagrant traders closely related to the Midianites, were apparently regarded as his descendants. The fact that Ishmael's wife and mother are both said to have been Egyptian suggests close ties between the Ishmaelites and Egypt. According to Genesis 25:17, Ishmael lived to the age of 137. Islamic tradition tends to ascribe a larger role to Ishmael than does the Bible. He is considered a prophet and, according to certain theologians, the offspring whom Abraham was commanded to sacrifice (although surah Judaism has generally regarded him as wicked, although repentance is also ascribed to him. According to some rabbinic traditions, his two wives were Aisha and Fatima, whose names are the same as those of Muhammad's wife and daughter Both Judaism and Islam see him as the ancestor of Arab peoples. Bibliography A survey of the Bible's patriarchal narratives can be found in Nahum M. Sarna's Understanding Genesis (New York, 1966). Postbiblical traditions, with reference to Christian and Islamic views, are collected in Louis Ginzberg's exhaustive Legends of the Jews, 2d ed., 2 vols., translated by Henrietta Szold and Paul Radin (Philadelphia, 2003). Frederick E. Greenspahn (1987 and 2005)
Noegel, Scott B.; Wheeler, Brannon M. (2010-04-01). The A to Z of Prophets in Islam and Judaism. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 9781461718956. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
"Ishmael and Isaac". Therefinersfire.org. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Inc, Encyclopædia Britannica (2012-01-01). Britannica Student Encyclopedia (A-Z Set). Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. ISBN 9781615355570.
^
MacArthur, John F. (2001-12-15). Terrorism, Jihad, and the Bible. Thomas Nelson Inc. ISBN 9781418518974.
^
"Arab people". Encyclopædia Britannica.
Grant, Christina Phelps (2003). The Syrian desert : caravans, travel and exploration. Hoboken: Taylor and Francis. ISBN 1136192719.
"The Nomadic Tribes of Arabia". Boundless. 2 October 2016.
electricpulp.com. "ʿARAB i. Arabs and Iran (pre-Islamic) – Encyclopaedia Iranica". Iranicaonline.org. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
^
Ruthven, Albert Hourani ; with a new afterword by Malise (2010). A history of the Arab peoples (1st Harvard Press pbk. ed.). Cambridge, Mass.: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0674058194.
"HISTORY OF MIGRATION". Historyworld.net. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
"Untitled Document". people.umass.edu. Archived from the original on 3 September 2016.
"History of the Arabs (book)". Historyworld.net. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
Bernard Ellis Lewis, Buntzie Ellis Churchill (2008). Islam: The Religion and the People. Pearson Prentice Hall. p. 137. Retrieved 21 August 2017.At the time of the Prophet's birth and mission, the Arabic language was more or less confined to Arabia, a land of deserts, sprinkled with oases. Surrounding it on land on every side were the two rival empires of Persia and Byzantium. The countries of what now make up the Arab world were divided between the two of them—Iraq under Persian rule, Syria, Palestine, and North Africa part of the Byzantine Empire. They spoke a variety of different languages and were for the most part Christians, with some Jewish minorities. Their Arabization and Islamization took place with the vast expansion of Islam in the decades and centuries following the death of the Prophet in 632 CE. The Aramaic language, once dominant in the Fertile Crescent, survives in only a few remote villages and in the rituals of the Eastern churches. Coptic, the language of Christian Egypt before the Arab conquest, has been entirely replaced by Arabic except in the church liturgy. Some earlier languages have survived, notably Kurdish in Southwest Asia and Berber in North Africa, but Arabic, in one form or another, has in effect become the language of everyday speech as well as of government, commerce, and culture in what has come to be known as "the Arab world."
CS1 maint: Uses authors parameter (link)
^
"Islam, The Arab Empire Of The Umayyads". history-world.org.
"The Arab Empire | Mohammed | Umayyad Empire History". Historybits.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
"Top 10 Greatest Empires In History". Listverse. 22 June 2010.
Pillalamarri, Akhilesh. "The 5 Most Powerful Empires in History". The National Interest.
"10 Greatest Empires in the History of World". Top Ten Lists. 24 March 2010.
^
Page 8 – The Arab Revolt, 1916–18 Published by New Zealand History at nzhistory.net.nz- Sean McMeekin (2012) The Berlin–Baghdad Express. Belknap Press. ISBN 0674064321. pp. 288, 297
^
L., Rogan, Eugene (1 January 2004). Frontiers of the state in the late Ottoman Empire : Transjordan, 1850–1921. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521892236. OCLC 826413749.- Schsenwald, William L. "The Vilayet of Syria, 1901–1914: A Re-Examination of Diplomatic Documents As Sources." Middle East Journal (1968), Vol 22, No. 1, Winter: p. 73.
^ Arab League formed — History.com This Day in History — 3/22/1945. History.com. Retrieved on 28 April 2014.
^
MacDonald, Robert W. (2015-12-08). The League of Arab States: A Study in Dynamics of Regional Organization. Princeton University Press. ISBN 9781400875283.
"Arab League from The Columbia Encyclopedia, 6th ed". Questia.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ *Kjeilen, Tore. "Arabs – LookLex Encyclopaedia". looklex.com.
"Who is an Arab?". al-bab.com.
Francis M. Deng (1 October 2011). War of Visions: Conflict of Identities in the Sudan. Brookings Institution Press. p. 405. ISBN 978-0-8157-2369-1.
^
"Culture and Tradition in the Arab Countries". Habiba.org. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
"Arabic Culture & Traditions – Online Resources | Pimsleur Approach™". Pimsleurapproach.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
El-Shamy, Hasan M. (1995). Folk traditions of the Arab world : a guide to motif classification (1. [Dr.]. ed.). Bloomington u.a.: Indiana Univ. Press. ISBN 0253352223.
^ abc
Jonathan Porter Berkey (2003). The Formation of Islam: Religion and Society in the Near East, 600–1800. Cambridge University Press. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-521-58813-3.
Robinson, Neal (2013). Islam: A Concise Introduction. Routledge. ISBN 9781136817731.
^ "Religious Diversity Around The World – Pew Research Center". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. 4 April 2014.
^
Phares, Walid (2001). "Arab Christians: An Introduction". Arabic Bible Outreach Ministry.
"Majority and Minorities in the Arab World: The Lack of a Unifying Narrative". Jerusalem Center For Public Affairs.
^
"Arab Civilization". Alhewar.org. Retrieved 1 November 2017.- Studies in the History of the Near East - Page 28 113627331X P.M. Holt - 2013 "He held the post until his death in 1624 and was succeeded by his former pupil, James Golius (1596–1667). Erpenius and Golius made outstanding contributions to the development of Arabic studies by their teaching, their preparation of texts, ..."
^
"Experience Arab Hospitality in the Middle East – Engaging Cultures". engagingcultures.com. Retrieved 1 November 2017.
Arab, The New. "Iraqis and Arabs are the world's 'most generous'". alaraby. Retrieved 1 November 2017.
^
ArabiCare. "ArabiCare - Values & Beliefs". Arabicare.org.au. Retrieved 1 November 2017.
"Understanding Arabic Culture". Feerepublic.com. Retrieved 1 November 2017.
^ ab Retsö, Jan (2003). The Arabs in Antiquity: Their History from the Assyrians to the Umayyads. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-7007-1679-1. , pages 105, 119, 125–127.
^ Hans Wehr & J M. Cowan. A dictionary of modern written Arabic. Third Edition. Ithaca, N.Y.: Spoken Language Services. p. 601.
^ William Bowden; Luke Lavan; Carlos Machado (2004). Recent Research on the Late Antique Countryside. Brill. p. 91.
^ Ira M. Lapidus (2014). A History of Islamic Societies. Cambridge University Press. p. 29.
^ Salles, Jean-François; Healey, J. F. (22 December 2015). "Arabs". doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780199381135.001.0001/acrefore-9780199381135-e-644 (inactive 2018-06-03).
^ The meaning of Arab land in the historical sources Archived 15 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Quran 34:15–17
^ "Saba / Sa'abia / Sheba". The History Files (http://www.historyfiles.co.uk). Retrieved 2008-06-27.The kingdom of Saba is known to have existed in the region of Yemen. By 1000 BC caravan trains of camels journeyed from Oman in south-east Arabia to the Mediterranean. As the camel drivers passed through the deserts of Yemen, experts believe that many of them would have called in at Ma'rib. Dating from at least 1050 BC, and now barren and dry, Ma'rib was then a lush oasis teeming with palm trees and exotic plants. Ideally placed, it was situated on the trade routes and with a unique dam of vast proportions. It was also one of only two main sources of frankincense (the other being East Africa), so Saba had a virtual monopoly. Ma'rib's wealth accumulated to such an extent that the city became a byword for riches beyond belief throughout the Arab world. Its people, the Sabeans - a group whose name bears the same etymological root as Saba - lived in South Arabia between the tenth and sixth centuries BC. Their main temple - Mahram Bilqis, or temple of the moon god (situated about three miles (5 km) from the capital city of Ma'rib) - was so famous that it remained sacred even after the collapse of the Sabean civilisation in the sixth century BC - caused by the rerouting of the spice trail. By that point the dam, now in a poor state of repair, was finally breached. The irrigation system was lost, the people abandoned the site within a year or so, and the temple fell into disrepair and was eventually covered by sand. Saba was known by the Hebrews as Sheba [Note that the collapse of the dam was actually in 575 CE, as shown in the timeline in the same article in the History Files, and attested by MacCulloch (2009)].
^- Both Judaism and Islam see him as the ancestor of Arab peoples. Jones, Lindsay (2005). Encyclopedia of religion. Macmillan Reference USA. ISBN 9780028657400.
- Ishmael is recognized by Muslims as the ancestor of several prominent Arab tribes and being the forefather of Muhammad. A–Z of Prophets in Islam and Judaism, Wheeler, Ishmael Muslims also believe that Muhammad was the descendant of Ishmael that would establish a great nation, as promised by God in the Old Testament.*Genesis 17:20Zeep, Ira G. (2000). A Muslim primer: beginner's guide to Islam, Volume 2. University of Arkansas Press. p. 5. ISBN 978-1-55728-595-9.
- Ishmael was considered the ancestor of the Northern Arabs and Muhammad was linked to him through the lineage of the patriarch Adnan. Ishmael may also have been the ancestor of the Southern Arabs through his descendant Qahtan.
- "Zayd ibn Amr" was another Pre-Islamic figure who refused idolatry and preached monotheism, claiming it was the original belief of their [Arabs] father Ishmael. *The Beginning and the End by Ibn Kathir – Vol. 3, p. 323 The History by Ibn Khaldun, Vol, 2, p. 4
- The tribes of Central West Arabia called themselves the "people of Abraham and the offspring of Ishmael". The Signs of Prophethood, Section 18, page 215."Signs of Prophethood in the Noble Life of Prophet Muhammad (part 1 of 2): Prophet Muhammad's Early Life – The Religion of Islam". Islamreligion.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- Gibb, Hamilton A.R. and Kramers, J.H. (1965) Shorter Encyclopedia of Islam. Ithaca:Cornell University Press. pp. 191–98
Maalouf, Tony. Arabs in the Shadow of Israel: The Unfolding of God's Prophetic Plan for Ishmael's Line. Kregel Academic. ISBN 9780825493638.
Urbain, Olivier (2008). Music and Conflict Transformation: Harmonies and Dissonances in Geopolitics. I.B.Tauris. ISBN 9781845115289.
- Both Judaism and Islam see him as the ancestor of Arab peoples. Jones, Lindsay (2005). Encyclopedia of religion. Macmillan Reference USA. ISBN 9780028657400.
^ Delitzsche (1912). Assyriesche Lesestuche. Leipzig. OCLC 2008786.
^ Montgomry (1934). Arabia and the Bible. Philadelphia: U of Pennsylvania. OCLC 639516.
^ Winnet (1970). Ancient Records from North Arabia. pp. 51, 52. OCLC 79767.king of kedar (Qedarites) is named alternatively as king of Ishmaelites and king of Arabs in Assyrian Inscriptions
^ Stetkevychc (2000). Muhammad and the Golden Bough. Indiana University Press. ISBN 0253332087.Assyrian records document Ishmaelites as Qedarites and as Arabs
^ Hamilton, Victor P. (1990). The book of Genesis ([Nachdr.] ed.). Grand Rapids, Mich.: William B. Eerdmans. ISBN 0802823092.
^ "PastPerfect Online". arabamerican.pastperfect-online.com.
^ "Levity.com, Islam". Levity.com. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
^ "Eyewitnesstohistory". Eyewitnesstohistory.com. Archived from the original on 2 April 2010. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
^ Bryce 2014, p. 278.
^ Bryce 2014, p. 359.
^ Burns 2007, p. 99.
^ ab Speake 1996, p. 568.
^ Le Strange 1890, p. 36.
^ ab Hillenbrand 1999, p. 87.
^ ab Bacharach 1996, p. 31.
^ Grabar et al. 1978, p. 156.
^ Hawting 1991, p. 624.
^ Cobb 2001, p. 73.
^ Cobb 2001, p. 47.
^ ab Cobb 2001, p. 48.
^ "Dionysius Periegetes". Cartographic-images.net. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Harold Bailey The Cambridge history of Iran: The Seleucid, Parthian and Sasanian periods, Volume 1, Cambridge University Press, 1983, ISBN 0-521-20092-X p. 59
^ Clifford Edmund Bosworth Historic cities of the Islamic world, Brill, Leyde, 2007, ISBN 90-04-15388-8 p. 264
^ ab Lunde, Paul (2002). Islam. New York: Dorling Kindersley Publishing. pp. 50–52. ISBN 0-7894-8797-7.
^ John Joseph Saunders, A history of medieval Islam, Routledge, 1965, page 13
^ Vartan Gregorian, "Islam: A Mosaic, Not a Monolith", Brookings Institution Press, 2003, pg 26–38 ISBN 0-8157-3283-X
^ Shorter Shi'ite Encyclopaedia, By: Hasan al-Amin, "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 June 2010. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
^ Shillington, Kevin (4 July 2013). Encyclopedia of African History 3-Volume Set. Routledge. p. 668. ISBN 9781135456702.
^ Joris, Pierre; Tengour, Habib (2012). Poems for the Millennium, Volume Four: The University of California Book of North African Literature. Univ of California Press. p. 42. ISBN 9780520269132.
^ Choueiri, pp.166–168.
^ Ori Stendel (1996). The Arabs in Israel. Sussex Academic Press. p. 45. ISBN 1898723249. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
^ Mohammad Hassan Khalil (2013-01-31). Between Heaven and Hell: Islam, Salvation, and the Fate of Others. Oxford University Press. p. 297. ISBN 9780199945412. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
^ Parolin, Gianluca Paolo (2009). Citizenship in the Arab World: Kin, Religion and Nation-state. Amsterdam University Press. ISBN 9789089640451.
^ Bowman, Alan; Garnsey, Peter; Cameron, Averil (2005). The Cambridge Ancient History: Volume 12, The Crisis of Empire, AD 193-337. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521301992.
^ Bowman, Alan; Garnsey, Peter; Cameron, Averil (2005). The Cambridge Ancient History: Volume 12, The Crisis of Empire, AD 193-337. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521301992.
^ Bowman, Alan; Garnsey, Peter; Cameron, Averil (2005). The Cambridge Ancient History: Volume 12, The Crisis of Empire, AD 193-337. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521301992.
^ https://books.google.fr/books?id=XjxyBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA13&lpg=PA13&dq=arabs+ruled+the+fertile+crescent+as+vassals+of+persians+and+romans&source=bl&ots=7uXWvm2nj4&sig=hhp8lN6ThsiKuWR7_SoAauwIUL0&hl=fr&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiA49He3pHaAhXqKcAKHfncBLEQ6AEIZjAH#v=onepage&q=arabs%20ruled%20the%20fertile%20crescent%20as%20vassals%20of%20persians%20and%20romans&f=false, « The Fertile Crescent, on the edges of northern Arabia, formed part of the frontier between the two rival empires of the day, the Sasanian (Persian) and the Byzantine (Eastern Roman). Each of which had a client or vassal state lying between itself and its rival. »
^ ab Quran 54:21–26
^ Quran 7:73–157
^ Daniel, E. L. "Arab settlements in Iran". Encyclopædia Iranica. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
^ Hugh Kennedy The Armies of the Caliphs: Military and Society in the Early Islamic State p.33 Routledge, 17 June 2013 ISBN 1134531133
^ Lowi, Miriam R., Water and power: the politics of a scarce resource in the Jordan River basin, Cambridge University Press, 1995, p.36
^ Fischbach, Michael R. (24 November 2017). "State, Society, and Land in Jordan". BRILL – via Google Books.
^ "Assessment for Palestinians in Jordan". Minorities at Risk. 2006. Archived from the original on 1 January 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
^ ab "World Directory of Minorities and Indigenous Peoples – Jordan – Palestinians". Minority Rights Group International. 2008. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
^ "Palestinians at the end of 2012" (PDF). Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics. 2009. Retrieved 22 December 2013.
^ Hall, Bruce S., A History of Race in Muslim West Africa, 1600–1960. Cambridge University Press, 2011.
^ Clio. "François Decret, Les invasions hilaliennes en Ifrîqiya – Clio – Voyage Culturel". www.clio.fr. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
^ Histoire des Berbères et des dynasties musulmanes de l'Afrique septentrionale par Ibn Khaldoun
^ "Pact of the League of Arab States, March 22, 1945". Yale Law School. Retrieved 9 July 2016.
^ "Ethnic Groups". CIA. Retrieved 10 July 2016.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Algeria". 20 March 2014. Archived from the original on 13 October 2012.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Bahrain". 23 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Comoros". 26 July 2016.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Djibouti". 23 June 2014.
^ "Egypt Population (2017)". 14 February 2017.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Iraq". 20 March 2014.
^ Ghazal, Mohammad (22 January 2016). "Population stands at around 9.5 million, including 2.9 million guests". The Jordan Times. The Jordan News. Retrieved 22 January 2016.
^ "Kuwait Population Census". 2015.
^ ab "CIA World Factbook: Lebanon". 20 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Libya". 20 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Mauritania". 20 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Morocco". 20 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Oman". 22 June 2014.
^ "Estimated Population in the Palestinian Territory Mid-Year by Governorate,1997–2016". Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics. State of Palestine. Archived from the original on 8 June 2014. Retrieved 8 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Qatar". 20 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Saudi Arabia". 20 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Somalia". 23 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Sudan". 20 June 2014.
^ ab "CIA World Factbook: Syria". 20 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Tunisia". 20 June 2014. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012.
^ "CIA World Factbook: United Arab Emirates". 20 June 2014.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Yemen". 20 March 2014.
^ Intra-Regional Labour Mobility in the Arab World, International Organization for Migration (IOM) Cairo
^ "Lebanese in west Africa: Far from home". The Economist. 20 May 2011.
^ "Tenacity and risk – the Lebanese in West Africa". BBC News. 10 January 2010.
^ "Zanzibar profile". BBC News. 18 July 2012.
^ "The world's successful diasporas". Managementtoday.co.uk. 3 April 2007.
^ France's ethnic minorities: To count or not to count. The Economist (26 March 2009). Retrieved on 2013-07-12.
^ Project, Joshua. "Arab, Maghrebi in Spain". Joshuaproject.net. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Project, Joshua. "Arab, Lebanese in Spain". Joshuaproject.net. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "¿Cuántos musulmanes hay en España?". Islamhoy.com. 4 December 2013. Archived from the original on 9 June 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ varios, EDICIONES EL PAIS, S.L., Miguel Ángel Medina,. "Los musulmanes son el 3,6% de la población en España (1,7 millones)". Blogs.elpais.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "Los musulmanes en España superan los 1,8 millones". Europapress.es. 30 March 2015. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "La cifra de musulmanes en España alcanza los 1,6 millones, de los que casi un tercio viven en Cataluña". Alertadigital.com. 9 October 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "spanish property". Villa.spain-property-costa-blanca.com. Archived from the original on 29 November 2017. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "Arab Influences on Spanish Language and Culture | don Quijote". donQuijote.
^ "BBC – Religions – Islam: Muslim Spain (711–1492)".
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 30 December 2013. Retrieved 27 September 2014.
^ "REPORT ON THE 2011 CENSUS – MAY 2013 – Arabs and Arab League Population in the UK". National Association of British Arabs. Archived from the original on 8 October 2014. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
^ "British Arabs". Naba.org.uk. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "Refugees, migrants reach 54,574 in Greece on Wednesday". Kathimerini. 19 May 2016. Retrieved 19 May 2016.
^ Hannes Kniffka (June 1995). Elements of culture-contrastive linguistics. P. Lang. p. 244. ISBN 978-0-8204-2927-4.
^ "People groups: Sweden". Joshua Project. Retrieved 24 October 2016.
^ "Dutch media perceived as much more biased than Arabic media – Media & Citizenship Report conducted by University of Utrecht" (PDF), Utrecht University, 10 September 2010, retrieved 29 November 2010 [permanent dead link]
^ Intra-Regional Labour Mobility in the Arab World, Facts and Figures (PDF), International Organization for Migration, 2010, retrieved 21 July 2010
^ "Turkey - Arabs". countrystudies.us.
^ Kayyali, Randa (2006). The Arab Americans. Greenwood Press. p. 26.
^ ab "Demographics – Arab American Institute". Aaiusa.org. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Kayyali, Randa (2006). The Arab Americans. Greenwood Press. p. 27.
^ Kayyali, Randa (2006). The Arab Americans. Greenwood Press. p. 35.
^ Orfalea, Gregory (2006). The Arab Americans: A History. Olive Branch Press. p. 189.
^ ab "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 July 2011. Retrieved 7 July 2011. Arab American Population Highlights Arab American Institute Foundation
^ de la Cruz, G. Patricia; Angela Brittingham (December 2003). "The Arab Population: 2000" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 17 October 2016.
^ "American FactFinder – Results". US Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 18 March 2015. [dead link]
^ "The Arab Community in Canada". Statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "Home". Canadians of Arab Origin – Who are they?. 12 March 2015.
^ Isaura Daniel (25 March 2013). "Os planos de Michel Temer para o mundo árabe". Agência de Notícias Brasil-Árabe. Archived from the original on 1 July 2016. Retrieved 26 April 2016.
^ "Conciliador, 'charmosão' e 'mordomo de filme de consternação': afinal, quem é Michel Temer". Entretenimento bit. 30 March 2016. Retrieved 26 April 2016.
^ Diogo Bercito (14 June 2015). "Origem de políticos brasileiros, Líbano tem rua com nome de Michel Temer". Folha de S. Paulo. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
^ "Out of MENA: Nine cities the Arab Diaspora calls home". Al Bawaba. 8 May 2015.
^ "Articles: The Arabs of South America". Americanthinker.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "Arab roots grow deep in Brazil's rich melting pot". Washington Times. Retrieved 17 April 2016.
^ "Origem e destino dos imigrantes do Levante". ibge. Retrieved 11 April 2016.
^ ab "Lebanese Republic". Itamaraty.gov.br. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "Lebanon: Geography". Embassy of Lebanon in Brazil (in Portuguese). 1996. Archived from the original on 29 May 2008.
^ IBGE. IBGE: Características Étnico-Raciais da População.
^ "The Arabs of Brazil". Saudi Aramco World. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
^ "Sleiman meets Brazilian counterpart, Lebanese community". The Daily Star. 23 April 2010.
^ "O Líbano: Geografia" [Lebanon: Geography] (in Portuguese). Lebanese Embassy in Brazil. 1996. Archived from the original on 12 November 2010.
^ "Estadão de Hoje". Estadao.com.br. Archived from the original on 1 January 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
^ "Inmigración sirio-libanesa en Argentina" [Syrian-Lebanese immigration in Argentina] (in Spanish). Fearab.org.ar. Archived from the original on 20 June 2010. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
^ "Sirios, turcos y libaneses" [Syrians, Turks and Lebanese] (in Spanish). oni.escuelas.edu.ar. Archived from the original on 11 December 2008.
^ "Mapping the Global Muslim Population: A Report on the Size and Distribution of the World's Muslim Population" (PDF). Pew Research Center. October 2009. p. 24. Retrieved 4 November 2016.
^ Barros, Carolina (23 August 2012). "Argentina's Syrians". www.buenosairesherald.com. Retrieved 4 November 2016.
^ http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2013/09/15/abdel-el-zabayar-from-parliament-to-the-frontlines.html "Venezuela, where the estimated 1.6 million people of Arab descent..."
^ Habeeb Salloum, "Arabs Making Their Mark in Latin America: Generations of Immigrants in Colombia, Venezuela and Mexico", Al Jadid, Vol. 6, no. 30 (Winter 2000).
^ "Estimación de la mortalidad, 1985–2005" [Estimation of mortality, 1985–2005] (PDF). Postcensal Studies (in Spanish). Bogotá, Colombia: DANE. March 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 November 2007. Retrieved 29 March 2016.
^ Randa Achmawi (21 July 2009). "Colombia awakens to the Arab world". Brazi-Arab News Agency. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved 22 September 2015.
^ "Proyecciones nacionales y departamentales de población. 2006–2020" [National and departmental population projections. 2006–2020] (PDF) (in Spanish). DANE National Statistical Service, Columbia. September 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 November 2007. Retrieved 22 September 2015.
^ S.A., Diario La Nación – Comunicaciones Lanet. " Zalaquett pone a Chile como modelo de convivencia palestino-judía". La Nación. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016.
^ "Arabs In The Andes? Chile, The Unlikely Long-Term Home Of A Large Palestinian Community". International Business Times. 31 October 2013.
^ Arab and Jewish immigrants in Latin America: images and realities, by Ignacio Klich, Jeff Lesser, 1998, p. 165.
^ Nemy, Enid (14 September 1969). "In Santiago Society, No One Cares If Your Name Is Carey or de Yrarrazaval". New York Times.
^ "The Arabs of Honduras". Saudiaramcoworld.com. 27 June 1936. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
^ "Chile: Palestinian refugees arrive to warm welcome". Adnkronos.com. 7 April 2003. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
^ "500,000 descendientes de primera y segunda generación de palestinos en Chile". Laventana.casa.cult.cu. Archived from the original on 22 July 2009. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
^ abc "From Lebanon to Haiti: A Story Going Back to the 19th Century". Retrieved 30 January 2014.
^ Genko, A. The Arabic Language and Caucasian Studies. USSR Academy of Sciences Publ. Moscow-Leningrad. 8–109
^ ab Zelkina, Anna. Arabic as a Minority Language. Walter de Gruyter, 2000; ISBN 3-11-016578-3 p. 101
^ Baynes, Thomas Spencer (ed). "Transcaucasia." Encyclopædia Britannica. 1888. p. 514
^ Golestan-i Iram by Abbasgulu Bakikhanov. Translated by Ziya Bunyadov. Baku: 1991, p. 21
^ Seferbekov, Ruslan. Characters Персонажи традиционных религиозных представлений азербайджанцев Табасарана. Archived 16 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Stephen Adolphe Wurm et al. Atlas of languages of intercultural communication. Walter de Gruyter, 1996; p. 966
^ History of Ibn Khaldun
^ Arabic As a Minority Language By Jonathan Owens, pg. 184
^ People of India: Vol. XIII: Andhra Pradesh (3 Parts-Set)Edited by D.L. Prasada Rao, N.V.K. Rao and S. Yaseen Saheb, Affiliated East-West Press
^ People of India: Volume XXII: Gujarat (3 Parts-Set): Edited by R.B. Lal, P.B.S.V. Padmanabham, Gopal Krishan and Md. Azeez Mohidden, Popular Prakashan for ASI, 2003.
^ Muslim society in transition Javed, Arifa Kulsoom ISBN 81-7169-096-3
^ Frontiers of embedded Muslim communities in India / editor, Vinod K. Jairath ISBN 9780415668880
^ Muslim caste in Uttar Pradesh: (a study of culture contact) by Ansari, G, (Ghaus)
^ Shahab, Alwi (21 January 1996). "Komunitas Arab Di Pekojan Dan Krukut: Dari Mayoritas Menjadi Minoritas" (in Indonesian). Archived from the original on 9 August 2008. Retrieved 19 April 2015.
^ ab Cribb & Kahin 2004, pp. 18–19.
^ "A2 : Population by ethnic group according to districts, 2012". Census of Population & Housing, 2011. Department of Census & Statistics, Sri Lanka.
^ "Race in Sri Lanka What Genetic evidence tells us". Retrieved 20 July 2014.
^ de Munck, Victor (2005). "Islamic Orthodoxy and Sufism in Sri Lanka". Anthropos: 401–414 [403]. JSTOR 40466546.
^ Mahroof, M. M. M. "Spoken Tamil Dialects Of The Muslims Of Sri Lanka: Language As Identity-Classifier". Islamic Studies. 34 (4): 407–426 [408]. JSTOR 20836916.
^ Romero, Patricia W. (1997). Lamu. Markus Wiener. p. 7. ISBN 1558761063. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
^ Gunnar M Ahmad Abdel Ghaffar Muhammad Chr Michelsens Institutt (2013). Sudan Divided: Continuing Conflict in a Contested State. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 90. ISBN 1137338245. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
^ "Ivory Coast – The Levantine Community". Countrystudies.us. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
^ Lebanese Immigrants Boost West African Commerce, By Naomi Schwarz, voanews.com, 10 July 2007
^ Lebanese man shot dead in Nigeria, BBC News
^ Joshua Project. "Sayyid Ethnic People in all Countries". Joshua Project. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
^ African Union Summit Archived 7 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Randall, Colin (19 November 2004). "The night westerners were hunted for being white". London: The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 26 June 2009.
^ Handloff, Robert E., ed. (1988). "The Levantine Community". Ivory Coast: A Country Study. Country Studies. Washington, DC: GPO for the Library of Congress.
^ https://joshuaproject.net/countries/CD, cumulative total of Arab communities
^ Project, Joshua. "Baggara, Shuwa Arab - Joshua Project". joshuaproject.net. Archived from the original on 20 November 2017.
^ "Niger's Arabs to fight expulsion". News.bbc.co.uk. 25 October 2006. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Baggara of Sudan: Culture and Environment – Culture, Traditions and Livelihood by Biraima M Adam
^ ab See, for example:
Ori Stendel (1996). The Arabs in Israel. Sussex Academic Press. p. 45. ISBN 1898723249. Retrieved 4 March 2014.
Mohammad Hassan Khalil (2013-01-31). Between Heaven and Hell: Islam, Salvation, and the Fate of Others. Oxford University Press. p. 297. ISBN 9780199945412. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
^ United Networks. "CHRISTIANS (in the Arab world)". Medea.be. Archived from the original on 11 June 2010. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
^ The Bahá'í World Centre: Focal Point for a Global Community, The Bahá'í International Community, archived from the original on 29 June 2007, retrieved 2 July 2007
^ "Shishakli and the Druzes: Integration and Intransigence"
^ "Is Hubal The Same As Allah?". Islamic-awareness.org. Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
^ Dictionary of Ancient Deities. Oxford University Press. 2001. ISBN 0-19-514504-6.
^ "From Marib The Sabean Capital To Carantania". Buzzle.com. Archived from the original on 16 March 2009. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
^ Msn Encarta entry on Himyarites. Archived from the original on 31 October 2009.
^ "History of Islam". Mnsu.edu. 6 January 2009. Archived from the original on 31 May 2010. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
^ "Encyclopedia of Politics and Religion". Cqpress.com. Archived from the original on 28 April 2010. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
^ Lionel Beehner. "Shia Muslims in the Mideast". Cfr.org. Archived from the original on 11 April 2010. Retrieved 13 April 2010.
^ Kamal S. Salibi (2003). A House of Many Mansions: The History of Lebanon Reconsidered (illustrated, reprint, revised ed.). I.B.Tauris. p. 88. ISBN 9781860649127.
^ Andrea Pacini, ed. (1998). Christian Communities in the Middle East. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-829388-7.
^ "CIA World Factbook: Gaza Strip". 3 November 2013.
^ "CIA World Factbook: West Bank". 3 November 2013.
^ Arab Christians – Who are they?. Arabicbible.com. Retrieved on 3 January 2011.
^ "CIA The World Factbook – Israel". Cia.gov. Archived from the original on 29 June 2011. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
^ "CIA The World Factbook – Jordan". Cia.gov. Archived from the original on 29 June 2011. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
^ "The Arab American Institute | Arab Americans". Aaiusa.org. Archived from the original on 3 April 2010. Retrieved 10 March 2010.
^ Mgaloblishvili, Tamila (1998). Ancient Christianity in the Caucasus. Routledge. p. 272. ISBN 0-7007-0633-X.
^ Doris., Behrens-Abouseif, (1 January 1999). Beauty in Arabic culture. Markus Wiener Publishers. ISBN 1558761993. OCLC 40043536.
^ "ARAB CUSTOMS AND CULTURE". webcache.googleusercontent.com. Archived from the original on 18 August 2016. CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
^ "Al-Jallad. The earliest stages of Arabic and its linguistic classification (Routledge Handbook of Arabic Linguistics, forthcoming)". Academia.edu. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
^ "Executive Summary". Future of the Global Muslim Population. Pew Research Center. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
^ "Table: Muslim Population by Country | Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project". Features.pewforum.org. 27 January 2011. Retrieved 18 May 2014.
^ "UN official languages". Un.org. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
^ "Executive Summary". Future of the Global Muslim Population. Pew Research Center. Retrieved 22 December 2011.
^ "Table: Muslim Population by Country | Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project". Features.pewforum.org. 27 January 2011. Retrieved 18 May 2014.
^ Bin-Muqbil 2006, p. 14.
^ "Arabs facts, information, pictures | Encyclopedia.com articles about Arabs". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Arabic culture : mosque, arabesque, arabian mythology, islamic philosophy, arabian horse,. [S.l.]: University-Press Org. 2013. ISBN 1230559965.
^ Stetkevych, Jaroslav (2000). Muhammad and the Golden Bough: Reconstructing Arabian Myth. Indiana University Press. ISBN 0253214130.
^ Wikipedia, Source: (2011). Arabian Mythology, Noah's Ark, Hafaza, Jesus, Khidr, Dhul-Qarnayn, Isra and Mi'raj, Luqman, Devil, Throne of God. General Books. ISBN 9781233180516.
^ Leeming, David (2004). Jealous Gods and Chosen People: The Mythology of the Middle East. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195348996.
^ "jinni | Arabian mythology". Encyclopedia Britannica.
^ Benjamin W. McCraw, Philosophical Approaches to Demonology Robert Arp Routledge 2017 ISBN 978-1-315-46675-0
^ Qur'ān 55:15
^ Amira El-Zein Islam, Arabs, and Intelligent World of the Jinn Syracuse University Press 2009 ISBN 9780815650706 page 19
^ "The Story of Sidi-Nouman". Retrieved 5 July 2012.
^ "Ghoul Facts, information, pictures | Encyclopedia.com articles about Ghoul". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 23 March 2011.
^ "ghoul | Arabian mythology". Encyclopedia Britannica.
^ "ghoul". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 22 January 2006.
^ Adamec, Ludwig W. (2009). The A to Z of Islam Volume 123 of The A to Z Guide Series. Scarecrow. pp. 165–166. ISBN 1461671930. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
^ Shawqi Daif, Introduction to Ibn Mada's Refutation of the Grammarians, pg. 48. Cairo, 1947.
^ "Arabic literature". Encyclopædia Britannica.
^ "Literature". Library.cornell.edu. Archived from the original on 2 January 2017.
^ Sawa, George Dimitri (2016). Erotica, Love and Humor in Arabia : Spicy Stories from The Book of Songs by al-Isfahani. McFarland & Company. p. 2. ISBN 9781476663654.
^ "Arabic literature". Infoplease.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Allen, edited by Roger; Richards, D.S. (2006). Arabic literature in the post-classical period (1st ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139053990. CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ Irwin, edited by Robert (2002). Night and horses and the desert : an anthology of classical Arabic literature (1st Anchor Books ed.). New York: Anchor Books. ISBN 978-0385721554. CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ "Islamic History in Arabia and Middle East". Islamicity.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "Arabic Literature". Indigenouspeople.net. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Gelder, Geert Jan Van (1 January 2012). "Classical Arabic Literature". NYU Press.
^ "Arabian literature". Slideshare.net. 17 September 2013.
^ Badawi, ed. by M.M. (1992). Modern Arabic literature (1. publ. ed.). Cambridge [u.a.]: Cambridge Univ. Press. ISBN 0521331978. CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ Cachia, Pierre (2002). Arabic literature : an overview (1. publ. ed.). New York: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 0700717250.
^ Flandrin, under the direction of Jean-Louis; al.], Massimo Montanari ; English edition by Albert Sonnenfeld ; translated by Clarissa Botsford ... et (1999). Food : a culinary history from Antiquity to the present (English ed.). New York: Penguin Books. ISBN 0-231-11154-1.
^ ab "Food and recipes". al-bab.com.
^ "Arabic Cuisine". Canadianarabcommunity.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ d?Avennes, Prisse (1 January 1978). Arabic Art in Color. Courier Corporation. ISBN 9780486236582.
^ 1807–1879., Prisse d'Avennes, (1 January 2007). Arabic art : after monuments in Cairo. L'Aventurine. ISBN 2914199600. OCLC 216662541.
^ "A Brief History on Arabic Art: Different Forms of Arabic Artworks Outlined". Bright Hub Education.
^ Fleming, John; Honour, Hugh (1977). Dictionary of the Decorative Arts. Penguin. ISBN 978-0-670-82047-4.
^ Rawson, 236
^ Robinson, Francis (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the Islamic World. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-66993-1.
^ "Khan Academy". Khan Academy.
^ Krautheimer, Richard. Early Christian and Byzantine Architecture Yale University Press Pelican History of Art, Penguin Books Ltd., 1965, p. 285.
^ Fletcher, Banister A History of Architecture on the Comparative Method 4th Edition, London, p. 476.
^ Copplestone, p.149
^ A Tour of Architecture in Islamic Cities Archived 17 March 2007 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Habib Hassan Touma – Review of Das arabische Tonsystem im Mittelalter by Liberty Manik[full citation needed].
^ abc Singing in the Jahili period – khaledtrm.net (in Arabic)
^ Smith, Douglas Alton (2002). A History of the Lute from Antiquity to the Renaissance. ISBN 0-9714071-0-X.
^ "Asian Music Tribal Music of India, 32, 1, Fall, 2000/ Winter, 2001". Web.archive.org. 20 December 2008. Archived from the original on 20 December 2008. Retrieved 18 December 2017. CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
^ Farmer 1988, p. 137
^ Farmer 1988, p. 140
^ Farmer 1988, pp. 140–41
^ Farmer 1988, p. 141
^ Farmer 1988, p. 142
^ Farmer 1988, p. 143
^ Farmer 1988, p. 144
^ O'Connor, Tom. "Lydia Canaan One Step Closer to Rock n' Roll Hall of Fame", The Daily Star, Beirut, 27 April 2016.
^ Justin Salhani, The Daily Star, 17 November 2014
^ David Livingstone, Campus, No. 8, p. 2, February 1997
^ Wafik Ajouz, Cedar Wings, No. 28, p. 2, July–August 1995
^ Youmna Aschkar, Eco News, No. 77, p. 2, 20 January 1997
^ George Hayek, Al-Hayat, No. 12,513, 3 June 1997
^ Mireille Khalife, Al-Hayat, Issue No. 13,732, 16 October 2000
^ "Lydia Canaan Receiving Lebanese International Success Award". A1-images.myspacecdn.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Neal Robinson (5 November 2013). Islam: A Concise Introduction. Routledge. p. 75. ISBN 978-1-136-81773-1.
^ Francis E. Peters (1994). Muhammad and the Origins of Islam. SUNY Press. p. 110. ISBN 978-0-7914-1875-8.
^ Daniel C. Peterson (26 February 2007). Muhammad, Prophet of God. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-8028-0754-0.
^ Karen Armstrong (2000). Islam: A Short History. p. 11. ISBN 0-8129-6618-X.
^ Robert G. Hoyland (11 September 2002). Arabia and the Arabs: From the Bronze Age to the Coming of Islam. Routledge. p. 139. ISBN 978-1-134-64634-0.
^ David Nicolle (20 June 2012). The Great Islamic Conquests AD 632–750. Osprey Publishing. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-78096-998-5.
^ abc Reza Aslan (2 December 2008). No God But God: The Origins, Evolution and Future of Islam. Random House. p. 6. ISBN 978-1-4070-0928-5.
^ Francis E. Peters (1994). Muhammad and the Origins of Islam. SUNY Press. p. 105. ISBN 978-0-7914-1875-8.
^ "Arabic philosophy". Encyclopædia Britannica.
^ "Arabic Philosophy – General – The Basics of Philosophy". Philosophybasics.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Street, Tony (1 January 2015). "Arabic and Islamic Philosophy of Language and Logic". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University.
^ "Arabic and Islamic Philosophy – Bibliography – PhilPapers". philpapers.org.
^ Al-Khalili, Jim (4 January 2009). "BBC News". BBC News. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
^ Falagas, Matthew E.; Zarkadoulia, Effie A.; Samonis, George (1 August 2006). "Arab science in the golden age (750–1258 CE) and today". The FASEB Journal. 20 (10): 1581–1586. doi:10.1096/fj.06-0803ufm. ISSN 0892-6638. PMID 16873881.
^ "Rediscovering Arabic Science | Muslim Heritage". Muslimheritage.com. Retrieved 18 December 2016.
^ Marshall Hodgson, The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 234.
^ Marshall Hodgson, The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 233.
^ Marshall Hodgson, The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 238.
^ ab Robinson (editor), Francis (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the Islamic World. Cambridge University Press. pp. 228–229. CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ "Arabic Sciences and Philosophy | Cambridge Core". Cambridge Core. Retrieved 18 December 2016.
^ "The Origins of Islamic Science | Muslim Heritage". Muslimheritage.com. Retrieved 18 December 2016.
^ O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Abu Abdallah Mohammad ibn Jabir Al-Battani", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews .
^ D. C. Lindberg, Theories of Vision from al-Kindi to Kepler, (Chicago, Univ. of Chicago Pr., 1976), pp. 60–7.
^ Weinberg, Steven (2015). To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern Science. Penguin Books Limited. ISBN 9780241196656.
^ Krebs, Robert E. (2004). Groundbreaking Scientific Experiments, Inventions, and Discoveries of the Middle Ages and the Renaissance. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 9780313324338.
^ Krebs, Robert E. (2004). Groundbreaking Scientific Experiments, Inventions, and Discoveries of the Middle Ages and the Renaissance. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 9780313324338.
^ Derewenda, Zygmunt S.; Derewenda, ZS (2007). "On wine, chirality and crystallography". Acta Crystallographica Section A. 64 (Pt 1): 246–258 [247]. Bibcode:2008AcCrA..64..246D. doi:10.1107/S0108767307054293. PMID 18156689.
^
John Warren (2005). "War and the Cultural Heritage of Iraq: a sadly mismanaged affair", Third World Quarterly, Volume 26, Issue 4 & 5, pp. 815–830.
^ Dr. A. Zahoor (1997), Jâbir ibn Hayyân (Geber)
^ Kahn, David (1996). The Codebreakers: The Comprehensive History of Secret Communication from Ancient Times to the Internet. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 9781439103555.Cryptology was born among the Arabs. They were the first to discover and write down the methods of cryptoanalysis.
^ Borda, Monica (2011). Fundamentals in Information Theory and Coding. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 122. ISBN 9783642203473.Al Kindi, an Arab scientist from 9th century is considered the father of cryptology, his book on this subject being, at this moment, the oldest available.
^ "Arab Code Breakers | Simon Singh". simonsingh.net.
^ Glick, Thomas F.; Livesey, Steven; Wallis, Faith (2014). Medieval Science, Technology, and Medicine: An Encyclopedia. Routledge. p. 237.
^ Kalin, Ibrahim (2014). The Oxford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Science, and Technology in Islam. Oxford University Press. p. 321.
^ Kidder, David S.; Oppenheim, Noah D. (2010). The Intellectual Devotional Biographies: Revive Your Mind, Complete Your Education, and Acquaint Yourself with the World's Greatest Personalities. Rodale. ISBN 9781605290881.
^ "Ibn an-Nafīs | Muslim physician". Encyclopedia Britannica.
^ Glick, Thomas F.; Livesey, Steven; Wallis, Faith (2014). Medieval Science, Technology, and Medicine: An Encyclopedia. Routledge. ISBN 9781135459321.
^ Akyeampong, Emmanuel Kwaku; Niven, Mr. Steven J (1970). Dictionary of African Biography. 1St- Ed.; 1970. ISBN 9780195382075.
^ "Al-Uqlidisi biography". www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk.
^ Selin, Helaine (2013). Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Westen Cultures. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 69. ISBN 9789401714167.Historian J. L. Berggren, for example, concludes that while the Hindus were the first to use a "cipherized, decimal positional system", the Arabs pioneered in extending this system to "represent parts of the unit by decimal fractions".
^ Selin, Helaine (2013). Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Westen Cultures. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9789401714167.
^ "Al-Qalasadi biography". www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk.
^ "Thabit number". planetmath.org.
^ Tonias, Elias C.; Tonias, Constantine N. (2016). Geometric Procedures for Civil Engineers. Springer. ISBN 9783319242958.
^ Ben-Menahem, Ari (2009). Historical Encyclopedia of Natural and Mathematical Sciences. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783540688310.
^ Holme, Audun (2010). Geometry: Our Cultural Heritage. Springer. p. 210. ISBN 3-642-14440-3.
^ Morris, T. J. A Paranormal History Guide. Lulu.com. ISBN 9781300192459.
^ Lorch, R. P. (1976). "The Astronomical Instruments of Jabir ibn Aflah and the Torquetum". Centaurus. 20 (1): 11–34. Bibcode:1976Cent...20...11L. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0498.1976.tb00214.x.
^ Dubey, N. B. (2009). Office Management: Developing Skills for Smooth Functioning. Global India Publications. ISBN 9789380228167.
^ May, Andrew (2017). The Telescopic Tourist's Guide to the Moon. Springer. ISBN 9783319607412.
^ "Al-Jazarī | Arab inventor". Encyclopedia Britannica.
^ "Ismaeel al-Jazari Biography (1150-1220)". www.madehow.com.
^ Rooney, Anne (2014). The Story of Physics. Arcturus Publishing. ISBN 9781784040710.
^ Physics Related to Anesthesia. PediaPress.
^ "Ibn al-Baitar - Dictionary definition of Ibn al-Baitar | Encyclopedia.com: FREE online dictionary". www.encyclopedia.com.
^ Bacharach, 2006, p. 140.
^ "Oldest university". Guinnessworldrecords.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ "Medina of Fez". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. UNESCO. Retrieved 7 April 2016.
^ Verger, Jacques: "Patterns", in: Ridder-Symoens, Hilde de (ed.): A History of the University in Europe. Vol. I: Universities in the Middle Ages, Cambridge University Press, 2003, ISBN 978-0-521-54113-8, pp. 35–76 (35)
^ Lebedel, p.113
^ "UT Austin's John B. Goodenough Wins Engineering's Highest Honor for Pioneering Lithium-Ion Battery". UT News | The University of Texas at Austin. 6 January 2014.
^ Salter, Jessica (14 November 2014). "Tony Fadell, father of the iPod, iPhone and Nest, on why he is worth $3.2bn to Google".
^ Jehad., Al-Omari, (1 January 2008). Understanding the Arab culture : a practical cross-cultural guide to working in the Arab world. How To Books. ISBN 1848036469. OCLC 408662262.
^ "Middle East Health Magazine". Middleeasthealthmag.com. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Bener A, Dafeeah EE, Samson N (2012). "Does consanguinity increase the risk of schizophrenia? Study based on primary health care centre visits". Ment Health Fam Med. 9 (4): 241–8. PMC 3721918 . PMID 24294299.
. PMID 24294299.
^ Consanguineous marriage: Keeping it in the family. Economist, 27 February 2016
^ abc "Inbreeding". As.wvu.edu. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ Surah chapter 4, verse 23
^ Al-Zahery, N; Pala, M; Battaglia, V; Grugni, V; Hamod, MA; Hooshiar Kashani, B; Olivieri, A; Torroni, A; Santachiara-Benerecetti, AS; Semino, O (4 October 2011). "In search of the genetic footprints of Sumerians: a survey of Y-chromosome and mtDNA variation in the Marsh Arabs of Iraq". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 11: 288. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-11-288. PMC 3215667 . PMID 21970613.
. PMID 21970613.
^ Regueiro; et al. (2004). "The Levantine versus the Horn of Africa:evidence for bi-directional corridors of human migrations". American Journal of Human Genetics. 74 (3): 532–44. doi:10.1086/382286. PMC 1182266 . PMID 14973781.
. PMID 14973781.
^ Cadenas at Al; Zhivotovsky, Lev A; Cavalli-Sforza, Luca L; Underhill, Peter A; Herrera, Rene J (10 October 2007). "Y-chromosome diversity characterizes the Gulf of Oman". European Journal of Human Genetics. 16 (3): 374–386. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201934. PMID 17928816.
^ "Family Tree DNA Arabian YDNA Project".
^ Černý, Viktor; et al. (2009). "Out of Arabia—the settlement of island Soqotra as revealed by mitochondrial and Y chromosome genetic diversity" (PDF). American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 138 (4): 439–447. doi:10.1002/ajpa.20960. PMID 19012329. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 20 October 2016.
^ Chiaroni; King, Roy J; Myres, Natalie M; Henn, Brenna M; Ducourneau, Axel; Mitchell, Michael J; Boetsch, Gilles; Sheikha, Issa; Lin, Alice A; Nik-Ahd, Mahnoosh; Ahmad, Jabeen; Lattanzi, Francesca; Herrera, Rene J; Ibrahim, Muntaser E; Brody, Aaron; Semino, Ornella; Kivisild, Toomas; Underhill, Peter A; et al. (14 October 2009). "The emergence of Y-chromosome haplogroup J1e among Arabic-speaking populations". European Journal of Human Genetics. 18 (3): 348–353. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2009.166. PMC 2987219 . PMID 19826455.
. PMID 19826455.
^ Hammer, MF; Behar, DM; Karafet, TM; et al. (November 2009). "Geographical distribution of J1-P58". Human Genetics. 126 (5): 707–17. doi:10.1007/s00439-009-0727-5. PMC 2771134 . PMID 19669163. CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al. (link)
. PMID 19669163. CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al. (link)
^ Hammer, Michael F.; Behar, Doron M.; Karafet, Tatiana M.; Mendez, Fernando L.; Hallmark, Brian; Erez, Tamar; Zhivotovsky, Lev A.; Rosset, Saharon; Skorecki, Karl (8 August 2009). "Extended Y chromosome haplotypes resolve multiple and unique lineages of the Jewish priesthood". Human Genetics. 126 (5): 707–717. doi:10.1007/s00439-009-0727-5. PMC 2771134 . PMID 19669163.
. PMID 19669163.
^ Semino; Magri, Chiara; Benuzzi, Giorgia; Lin, Alice A.; Al-Zahery, Nadia; Battaglia, Vincenza; MacCioni, Liliana; Triantaphyllidis, Costas; Shen, Peidong; Oefner, Peter J.; Zhivotovsky, Lev A.; King, Roy; Torroni, Antonio; Cavalli-Sforza, L. Luca; Underhill, Peter A.; Santachiara-Benerecetti, A. Silvana; et al. (1 May 2004). "Origin, Diffusion, and Differentiation of Y-Chromosome Haplogroups E and J: Inferences on the Neolithization of Europe and Later Migratory Events in the Mediterranean Area". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 74 (5): 1023–1034. doi:10.1086/386295. PMC 1181965 . PMID 15069642.
. PMID 15069642.
^ "J1-P58 contain the Arabic cluster L147.1 that contain the all J1-CMH haplotypes and is YCAII=22–22".
^ Robino, C; Crobu, F; Di Gaetano, C; Bekada, A; Benhamamouch, S; Cerutti, N; Piazza, A; Inturri, S; Torre, C (May 2008). "Analysis of Y-chromosomal SNP haplogroups and STR haplotypes in an Algerian population sample". International journal of legal medicine. 122 (3): 251–5. doi:10.1007/s00414-007-0203-5. PMID 17909833.
^ Capelli, C.; Redhead, N.; Romano, V.; Cali, F.; Lefranc, G.; Delague, V.; Megarbane, A.; Felice, A. E.; Pascali, V. L.; Neophytou, P. I.; Poulli, Z.; Novelletto, A.; Malaspina, P.; Terrenato, L.; Berebbi, A.; Fellous, M.; Thomas, M. G.; Goldstein, D. B. (1 March 2006). "Population Structure in the Mediterranean Basin: A Y Chromosome Perspective". Annals of Human Genetics. 70 (2): 207–225. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.00224.x. PMID 16626331.
^ Hayes, JM; Budowle, B; Freund, M (September 1995). "Arab population data on the PCR-based loci: HLA-DQA1, LDLR, GYPA, HBGG, D7S8, Gc, and D1S80". Journal of forensic sciences. 40 (5): 888–92. PMID 7595333.
^ Bekada, A; Fregel, R; Cabrera, VM; Larruga, JM; Pestano, J; et al. (2013). "Introducing the Algerian Mitochondrial DNA and Y-Chromosome Profiles into the North African Landscape". PLoS ONE. 8 (2): e56775. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...856775B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056775. PMC 3576335 . PMID 23431392. CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al. (link)
. PMID 23431392. CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al. (link)
^ Table S6. Y-chromosome haplogroup frequencies (%) in the studied populations. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056775.s006 (XLS)
^ ab Cinnioglu; et al. (29 October 2003). "Excavating Y-chromosome haplotype strata in Anatolia" (PDF). Human Genetics. Human Genetics. 114 (2): 127–148. doi:10.1007/s00439-003-1031-4. PMID 14586639.
^ "DNA Haplogroup Definitions – J". Rootsweb.com. Retrieved 22 April 2009.
^ "In Lebanon DNA may yet heal rifts". Reuters. 10 September 2016.
^ abcde Marc Haber; Dominique Gauguier; Sonia Youhanna; Nick Patterson; Priya Moorjani; Laura R. Botigué; Daniel E. Platt; Elizabeth Matisoo-Smith; David F. Soria-Hernanz; R. Spencer Wells; Jaume Bertranpetit; Chris Tyler-Smith; David Comas; Pierre A. Zalloua (14 October 2016). "Genome-Wide Diversity in the Levant Reveals Recent Structuring by Culture". PLOS Genetics. 9 (2): e1003316. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003316. PMC 3585000 . PMID 23468648. Retrieved 17 May 2015.
. PMID 23468648. Retrieved 17 May 2015.
^ NEBEL; et al. (1 June 2002). "Genetic Evidence for the Expansion of Arabian Tribes into the Southern Levant and North Africa". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 70 (6): 1594–1596. doi:10.1086/340669. PMC 379148 . PMID 11992266.
. PMID 11992266.
^ ab Cadenas, Alicia M; Zhivotovsky, Lev A; Cavalli-Sforza, Luca L; Underhill, Peter A; Herrera, Rene J (2007). "Y-chromosome diversity characterizes the Gulf of Oman". European Journal of Human Genetics. 16 (3): 374–86. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201934. PMID 17928816.
^ *Alshamali 2009: 81% (84/104)
−
Malouf 2008: 70% (28/40)
−
Cadenas 2008: 45/62=72.6% J-M267
−
^ Khaled K Abu-Amero; Ali Hellani; Ana M González; Jose M Larruga; Vicente M Cabrera; Peter A Underhill (2009). "Saudi Arabian Y-Chromosome diversity and its relationship with nearby regions". BMC Genet. 10: 59. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-10-59. PMC 2759955 . PMID 19772609.
. PMID 19772609.
^ Ollier, W; Doyle, P; Alonso, A; Awad, J; Williams, E; Gill, D; Welch, S; Klouda, P; Bacchus, R; Festenstein, H (February 1985). "HLA polymorphisms in Saudi Arabs". Tissue Antigens. 25 (2): 87–95. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.1985.tb00420.x. PMID 3857723.
^ Luis, J; Rowold, D; Regueiro, M; Caeiro, B; Cinnioglu, C; Roseman, C; Underhill, P; Cavallisforza, L; Herrera, R (2004). "The Levant versus the Horn of Africa: Evidence for Bidirectional Corridors of Human Migrations". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 74 (3): 532–44. doi:10.1086/382286. PMC 1182266 . PMID 14973781. (Errata Archived 16 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine.)
. PMID 14973781. (Errata Archived 16 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine.)
^ "The Genetic Atlas". www.thegeneticatlas.com. Archived from the original on 25 May 2015. Retrieved 11 October 2015.
^ Hunter-Zinck, H; Musharoff, S; Salit, J; Al-Ali, KA; Chouchane, L; Gohar, A; Matthews, R; Butler, MW; Fuller, J; Hackett, NR; Crystal, RG; Clark, AG (9 July 2010). "Population genetic structure of the people of Qatar". American Journal of Human Genetics. 87 (1): 17–25. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.05.018. PMC 2896773 . PMID 20579625.
. PMID 20579625.
^ ab Semino, O.; Passarino, G; Oefner, PJ; Lin, AA; Arbuzova, S; Beckman, LE; De Benedictis, G; Francalacci, P; et al. (2000). "The Genetic Legacy of Paleolithic Homo sapiens sapiens in Extant Europeans: A Y Chromosome Perspective". Science. 290 (5494): 1155–9. Bibcode:2000Sci...290.1155S. doi:10.1126/science.290.5494.1155. PMID 11073453.
^ Badro, DA; Douaihy, B; Haber, M; et al. (30 January 2013). "Y-Chromosome and mtDNA Genetics Reveal Significant Contrasts in Affinities of Modern Middle Eastern Populations with European and African Populations". PLoS ONE. 8 (1): e54616. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...854616B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054616. PMC 3559847 . PMID 23382925. Retrieved 11 March 2015. CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al. (link)
. PMID 23382925. Retrieved 11 March 2015. CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al. (link)
^ ab El-Sibai, M; Platt, DE; Haber, M; Xue, Y; Youhanna, SC; Wells, RS; Izaabel, H; Sanyoura, MF; Harmanani, H; Bonab, MA; Behbehani, J; Hashwa, F; Tyler-Smith, C; Zalloua, PA (16 August 2009). "Geographical Structure of the Y-chromosomal Genetic Landscape of the Levant: A coastal-inland contrast". Annals of Human Genetics. 73 (Pt 6): 568–581. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2009.00538.x. PMC 3312577 . PMID 19686289. Retrieved 11 March 2015.
. PMID 19686289. Retrieved 11 March 2015.
^ Nebel, A; Filon, D; Brinkmann, B; Majumder, P; Faerman, M; Oppenheim, A (2001). "The Y Chromosome Pool of Jews as Part of the Genetic Landscape of the Middle East". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 69 (5): 1095–112. doi:10.1086/324070. PMC 1274378 . PMID 11573163.
. PMID 11573163.
^ E. Levy- Coffman (2005). "A Mosaic of People". Journal of Genetic Genealogy: 12–33. "J1 is the only haplogroup that researchers consider "Semitic" in origin"
^ Abu Amero et al. (2009)
^ Semino, O; Magri, C; Benuzzi, G; Lin, AA; Al-Zahery, N; Battaglia, V; MacCioni, L; Triantaphyllidis, C; et al. (2004). "Origin, diffusion, and differentiation of Y-chromosome haplogroups E and J: inferences on the neolithization of Europe and later migratory events in the Mediterranean area". American Journal of Human Genetics. 74 (5): 1023–34. doi:10.1086/386295. PMC 1181965 . PMID 15069642.
. PMID 15069642.
^ "N. Al-Zahery et al. "Y-chromosome and mtDNA polymorphisms in Iraq, a crossroad of the early human dispersal and of post-Neolithic migrations" (2003)" (PDF). Retrieved 10 December 2010.
^ Wood, ET; Stover, DA; Ehret, C; Destro-Bisol, G; Spedini, G; McLeod, H; Louie, L; Bamshad, M; et al. (2005). "Contrasting patterns of Y chromosome and mtDNA variation in Africa: evidence for sex-biased demographic processes" (PDF). European Journal of Human Genetics. 13 (7): 867–76. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201408. PMID 15856073.
^ Hassan, HY; Underhill, PA; Cavalli-Sforza, LL; Ibrahim, ME (2008). "Y-chromosome variation among Sudanese: restricted gene flow, concordance with language, geography, and history". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 137 (3): 316–23. doi:10.1002/ajpa.20876. PMID 18618658.
^ Hassan, HY; Underhill, PA; Cavalli-Sforza, LL; Ibrahim, ME (November 2008). "Y-chromosome variation among Sudanese: restricted gene flow, concordance with language, geography, and history". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 137 (3): 316–23. doi:10.1002/ajpa.20876. PMID 18618658.
^ Phylogeographic Analysis of Haplogroup E3b (E-M215) Y Chromosomes Reveals Multiple Migratory Events Within and Out Of Africa. Volume 74, Issue 5, May 2004, Pages 1014–1022. Fulvio Cruciani, Roberta La Fratta, Piero Santolamazza, Daniele Sellitto, Roberto Pascone, Pedro Moral, Elizabeth Watson, Valentina Guida, Eliane Beraud Colomb, Boriana Zaharo, João Lavinh, Giuseppe Vona, Rashid Aman, Francesco Calì, Nejat Akar, Martin Richards, Antonio Torroni, Andrea Novelletto, Rosaria Scozzari. Date:07-08-2016
^ Cruciani, La Fratta R; Trombetta, B; Santolamazza, P; Sellitto, D; Colomb, EB; Dugoujon, JM; Crivellaro, F; Benincasa, T; Pascone, R; Moral, P; Watson, E; Melegh, B; Barbujani, G; Fuselli, S; Vona, G; Zagradisnik, B; Assum, G; Brdicka, R; Kozlov, AI; Efremov, GD; Coppa, A; Novelletto, A; Scozzari, R (June 2007). "Tracing past human male movements in northern/eastern Africa and western Eurasia: new clues from Y-chromosomal haplogroups E-M78 and J-M12". Mol Biol Evol. 24 (6): 1300–11. doi:10.1093/molbev/msm049. PMID 17351267.
^ ab Arredi, B; Poloni, E; Paracchini, S; Zerjal, T; Fathallah, D; Makrelouf, M; Pascali, V; Novelletto, A; Tylersmith, C (2004). "A Predominantly Neolithic Origin for Y-Chromosomal DNA Variation in North Africa". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 75 (2): 338–45. doi:10.1086/423147. PMC 1216069 . PMID 15202071.
. PMID 15202071.
^ Karima Fadhlaoui-Zid et al. (2013) Genome-Wide and Paternal Diversity Reveal a Recent Origin of Human Populations in North Africa" PLoS One 2013; 8(11): e80293. See Table S2
^ Immel, U.-D.; Erhuma, M.; Mustafa, T.; Kleiber, M.; Klintschar, M. (2006). "Population genetic analysis in a Libyan population using the PowerPlex 16 system". International Congress Series. 1288: 421–3. doi:10.1016/j.ics.2005.08.036.
^ ab Pala, M; Olivieri, A; Achilli, A; Accetturo, M; Metspalu, E; Reidla, M; Tamm, E; Karmin, M; Reisberg, T; Hooshiar Kashani, B; Perego, UA; Carossa, V; Gandini, F; Pereira, JB; Soares, P; Angerhofer, N; Rychkov, S; Al-Zahery, N; Carelli, V; Sanati, MH; Houshmand, M; Hatina, J; Macaulay, V; Pereira, L; Woodward, SR; Davies, W; Gamble, C; Baird, D; Semino, O; Villems, R; Torroni, A; Richards, MB (4 May 2012). "Mitochondrial DNA Signals of Late Glacial Recolonization of Europe from Near Eastern Refugia". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 90 (5): 915–924. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.04.003. PMC 3376494 . PMID 22560092.
. PMID 22560092.
^ "Mitochondrial DNA Signals of Late Glacial Recolonization of Europe..." Haplogroup.org. 31 December 2012. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
^ ab Non, Amy. "ANALYSES OF GENETIC DATA WITHIN AN INTERDISCIPLINARY FRAMEWORK TO INVESTIGATE RECENT HUMAN EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY AND COMPLEX DISEASE" (PDF). University of Florida. Retrieved 21 December 2016.
^ Mohamed, Hisham Yousif Hassan. "Genetic Patterns of Y-chromosome and Mitochondrial DNA Variation, with Implications to the Peopling of the Sudan" (PDF). University of Khartoum. Retrieved 21 December 2016.
^ abc Brenna M. Henn; Laura R. Botigué; Simon Gravel; Wei Wang; Abra Brisbin; Jake K. Byrnes; Karima Fadhlaoui-Zid; Pierre A. Zalloua; Andres Moreno-Estrada; Jaume Bertranpetit; Carlos D. Bustamante; David Comas (12 January 2012). "Genomic Ancestry of North Africans Supports Back-to-Africa Migrations". PLOS Genetics. 8 (1): e1002397. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002397. PMC 3257290 . PMID 22253600. Retrieved 14 October 2016.
. PMID 22253600. Retrieved 14 October 2016.
^ Begoña Dobon; Hisham Y. Hassan; Hafid Laayouni; Pierre Luisi; Isis Ricaño-Ponce; Alexandra Zhernakova; Cisca Wijmenga; Hanan Tahir; David Comas; Mihai G. Netea; Jaume Bertranpetit (28 May 2015). "The genetics of East African populations: a Nilo-Saharan component in the African genetic landscape". Scientific Reports. 5: 9996. Bibcode:2015NatSR...5E9996D. doi:10.1038/srep09996. PMC 4446898 . PMID 26017457. Retrieved 14 October 2016.
. PMID 26017457. Retrieved 14 October 2016.
^ ab Jason A. Hodgson; Connie J. Mulligan; Ali Al-Meeri; Ryan L. Raaum (12 June 2014). "Early Back-to-Africa Migration into the Horn of Africa". PLOS Genetics. 10 (6): e1004393. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004393. PMC 4055572 . PMID 24921250. ; "Supplementary Text S1: Affinities of the Ethio-Somali ancestry component". doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004393.s017. Retrieved 14 October 2016.
. PMID 24921250. ; "Supplementary Text S1: Affinities of the Ethio-Somali ancestry component". doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004393.s017. Retrieved 14 October 2016.
- Bibliography
.mw-parser-output .refbeginfont-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ullist-style-type:none;margin-left:0.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>ddmargin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100font-size:100%
Ankerl, Guy (2000). Coexisting Contemporary Civilizations: Arabo-Muslim, Bharati, Chinese, and Western. Geneva: INU PRESS. ISBN 2-88155-004-5.
Retso, Jan (2002). Arabs in Antiquity: Their History from the Assyrians to the Umayyads. Routledge. ISBN 9780700716791.
Cragg, Kenneth (1991). The Arab Christian: A History in the Middle East. Westminster John Knox Press. ISBN 978-0-664-22182-9.
Deng, Francis Mading (1995). War of Visions: Conflict of Identities in the Sudan. Brookings Institution Press.- Touma, Habib Hassan. The Music of the Arabs. Portland, Oregon: Amadeus P, 1996. ISBN 0-931340-88-8.
- Lipinski, Edward. Semitic Languages: Outlines of a Comparative Grammar, 2nd ed., Orientalia Lovanensia Analecta: Leuven 2001
Kees Versteegh, The Arabic Language, Edinburgh University Press (1997)- The Catholic Encyclopedia, Robert Appleton Company, 1907, Online Edition, K. Night 2003: article Arabia
History of Arabic language(1894), Jelsoft Enterprises Ltd.- The Arabic language, National Institute for Technology and Liberal Education web page (2006)
Ankerl, Guy (2000) [2000]. Global communication without universal civilization. INU societal research. Vol.1: Coexisting contemporary civilizations : Arabo-Muslim, Bharati, Chinese, and Western. Geneva: INU Press. ISBN 2-88155-004-5.- Hooker, Richard. "Pre-Islamic Arabic Culture." WSU Web Site. 6 June 1999. Washington State University.
- Owen, Roger. "State Power and Politics in the Making of the Modern Middle East 3rd Ed" Page 57 ISBN 0-415-29714-1
Levinson, David (1998). Ethnic groups worldwide: a ready reference handbook. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-1-57356-019-1inconsistent citations
Further reading
- Price-Jones, David. The Closed Circle: an Interpretation of the Arabs. Pbk. ed., with a new preface by the author. Chicago: I. R. Dee, 2002. xiv, 464 p. ISBN 1-56663-440-7
- Ankerl, Guy. Coexisting Contemporary Civilizations: Arabo-Muslim, Bharati, Chinese, and Western. INU PRESS, Geneva, 2000. ISBN 2-88155-004-5.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Arab. |
- www.LasPortal.org
- ArabCultureFund AFAC