Organ (anatomy)

Multi tool use

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
| Organ | |
|---|---|
 Many of the internal organs of the human body | |
| Details | |
| System | Organ systems |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | organi |
| Greek | Οργανο |
| FMA | 67498 |
Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
Organs are collections of tissues with similar functions. Plant and animal life relies on many organs that coexist in organ systems.[1]
Organs are composed of main tissue, parenchyma, and "sporadic" tissues, stroma. The main tissue is that which is unique for the specific organ, such as the myocardium, the main tissue of the heart, while sporadic tissues include the nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissues. The main tissues that make up an organ tend to have common embryologic origins, such as arising from the same germ layer. Functionally-related organs often cooperate to form whole organ systems. Organs exist in all organisms. In single-celled organisms such as bacteria, the functional analogue of an organ is known as an organelle. In plants there are three main organs.[2] A hollow organ is an internal organ that forms a hollow tube, or pouch such as the stomach, intestine, or bladder.
In the study of anatomy, the term viscus is used to refer to an internal organ, and viscera is the plural form.[3][4] 79 organs have been identified in the human body.[5]
Contents
1 Structure
1.1 Tissue
1.2 Organ systems
2 Function
2.1 Animals
2.2 Plants
3 Society and culture
4 History
4.1 Antiquity
4.2 Modern times
5 Origin and evolution
6 See also
7 References
8 External links
Structure
Tissue
In biology, tissue is a cellular organizational level between cells and complete organs. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues.
The study of human and animal tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, histopathology. For plants, the discipline is called plant anatomy. The classical tools for studying tissues are the paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the histological stain, and the optical microscope. In the last couple of decades, developments in electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, and the use of frozen tissue sections have enhanced the detail that can be observed in tissues. With these tools, the classical appearances of tissues can be examined in health and disease, enabling considerable refinement of medical diagnosis and prognosis.
Organ systems
Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. The functions of organ systems often share significant overlap. For instance, the nervous and endocrine system both operate via a shared organ, the hypothalamus. For this reason, the two systems are combined and studied as the neuroendocrine system. The same is true for the musculoskeletal system because of the relationship between the muscular and skeletal systems.
Function
Animals
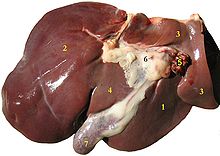
The liver and gallbladder of a sheep
Animals such as humans have a variety of organ systems. These specific systems are also widely studied in human anatomy.
Cardiovascular system: pumping and channeling blood to and from the body and lungs with heart, blood and blood vessels.
Digestive system: digestion and processing food with salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, intestines, colon, rectum and anus.
Endocrine system: communication within the body using hormones made by endocrine glands such as the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal body or pineal gland, thyroid, parathyroids and adrenals, i.e., adrenal glands.
Excretory system: kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra involved in fluid balance, electrolyte balance and excretion of urine.
Lymphatic system: structures involved in the transfer of lymph between tissues and the blood stream, the lymph and the nodes and vessels that transport it including the Immune system: defending against disease-causing agents with leukocytes, tonsils, adenoids, thymus and spleen.
Integumentary system: skin, hair and nails of mammals. Also scales of fish, reptiles, and birds, and feathers of birds.
Muscular system: movement with muscles.
Nervous system: collecting, transferring and processing information with brain, spinal cord and nerves.
Reproductive system: the sex organs, such as ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vulva, vagina, testes, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate and penis.
Respiratory system: the organs used for breathing, the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs and diaphragm.
Skeletal system: structural support and protection with bones, cartilage, ligaments and tendons.
Plants

The flower is the angiosperm's reproductive organ. This Hibiscus flower is hermaphroditic, and it contains stamen and pistils.

Strobilus of Equisetum telmateia
The study of plant organs is referred to as plant morphology, rather than anatomy, as in animal systems. Organs of plants can be divided into vegetative and reproductive. Vegetative plant organs are roots, stems, and leaves. The reproductive organs are variable. In flowering plants, they are represented by the flower, seed and fruit. In conifers, the organ that bears the reproductive structures is called a cone. In other divisions (phyla) of plants, the reproductive organs are called strobili, in Lycopodiophyta, or simply gametophores in mosses.
The vegetative organs are essential for maintaining the life of a plant. While there can be 11 organ systems in animals, there are far fewer in plants, where some perform the vital functions, such as photosynthesis, while the reproductive organs are essential in reproduction. However, if there is asexual vegetative reproduction, the vegetative organs are those that create the new generation of plants (see clonal colony).
Society and culture
Many societies have a system for Organ donation, in which a living or deceased donor's organ is transplanted into a person with a failing organ. The transplantation of larger solid organs often requires immunosuppression to prevent organ rejection or graft vs host disease.
There is considerable interest throughout the world in creating laboratory-grown or artificial organs.[citation needed]
History
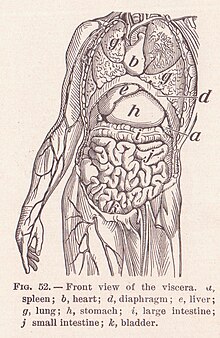
Human viscera
The English word "organism" is a neologism coined in the 17th century, probably formed from the verb to organize. At first the word referred to an organization or social system. The meaning of a living animal or plant is first recorded in 1842.[6] Plant organs are made from tissue built up from different types of tissue. When there are three or more organs it is called an organ system.[7]
The adjective visceral, also splanchnic, is used for anything pertaining to the internal organs. Historically, viscera of animals were examined by Roman pagan priests like the haruspices or the augurs in order to divine the future by their shape, dimensions or other factors. This practice remains an important ritual in some remote, tribal societies.
The term "visceral" is contrasted with the term "parietal", meaning "of or relating to the wall of a body part, organ or cavity"[8] The two terms are often used in describing a membrane or piece of connective tissue, referring to the opposing sides.[citation needed]
Antiquity
Aristotle used the word frequently in his philosophy, both to describe the organs of plants or animals (e.g. the roots of a tree, the heart or liver of an animal), and to describe more abstract "parts" of an interconnected whole (e.g. his logical works, taken as a whole, are referred to as the "organon").
Some alchemists (e.g. Paracelsus) adopted the Hermetic Qabalah assignment between the seven vital organs and the seven classical planets as follows:[9]
| Planet | Organ |
| Sun | Heart |
| Moon | Brain |
| Mercury | Lungs |
| Venus | Kidneys |
| Mars | Gall bladder |
| Jupiter | Liver |
| Saturn | Spleen |
Modern times
The variations in natural language definitions of what constitutes an organ, their degree of precision, and the variations in how they map to ontologies and taxonomies in information science (for example, to count how many organs exist in a typical human body) are topics explored by writer Carl Engelking of Discover magazine in 2017 as he analyzed the science journalism coverage of the evolving scientific understanding of the mesentery.[10] He explored a challenge now faced by anatomists: as human understanding of ontology generally (that is, how things are defined, and how the relationship of one thing to another is defined) meets applied ontology and ontology engineering, unification of varying views is in higher demand.[10] However, such unification always faces epistemologic frontiers, as humans can only declare computer ontologies with certainty and finality to the extent that their own cognitive taxonomy (that is, science's understanding of the universe) is certain and final. For example, the fact that the tissues of the mesentery are continuous was something that was simply not known for sure until it was demonstrated with microscopy.[11] Because humans cannot predict all future scientific discoveries, they cannot build a unified ontology that is totally certain and will never again change. However, one of the points made by an anatomist interviewed by Engelking is that, finality aside, much more could be done even now to represent existing human knowledge more clearly for computing purposes.
Origin and evolution

Relationship of major animal lineages with indication of how long ago these animals shared a common ancestor. On the left, important organs are shown, which allows us to determine how long ago these may have evolved.
The organ level of organisation in animals can be first detected in flatworms and the more derived phyla. The less-advanced taxa (like Placozoa, Sponges and Radiata) do not show consolidation of their tissues into organs.
Complex animals are composed of organs and many of these organs evolved a very long time ago. For example, the liver evolved in the stem vertebrates more than 500 million years ago, while the gut and brain are even more ancient, arising in the ancestor of vertebrates, insects, and worms more than 600 million years ago.
Given the ancient origin of most vertebrate organs, researchers have looked for model systems, where organs have evolved more recently, and ideally have evolved multiple times independently. An outstanding model for this kind of research is the placenta, which has evolved more than 100 times independently in vertebrates, has evolved relatively recently in some lineages, and exists in intermediate forms in extant taxa.[12] Studies on the evolution of the placenta have identified a variety of genetic and physiological processes that contribute to the origin and evolution of organs, these include the re-purposing of existing animal tissues, the acquisition of new functional properties by these tissues, and novel interactions of distinct tissue types.[12]
See also
 Organs (anatomy) portal
Organs (anatomy) portal- Organoid
References
^ Widmaier EP; Raff H; Strang KT (2014). Vander's Human Physiology (12th ed.). ISBN 978-0-07-128366-3..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
[page needed]
^ "Botany/Plant structure - Wikibooks, open books for an open world". en.wikibooks.org.
^ "Viscus - Definition". Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary. Retrieved 14 December 2009.
^ "Viscera". MeSH. Retrieved 14 December 2009.
^ "New organ named in digestive system". BBC News. 2017. Retrieved 2018-02-05.
^ Barnhart's Concise Dictionary of Etymology[page needed]
^ "Organ System - Definition and Examples | Biology Dictionary". Biology Dictionary. 2016-10-31. Retrieved 2018-02-10.
^ "Parietal – Learning brain structure, function and variability from neuroimaging data". team.inria.fr. Retrieved 2018-02-10.
^ Philip Ball, The Devil's Doctor: Paracelsus and the World of Renaissance Magic and Science,
ISBN 978-0-09-945787-9[page needed]
^ ab Engelking, Carl (2017-01-06), "We got the mesentery news all wrong", The Crux (a group blog by Discover writers).
^ Coffey, J Calvin; O'Leary, D Peter (2016). "The mesentery: structure, function, and role in disease". The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 1 (3): 238–247. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30026-7.
^ ab Griffith, Oliver W.; Wagner, G?nter P. (23 March 2017). "The placenta as a model for understanding the origin and evolution of vertebrate organs". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 1 (4): 0072. doi:10.1038/s41559-017-0072.
External links
 Media related to Organs (anatomy) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Organs (anatomy) at Wikimedia Commons