National Assembly of Burkina Faso

 Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP
Clash Royale CLAN TAG#URR8PPP National Assembly l’Assemblée nationale | |
|---|---|
| 7th National Assembly | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | Unicameral |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 127 |
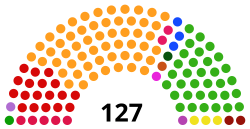 | |
Political groups | MPP (55) UPC (33) CDP (18) UNIR / PS (5) ADF–RDA (3) NTA (3) PRN (2) NAFA (2) NAFA (1) ODT (1) PDS/Metba (1) RDS (1) UBN (1) MDA (1) |
| Elections | |
Voting system | Proportional representation |
Last election | 29 November 2015 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Parliament Building, Ouagadougou | |
| Website | |
| www.assembleenationale.bf | |
| Constitution | |
| Constitution of Burkina Faso | |
Burkina Faso |
|---|
 |
This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Burkina Faso |
Constitution
|
Government
|
Parliament
|
Administrative divisions
|
Elections
|
Foreign relations
|
|
The Unicameral National Assembly is Burkina Faso's legislative body. In 1995, it became the lower house of a bicameral Parliament, but the upper house (Chamber of Representatives) was abolished in 2002. The upper house was to have been restored under the name "Senate" in the June 2012 constitutional amendments.[1] This revision was never executed due to an extended and unresolved political confrontation over the Senate's establishment, which left the country effectively with a unicameral legislature as of the October 2014 constitutional crisis.[2]
On 30 October 2014, as part of the 2014 Burkinabé uprising, protesters stormed the parliament building and set fire to it, in anger at the Parliament's decision to amend the Constitution of Burkina Faso to abolish term limits, which would have effectively paved the way for President Blaise Compaoré to remain in office for another five-year term.[3]
Contents
1 Electing the National Assembly
2 2015 National Assembly elections
2.1 Results by electoral province: 111 seats
2.2 National results: 16 seats
3 See also
4 References
5 External links
Electing the National Assembly
Burkina Faso is divided into 45 electoral provinces within their 13 regions. Each province elects between two and nine representatives, and these representatives are members of political parties. There are 111 members of the National Assembly elected to represent provinces, and 16 nationally elected, totaling 127.[4]
In Burkina Faso, the National Assembly is elected by a proportional representational system.[4] Proportional representation in Burkina Faso means that each person marks one party on the ballot, and after tallying the votes, the top parties chosen are elected to the Assembly. Each electoral province has a simple electoral quotient. This is the number of valid votes counted divided by the number of seats available. If a party wins a seat by the electoral quotient, usually half of the votes, then the remainder of the seats are transferred to a "rest" category, which are compared to the other votes gathered. For example, in the province of Boulkiemde, the MPP received 29,445 votes, which is 35.1% of the total votes of the province.[5] Boulkiemde elects four representatives to their legislature, so their electoral quotient is 21002 votes (84007÷4). This means that the MPP will receive one seat from the electoral quotient. The remaining votes are transferred to another category, which is compared among the other candidates. These remaining votes in Boulkiemde won the MPP another seat in the legislature, since the remaining votes (8443) are the second highest compared to the rest of the parties (CDP=16968, UPC=8099). Thus, since the MPP received 35.1% of the votes, they received 50% of the seats due to the electoral quotient.
Elections are led by teachers in Burkina Faso, who are not allowed to be a member of any political party. The ballot has ballot has a name, acronym, or symbol of the party and a space for voters to mark.[6] The ballots are placed in envelopes, and then placed in ballot boxes. The leader of the election officials ensures that the seal is not broken before counting all of the votes. The teachers who are trained as election officials become counting officials.[6] Invalid ballots include those that have no marks, more than one mark, or ballots not in an envelope. The ballots are sent to the district level after counting them, where the winner of a legislative seat will be determined based on the number of votes. The districts are divided by one seat per 100,000 people, so the capital, Ouagadougou, has nine seats.
2015 National Assembly elections
In the 2015 parliamentary election, the People’s Movement for Progress party received 51.3% of the national vote, winning 55 seats. The Union for Progress and Change, or UPC, received 20.5% of the vote, which won them 33 seats. The Congress for Democracy and Progress party won 18 seats with 13.2% of the vote, and the New Alliance of Faso party received two seats, with 4.1% of the vote.
Results by electoral province: 111 seats
| Electoral province | Total votes | Seats | Party | Votes | Proportion of vote | Party | Votes | Proportion of vote | Party | Votes | Proportion of vote | Party | Votes | Proportion of vote |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Bale | 41073 | 2 | MPP | 19371 | 0.471624 | UPC | 9812 | 0.238892 | ||||||
BAM | 63247 | 2 | MPP | 25934 | 0.410043 | CDP | 11145 | 0.176214 | ||||||
Banwa | 42014 | 2 | MPP | 19941 | 0.474628 | Unir/PS | 6268 | 0.149188 | ||||||
Bazega | 50346 | 2 | MPP | 17870 | 0.354944 | UPC | 11301 | 0.224467 | ||||||
Bougouriba | 18450 | 2 | MPP | 5694 | 0.308618 | UPC | 5445 | 0.295122 | ||||||
Boulgou | 127210 | 4 | MPP | 22695 | 0.178406 | UPC (2) | 67552 | 0.531027 | CDP | 8696 | 0.068359 | |||
Boulkiemde | 84007 | 4 | MPP | 29445 | 0.350507 | CDP | 16968 | 0.201983 | UPC | 8099 | 0.096409 | |||
Comoe | 69488 | 2 | MPP | 25270 | 0.36366 | UPC | 11242 | 0.161783 | ||||||
Fada Gourma | 58041 | 2 | MPP | 18357 | 0.316276 | UPC | 15554 | 0.267983 | ||||||
Ganzourgou | 69710 | 2 | MPP (2) | 52913 | 0.759045 | 0 | ||||||||
Gnagna | 91655 | 3 | MPP | 29178 | 0.318346 | UPC | 27498 | 0.300016 | NTD | 10377 | 0.113218 | |||
Houet | 225085 | 6 | MPP (2) | 69802 | 0.310114 | CDP | 26360 | 0.117111 | UPC | 45534 | 0.202297 | UNIR | 9376 | 0.041655 |
Ioba | 42233 | 2 | MPP | 12751 | 0.30192 | UPC | 14623 | 0.346246 | ||||||
Kadiogo | 617782 | 9 | MPP (3) | 213179 | 0.345072 | UPC (2) | 150492 | 0.2436 | UNIR/PS | 38896 | 0.062961 | CDP | 56143 | 0.090878 |
Kenedougou | 53261 | 2 | MPP | 19093 | 0.35848 | UPC | 17611 | 0.330655 | ||||||
Komondjari | 20159 | 2 | MPP | 9462 | 0.469369 | UPC | 6862 | 0.340394 | ||||||
Kossi | 48419 | 2 | MPP | 15154 | 0.312976 | UPC | 9888 | 0.204217 | ||||||
Kompienga | 18401 | 2 | CDP | 5205 | 0.282865 | UPC | 6409 | 0.348296 | ||||||
Koulpelogo | 53070 | 2 | MPP | 18170 | 0.342378 | UPC | 13445 | 0.253345 | ||||||
Kouritenga | 77784 | 2 | MPP | 32552 | 0.418492 | UPC | 18014 | 0.23159 | ||||||
Kourweogo | 25441 | 2 | MPP | 7360 | 0.289297 | CDP | 4933 | 0.1939 | ||||||
Leraba | 27966 | 2 | MPP | 9355 | 0.334513 | UPC | 7818 | 0.279554 | ||||||
Lorum | 34287 | 2 | MPP | 9878 | 0.288098 | MDA | 11170 | 0.325779 | ||||||
Mouhoun | 51444 | 2 | MPP | 19909 | 0.387003 | UPC | 11099 | 0.215749 | ||||||
Nahouri | 44028 | 2 | MPP | 13832 | 0.314164 | UPC | 12941 | 0.293927 | ||||||
Namentenga | 56533 | 2 | MPP | 23028 | 0.407337 | CDP | 9969 | 0.176339 | ||||||
Nayala | 34643 | 2 | MPP | 15171 | 0.437924 | CDP | 7259 | 0.209537 | ||||||
Noumbiel | 14842 | 2 | MPP | 4924 | 0.331761 | UPC | 4193 | 0.282509 | ||||||
Oubritenga | 49117 | 2 | MPP | 11986 | 0.24403 | CDP | 26189 | 0.533196 | ||||||
Oudalan | 52303 | 2 | MPP | 16194 | 0.309619 | UBN | 15745 | 0.301034 | ||||||
Passore | 65708 | 3 | MPP | 18252 | 0.277774 | CDP | 10648 | 0.16205 | UNIR/PS | 17237 | 0.262327 | |||
Poni | 38461 | 2 | MPP | 10154 | 0.264008 | UPC | 11294 | 0.293648 | ||||||
Sanguie | 56181 | 2 | MPP | 14621 | 0.260248 | NAFA | 17605 | 0.313362 | ||||||
Sanmatenga | 112624 | 4 | MPP | 31442 | 0.279177 | UPC | 8755 | 0.077737 | RDS | 15794 | 0.140237 | CDP | 21013 | 0.186577 |
Seno | 73007 | 2 | MPP | 17670 | 0.242032 | PDS | 28165 | 0.385785 | ||||||
Sissili | 39556 | 2 | MPP | 15118 | 0.382192 | UPC | 8600 | 0.217413 | ||||||
Soum | 79247 | 2 | MPP | 18583 | 0.234495 | CDP | 20752 | 0.261865 | ||||||
Sourou | 38569 | 2 | MPP | 10875 | 0.281962 | CDP | 9117 | 0.236382 | ||||||
Tapoa | 61826 | 2 | MPP | 28171 | 0.45565 | UPC | 19121 | 0.309271 | ||||||
Tuy | 36948 | 2 | MPP | 17322 | 0.468821 | UPC | 7018 | 0.189943 | ||||||
Yagha | 39735 | 2 | MPP | 12236 | 0.30794 | NTD | 8751 | 0.220234 | ||||||
Yatenga | 138773 | 4 | MPP(2) | 68883 | 0.496372 | ADF-RDA | 22692 | 0.163519 | CDP | 12807 | 0.092287 | |||
Ziro | 28638 | 2 | MPP | 10271 | 0.358649 | LFA | 7028 | 0.245408 | ||||||
Zondoma | 36902 | 2 | MPP | 21655 | 0.586825 | CDP | 6489 | 0.175844 | ||||||
Zoundweogo | 54207 | 2 | CDP | 13097 | 0.241611 | UPC | 26744 | 0.493368 |

A pie chart showing how many seats won in the 2015 Burkina Faso National Assembly Elections. The "other" category includes 6 separate political parties.[7]
National results: 16 seats
| Political party | Number of votes | Number of seats | Proportion of vote |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADF-RDA | 96614 | 1 | 0.030577 |
| CDP | 417058 | 2 | 0.131995 |
| MPP | 1096814 | 6 | 0.347131 |
| NAFA | 130963 | 1 | 0.041449 |
| NTD | 70374 | 1 | 0.022273 |
| PAREN | 59421 | 1 | 0.018806 |
| UNIR/PC | 118662 | 1 | 0.037555 |
| UPC | 648784 | 3 | 0.205334 |

The frequency for the number of seats reserved for provinces. The majority of electoral provinces have two seats reserved, while few have more than two.
See also
- List of Presidents of the National Assembly of Burkina Faso
- History of Burkina Faso
- Politics of Burkina Faso
- List of legislatures by country
- Legislative Branch
References
^ Kere, Barthélemy. "Constitution of Burkina Faso - WIPO (français)" (PDF). WIPO.int. WIPO. Retrieved 1 November 2014..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Coulibaly, Nadoun. "Burkina Faso : vers un référendum constitutionnel pour Blaise Compaoré?". Groupe Jeune Afrique. Jeune Afrique. Retrieved 1 November 2014.
^ Taoko, Herve; Cowell, Alan; Callimachi, Rukmini (30 October 2014). "Violent Protests Topple Government in Burkina Faso". New York Times Company. New York Times. Retrieved 30 October 2014.
^ ab "Sahel Research Group | Burkina Faso". sahelresearch.africa.ufl.edu. Retrieved 2016-05-03.
^ "ELECTIONS LEGISLATIVES A CIRCONSCRIPTION PROVINCIALE" (PDF). Ceni.gov. CENI. December 1, 2015. Retrieved May 2, 2016.
^ ab "Electoral Systems Counting Requirements —". aceproject.org. Retrieved 2016-05-03.
^ "IFES Election Guide - Elections: Parliament". www.electionguide.org. Retrieved 2016-05-03.
External links
(in French) Assemblée Nationale du Burkina Faso (no website exists under .bf subdomain)